Ever feel like you’re shouting into the void with your WordPress site? You publish great content, but crickets. Meanwhile, your competitor with mediocre posts is ranking on page one of Google.
Here’s the truth: WordPress doesn’t automatically make your site SEO-friendly. It’s like buying a Ferrari and never learning to drive it. You’ve got the power under the hood, but without the right optimization, you’re just spinning your wheels.
This WordPress SEO guide will change that. Whether you’re a blogger trying to grow your audience, a small business owner chasing local customers, or just someone tired of invisible content, I’ll walk you through everything you need to rank higher in 2025.
No jargon. No fluff. Just practical steps that actually work.
Let’s dive in.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is WordPress SEO (And Why Should You Care)?
WordPress SEO is the art and science of optimizing your WordPress website so search engines like Google can find, understand, and rank your content higher.
Think of Google as a librarian. When someone searches for “best pizza recipe,” Google scans billions of web pages to find the most relevant, trustworthy answer. Your job is to make your WordPress site the obvious choice.
Here’s why this matters: 75% of users never scroll past the first page of search results. If you’re not ranking there, you’re practically invisible.
The good news? WordPress powers 43% of all websites, and it’s built with SEO-friendly features right out of the box. You’re already ahead of the game—you just need to optimize what you’ve got.
Is WordPress Already SEO-Friendly?
Yes and no. (I know, helpful answer, right?)
WordPress core is technically SEO-friendly. It generates clean code, creates automatic sitemaps, and uses semantic HTML that search engines love. Matt Cutts, former head of Google’s webspam team, has publicly praised WordPress for its SEO foundation.
But here’s the catch: default WordPress is like a house with great bones but no furniture. You still need to:
- Optimize your permalink structure
- Install an SEO plugin
- Compress images
- Improve site speed
- Build quality backlinks
- Create search-optimized content
Out of the box, WordPress won’t automatically rank you #1. But with the right tweaks (which I’ll show you), it becomes an SEO powerhouse.
How Do Search Engines Actually Rank WordPress Sites?
Before we get tactical