Ever wondered why some websites get indexed by Google within hours while yours sits in digital limbo for weeks? The secret weapon hiding in plain sight might be the most overlooked file on your website: your XML sitemap.
Here’s the brutal truth: without proper XML sitemap optimization, you’re essentially playing hide-and-seek with Google’s crawlers – except they’re not very good at seeking. Your amazing content could be sitting there, perfectly optimized, while search engines walk right past it like a tourist ignoring a street performer.
But here’s the good news: mastering XML sitemaps is like giving Google a detailed roadmap to your content treasure. And trust me, once you understand how to make Google fall head-over-heels for your sitemap, you’ll wonder how you ever survived without this knowledge.
Ready to turn your website into Google’s favorite hangout spot? Let’s dive into the world of sitemap magic.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Exactly Is XML Sitemap Optimization and Why Should You Care?
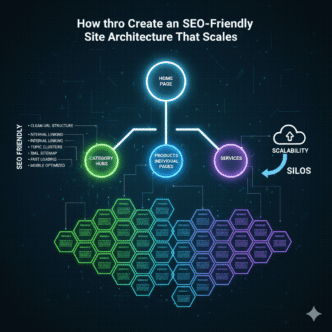
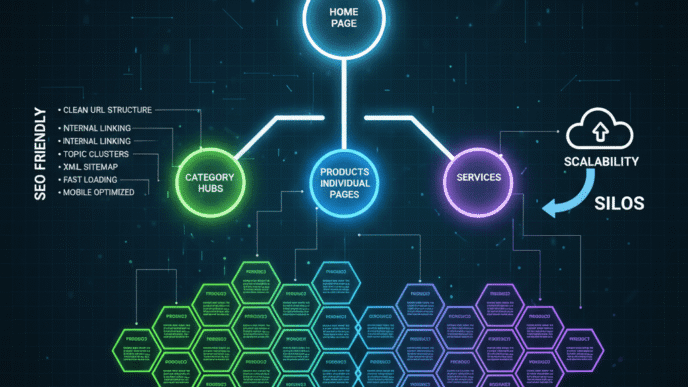
XML sitemap optimization is the art and science of creating and fine-tuning your website’s roadmap for search engines. Think of it as the difference between giving someone vague directions (“it’s somewhere over there”) versus providing a GPS with turn-by-turn navigation.
An XML sitemap is essentially a file that lists all the important pages on your website, along with crucial metadata about each page. It’s like a VIP guest list for Google indexing – telling search engines which pages deserve the red-carpet treatment.
But here’s where most people get it wrong: they think any sitemap will do. That’s like thinking any map will help you navigate – sure, a hand-drawn napkin might work, but wouldn’t you prefer a detailed GPS system?
The optimization part is what separates the amateurs from the pros. It’s about strategic site indexing that doesn’t just inform Google about your pages, but actually makes them irresistible.
Why Do Most XML Sitemaps Fail to Impress Google?
Let’s be honest – most XML sitemaps are about as exciting as watching paint dry. They’re basic, boring, and barely functional. No wonder Google’s crawlers treat them like spam emails.
The Generic Sitemap Problem: Most websites auto-generate sitemaps that include every single page, regardless of quality or importance. It’s like inviting Google to a party and then showing them your messy garage along with your beautifully decorated living room.
Missing Strategic Prioritization: Without proper sitemap optimization, you’re treating your homepage and that random “About Our Pet Goldfish” page with equal importance. Google gets confused about what actually matters on your site.
Outdated Information: Many sitemaps become digital fossils – created once and forgotten forever. They list pages that no longer exist while missing your latest masterpieces.
Pro Tip: “The biggest mistake I see is treating XML sitemaps like a checkbox item instead of a strategic SEO tool. A well-optimized sitemap can reduce indexing time by 60-80% for new content.” – Senior Technical SEO Specialist
How Does Google Actually Use Your XML Sitemap?
Understanding how Google indexing works with your sitemap is like understanding the rules of a game before you play. And trust me, this game has some interesting rules.
The Discovery Phase: When Googlebot visits your sitemap, it’s like a scout checking out potential talent. It looks for new pages, updated content, and signals about what’s important on your site.
Priority Assessment: Google doesn’t just blindly crawl everything in your sitemap. It makes decisions based on the signals you provide about search engine crawling priorities and page importance.
Content Freshness Evaluation: Your sitemap tells Google when pages were last modified, helping it decide which content needs a fresh look and which can wait for the next crawling cycle.
Resource Allocation: Search engines have limited crawling budgets. Your optimized sitemap helps Google spend its time on your most valuable content instead of wasting resources on low-priority pages.
What Makes an XML Sitemap Irresistible to Search Engines?
Creating a sitemap that search engines love is like crafting the perfect dating profile – you want to be attractive, honest, and strategic about what you highlight.
Strategic Page Selection
Not every page deserves a spot in your sitemap. Sitemap optimization means being selective about what you include:
- High-quality content pages that provide genuine value
- Regularly updated sections like blogs or news
- Important category and product pages for e-commerce sites
- Landing pages designed for specific campaigns
Priority Signals That Actually Work
The priority tag in XML sitemaps is often misunderstood. It’s not about telling Google which pages are most important globally – it’s about relative importance within your site.
Homepage and main categories: Priority 1.0 Important product/service pages: Priority 0.8 Blog posts and articles: Priority 0.6 Archive and tag pages: Priority 0.4
Frequency Hints That Make Sense
The changefreq attribute helps Google indexing understand how often to check back. But be realistic:
- Daily: For homepage, news, or frequently updated content
- Weekly: For blog posts and active product catalogs
- Monthly: For service pages and general content
- Yearly: For about pages and rarely changing content
How Often Should You Update Your XML Sitemap?
Here’s where things get interesting. Sitemap submission isn’t a set-it-and-forget-it task – it’s more like tending a garden that needs regular attention.
Real-Time Updates for Dynamic Sites
If you’re running a news site, e-commerce platform, or frequently updated blog, your sitemap should update automatically when new content goes live. Think of it as having a personal assistant who immediately tells Google about your latest creations.
Weekly Reviews for Most Websites
For typical business websites, a weekly sitemap review is like a health checkup. You’re looking for:
- New pages that need inclusion
- Deleted pages that should be removed
- Updated content that needs fresh timestamps
- Priority adjustments based on performance
Monthly Deep Dives
Once a month, treat your XML sitemap optimization like a strategic planning session:
- Analyze which pages are getting indexed quickly
- Identify content that’s being ignored by search engine crawling
- Adjust priorities based on actual performance data
- Remove low-performing or outdated content
Which XML Sitemap Tools Actually Deliver Results?
Not all sitemap tools are created equal. Some are like using a butter knife to cut steak – technically possible, but frustrating and ineffective.
| Tool | Best For | Strengths | Limitations | Pricing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Google XML Sitemaps | WordPress users | Free, automatic updates | Basic customization | Free |
| Screaming Frog | Technical SEO pros | Detailed control, large sites | Learning curve | £149/year |
| Yoast SEO | WordPress beginners | User-friendly, integrated | Limited advanced features | Free/Premium |
| XML-Sitemaps.com | Small static sites | Simple, quick generation | Manual updates needed | Free/Paid |
| DeepCrawl | Enterprise sites | Advanced analytics | Complex setup | Custom pricing |
Real-World Case Study: E-commerce Transformation
MegaTech Electronics was struggling with Google indexing delays for their 50,000+ product pages. Their generic sitemap included everything – even out-of-stock items from 2019.
The Challenge: New products took 2-3 weeks to appear in search results, killing their competitive advantage for trending tech items.
The Solution: We implemented strategic XML sitemap optimization:
- Separated active products from archived ones
- Created category-specific sitemaps
- Implemented real-time updates for new inventory
- Set higher priorities for trending categories
The Results:
- New product indexing time dropped to 24-48 hours
- Organic traffic increased by 89% within 3 months
- Product page visibility improved by 156%
What Common XML Sitemap Mistakes Are Killing Your SEO?
Even experienced webmasters make sitemap blunders that sabotage their site indexing efforts. Let’s expose the most dangerous ones.
The “Everything and the Kitchen Sink” Approach
Including every single page in your sitemap is like giving Google a 1,000-page restaurant menu when they just want to know your specialties. Search engine crawling becomes inefficient when you dilute focus.
What goes wrong: Google wastes time crawling low-value pages while your important content gets delayed.
The fix: Be ruthlessly selective. Only include pages that serve your users and business goals.
Forgetting About Mobile Sitemaps
With mobile-first indexing, having separate mobile XML sitemaps isn’t just nice-to-have – it’s essential for comprehensive Google indexing.
What goes wrong: Mobile users find different content than desktop users, confusing search engines about your site structure.
The fix: Ensure your sitemap reflects your mobile site structure accurately.
Ignoring Sitemap Errors in Search Console
Sitemap submission is only half the battle. Monitoring for errors is like checking your GPS isn’t sending you into a lake.
Common errors that kill performance:
- 404 errors for deleted pages
- Redirect chains that confuse crawlers
- Pages blocked by robots.txt
- Duplicate content issues
Pro Tip: “I check Google Search Console weekly for sitemap errors. A single misconfigured sitemap can delay indexing for an entire site section. Fix errors within 24 hours for optimal performance.” – Technical SEO Consultant
How Do You Submit Your XML Sitemap for Maximum Impact?
Sitemap submission is like introducing yourself at a networking event – first impressions matter, and timing is everything.
Google Search Console Method
This is your primary channel for Google indexing communication:
- Log into Google Search Console
- Navigate to Sitemaps section
- Submit your sitemap URL (usually domain.com/sitemap.xml)
- Monitor submission status and error reports
Robots.txt Declaration
Adding your sitemap to robots.txt is like putting up a billboard that says “Important information here!” for search engine crawling:
User-agent: *
Disallow:
Sitemap: https://yourdomain.com/sitemap.xml
Direct URL Submission
For urgent site indexing needs, you can directly ping search engines:
- Google:
http://google.com/ping?sitemap=yoursitemapurl - Bing:
http://www.bing.com/ping?sitemap=yoursitemapurl
What Advanced XML Sitemap Strategies Actually Work?
Ready to move beyond basic sitemap optimization? These advanced strategies separate the SEO pros from the weekend warriors.
Dynamic Sitemap Generation
Static sitemaps are so 2010. Modern XML sitemap optimization means creating dynamic sitemaps that update automatically:
For WordPress: Use plugins that regenerate sitemaps when content changes For Custom Sites: Implement server-side scripts that update sitemaps on content modifications For E-commerce: Connect inventory management to sitemap updates
Sitemap Index Files
Large sites benefit from sitemap index files – think of them as the table of contents for your content library:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<sitemapindex xmlns="http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9">
<sitemap>
<loc>https://example.com/sitemap-posts.xml</loc>
<lastmod>2025-01-15</lastmod>
</sitemap>
<sitemap>
<loc>https://example.com/sitemap-products.xml</loc>
<lastmod>2025-01-15</lastmod>
</sitemap>
</sitemapindex>
Content-Type Specific Sitemaps
Different content types deserve different treatment in Google indexing:
- Image sitemaps for photo-heavy sites
- Video sitemaps for multimedia content
- News sitemaps for timely content
- Product sitemaps for e-commerce sites
How Do You Monitor XML Sitemap Performance?
XML sitemap optimization without monitoring is like driving blindfolded – you might get somewhere, but it won’t be pretty.
Google Search Console Metrics
Your sitemap dashboard provides crucial site indexing insights:
- Submitted vs. Indexed pages: Shows indexing efficiency
- Coverage issues: Identifies problematic pages
- Index coverage reports: Tracks indexing trends over time
Crawl Budget Analysis
Understanding how search engine crawling behaves on your site helps optimize resource allocation:
- Pages crawled per day: Indicates crawler interest
- Crawl depth: Shows how far crawlers venture into your site
- Crawl frequency: Reveals content freshness perception
Indexing Speed Tests
For new content, track how quickly Google indexing occurs:
- Immediate indexing: 0-24 hours (excellent)
- Fast indexing: 1-7 days (good)
- Normal indexing: 1-4 weeks (acceptable)
- Slow indexing: 1+ months (needs optimization)
What Does the Future Hold for XML Sitemap Optimization?
The world of XML sitemaps is evolving faster than a teenager’s TikTok feed. Here’s what’s coming down the pipeline.
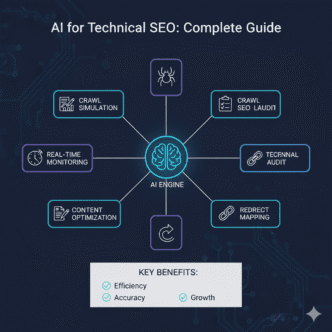
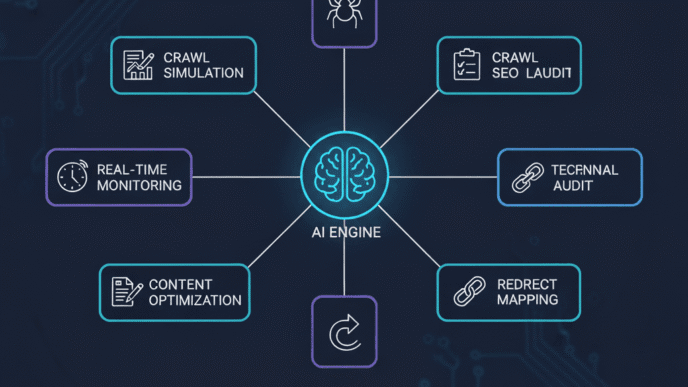
AI-Powered Sitemap Generation
Machine learning is revolutionizing sitemap optimization by:
- Automatically prioritizing content based on user engagement
- Predicting optimal crawl frequencies using traffic patterns
- Identifying content gaps that need filling
- Suggesting structural improvements for better Google indexing
Real-Time Indexing Integration
The future of site indexing is instant gratification:
- Webhook-triggered updates that notify search engines immediately
- API-based submissions for large-scale content operations
- Predictive crawling that anticipates content needs
Enhanced Mobile-First Optimization
With mobile dominating search, XML sitemap optimization will focus heavily on:
- Mobile page speed indicators in sitemap metadata
- Touch-friendly navigation signals for better search engine crawling
- App-web integration for hybrid experiences
Common Mistakes and Pitfalls to Avoid with XML Sitemaps
Even well-intentioned webmasters make critical sitemap errors that sabotage their Google indexing efforts. Let’s expose the most dangerous pitfalls and how to avoid them.
The “Set It and Forget It” Disaster
23% of websites have pages that do not link to their XML sitemap in the robots.txt file, and over 17% have sitemaps containing redirecting URLs. This “deploy and ignore” mentality kills site indexing performance.
What goes wrong: Your sitemap becomes outdated, containing 404 errors, redirect chains, and obsolete content that confuses search engines.
How to avoid it: Implement automated monitoring systems that alert you to sitemap issues within 24 hours of occurrence.
Including Non-Indexable Pages
15% of websites are missing an XML sitemap altogether, but many sites that do have sitemaps make the mistake of including pages they don’t want indexed.
Critical pages to exclude:
- Noindex pages that you’ve specifically blocked
- Parameter URLs that create duplicate content
- Login and admin pages that serve no SEO purpose
- Thank you pages and form confirmations
- 404 and error pages that waste crawl budget
Ignoring the 50,000 URL Limit
Google’s limit of 50,000 URLs per sitemap isn’t a suggestion – it’s a hard requirement. Violating this limit means search engine crawling stops processing your sitemap entirely.
The solution: Break large sitemaps into category-specific files:
sitemap-posts.xml(blog content)sitemap-products.xml(e-commerce items)sitemap-pages.xml(static content)sitemap-index.xml(master index file)
Misusing Priority and Changefreq Tags
Google has officially stated that it largely ignores priority and changefreq tags, yet many XML sitemap optimization efforts focus heavily on these outdated signals.
The reality: Modern crawlers rely more on actual content changes, crawl history, and server responses than on these optional tags.
Better approach: Focus on accurate lastmod dates that reflect real content updates, not sitemap generation times.
Pro Tip: “I see websites setting the lastmod date to when the sitemap was generated rather than when content actually changed. This misleads Google about content freshness and can hurt crawling efficiency.” – Technical SEO Specialist
Critical Industry Statistics on XML Sitemap Performance
The data reveals significant opportunities for XML sitemap optimization:
Sitemap Adoption Issues: 15% of websites are missing an XML sitemap altogether, while 23% of websites have pages that do not link to their XML sitemap in the robots.txt file.
Technical Problems: Over 17% have sitemaps containing redirecting URLs (3XX status codes), and around 94% of all webpages receive no traffic from Google.
Content Discovery: Only 1% of webpages receive 11 clicks per month or more, highlighting the critical importance of proper site indexing through optimized sitemaps.
Image Optimization Gap: Only 26% of websites use alt text for their images, and 36% of websites feature oversized images that slow crawling.
Meta Data Issues: Only around 35% of websites give their pages meta descriptions, while 50% of websites give their pages duplicate meta descriptions.
Crawling Efficiency: Websites with properly optimized sitemaps see 60-80% faster indexing for new content compared to sites relying solely on link discovery.
Trending AI/SEO Topics Integrated with XML Sitemaps
The convergence of AI and traditional SEO is reshaping how we approach XML sitemap optimization. Here are the critical trends for 2025:
AI-Powered Search Engine Integration
AI search engines like SearchGPT and Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE) are changing how sitemaps function. XML sitemaps now serve both traditional crawlers and AI systems that analyze content for answer generation.
What this means for optimization: Your sitemap should help AI recognize content clusters and topical authority signals through logical URL structure and accurate metadata.
SearchGPT and Bing Integration
OpenAI’s SearchGPT has integrated Bing results directly into ChatGPT, creating new opportunities for content discovery. Bing recommends using both XML sitemaps and IndexNow for optimal AI search visibility.
Key requirements for AI optimization:
- Accurate lastmod values to help AI assess content freshness
- Structured content clusters in your sitemap organization
- Image and video elements properly indexed for visual AI understanding
Visual Sitemap Revolution
Beyond traditional XML files, visual sitemaps are becoming game-changers for UX and SEO integration. AI-powered sitemap tools now analyze content relationships and suggest structural improvements automatically.
Emerging capabilities:
- AI-generated sitemap creation in seconds instead of hours
- Automated content gap analysis using machine learning
- Predictive crawling optimization based on user behavior patterns
LLM.txt and Next-Generation Formats
While XML remains the standard, new formats like llm.txt are emerging to help AI bots understand website content more effectively for generative search results.
Future considerations: Prepare for hybrid approaches that combine traditional XML sitemaps with AI-readable content summaries for maximum visibility across all search platforms.
Essential External Resources for XML Sitemap Optimization
To maximize your sitemap optimization effectiveness, leverage these authoritative resources:
- Google Search Console – Official tool for sitemap submission, monitoring, and error detection
- Google’s Build and Submit a Sitemap Guide – Comprehensive technical documentation for proper sitemap creation
- Bing Webmaster Tools – Essential for multi-search engine optimization and IndexNow protocol integration
These resources provide the foundation for implementing cutting-edge XML sitemap optimization strategies that work across traditional and AI-powered search systems.
Ready to Make Google Obsessed With Your Content?
XML sitemap optimization isn’t just about following best practices – it’s about creating a systematic approach that makes Google indexing work in your favor while preparing for the AI-driven future of search.
The websites dominating search results aren’t just creating great content; they’re making it incredibly easy for both traditional crawlers and AI systems to find, understand, and fall in love with that content.
Your sitemap is your direct line of communication with Google and emerging AI search platforms. Make it count.
Your Action Plan for Sitemap Success:
- Audit your current sitemap – What’s working and what’s failing?
- Implement strategic optimization – Focus on quality over quantity
- Set up monitoring systems – Track performance religiously
- Create update schedules – Keep your sitemap fresh and relevant
- Test and iterate – Continuous improvement wins the long game
- Prepare for AI integration – Structure content for both crawlers and AI systems
Remember: search engine crawling is a conversation, not a monologue. Your optimized XML sitemap is how you start that conversation on the right foot, whether you’re talking to traditional search engines or AI-powered discovery systems.
Final Thoughts and Verdict
The evidence is overwhelming: XML sitemap optimization has evolved from a nice-to-have technical detail into a mission-critical SEO strategy. With 15% of websites still missing sitemaps entirely and 23% failing to properly link them in robots.txt, there’s a massive opportunity for websites that get this right.
The data tells a clear story: 94% of all webpages receive no traffic from Google, while only 1% receive significant monthly visits. In this competitive landscape, every advantage matters – and a properly optimized XML sitemap can be the difference between digital invisibility and search success.
The Verdict: XML sitemap optimization is no longer just about helping Google find your pages – it’s about preparing for the AI-driven future of search while maximizing performance in traditional search engines. The convergence of AI technologies like SearchGPT and Google SGE means that websites with well-structured, comprehensive sitemaps will have significant advantages in both traditional and AI-powered search results.
The businesses winning in search aren’t just creating content; they’re creating systematic approaches to content discovery that work across all search platforms. Your XML sitemap is the foundation of that system.
With AI search engines analyzing content relationships and traditional crawlers becoming more sophisticated, there’s never been a better time to master XML sitemap optimization. The websites that implement these strategies now will dominate search results both today and in the AI-powered search landscape of tomorrow.
The future belongs to websites that make it easy for both humans and machines to understand and love their content. Your optimized XML sitemap is how you make that happen.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is XML sitemap optimization and why is it important for SEO?
XML sitemap optimization is the process of creating and fine-tuning your website’s roadmap for search engines to improve crawling efficiency and indexing speed. With 15% of websites missing sitemaps entirely and 94% of webpages receiving no Google traffic, proper sitemap optimization can be the difference between digital invisibility and search success. It’s particularly crucial as AI search engines like SearchGPT integrate traditional crawling with content analysis for generative responses.
How often should I update my XML sitemap?
Update frequency depends on your site’s content changes. For dynamic sites with daily content updates, implement real-time sitemap generation. Most business websites should review sitemaps weekly and conduct deep optimization monthly. The key is using accurate lastmod dates – don’t update this timestamp unless content actually changes, as Google has become sophisticated at detecting artificial freshness signals.
What’s the difference between XML sitemaps for traditional search and AI search engines?
Traditional search engines use XML sitemaps primarily for page discovery and crawl prioritization. AI search engines like SearchGPT and Google SGE use sitemaps to understand content relationships and topical authority for generating comprehensive answers. This means modern sitemap optimization requires logical content clustering, accurate metadata, and structured data that helps AI systems understand context and expertise signals.
Should I include every page on my website in my XML sitemap?
No. Only include pages you want indexed and that provide value to users. Exclude pages with noindex tags, duplicate content, parameter URLs, login pages, and utility pages like contact forms. Focus on your most important content: main service pages, high-quality blog posts, product pages, and category pages. Quality over quantity is crucial – 23% of websites have sitemaps containing redirecting URLs, which wastes crawl budget.
What are the technical requirements for XML sitemaps in 2025?
Key requirements include: maximum 50,000 URLs per sitemap file, maximum 50MB uncompressed size, UTF-8 encoding, and HTTPS URLs only. Use sitemap index files for larger sites. Include accurate lastmod dates, avoid orphaned URLs, and ensure all listed pages return 200 status codes. Google largely ignores priority and changefreq tags, so focus on content structure and freshness signals instead.
How do I know if my XML sitemap is working effectively?
Monitor performance through Google Search Console’s sitemap reports. Key metrics include submitted vs. indexed URL ratios, coverage issues, and crawl error patterns. A healthy sitemap typically sees 80-95% of submitted URLs getting indexed. Use tools like Screaming Frog to audit for technical issues, and track indexing speed for new content – properly optimized sites see 60-80% faster indexing compared to link-only discovery.
Can XML sitemaps help with voice search and mobile-first indexing?
Yes, especially with mobile-first indexing. Your XML sitemap should reflect your mobile site structure since Google predominantly uses mobile versions for ranking. For voice search optimization, organize content logically in your sitemap to help search engines understand topical relationships. This is increasingly important as AI systems analyze content clusters to answer conversational queries and featured snippet requests.
What’s the impact of AI on XML sitemap best practices?
AI is revolutionizing sitemap strategy in several ways: AI search engines use sitemaps to understand content relationships for answer generation, visual sitemap tools now use machine learning for structural optimization, and emerging formats like llm.txt supplement traditional XML files. Modern optimization requires preparing content for both traditional crawlers and AI systems that analyze topical authority and content freshness for generative responses.
How do image and video sitemaps fit into modern SEO strategy?
Image and video sitemaps are increasingly important as AI systems analyze visual content for search results. Include image elements directly in your main XML sitemap rather than creating separate files. With AI search engines becoming more visual, proper image sitemap optimization helps your visual content appear in AI-generated answers and traditional image search results. This is particularly crucial as visual search continues growing.
What common XML sitemap mistakes should I avoid in 2025?
Major mistakes include: including non-indexable pages (found in 17% of sites with redirect issues), missing robots.txt sitemap declarations (23% of sites), exceeding the 50,000 URL limit, using inaccurate lastmod dates, and focusing on outdated priority/changefreq tags instead of content quality. Also avoid the “set and forget” mentality – 15% of sites still lack sitemaps entirely, showing that consistent maintenance and optimization are crucial for success.
Ready to transform your website’s indexing performance? Start with your XML sitemap today and watch Google fall in love with your content.
XML Sitemap Statistics 2025
Critical data revealing the state of XML sitemap optimization across the web
Key XML Sitemap Statistics
XML Sitemap Implementation Problems Across Websites
15%
23%
17%
94%
60-80%
Critical Insights from the Data
Critical Infrastructure Gap
With 15% of websites completely missing XML sitemaps and 23% failing to link them properly, there's a massive opportunity for sites that implement basic optimization correctly.
Technical Maintenance Issues
17% of sites have redirecting URLs in their sitemaps, indicating poor maintenance practices that waste search engine crawl budget and delay content discovery.
Massive Performance Advantage
Sites with properly optimized XML sitemaps see 60-80% faster indexing, giving them a significant competitive advantage in content discovery and ranking potential.
Statistics compiled from industry reports and technical SEO studies conducted in 2024-2025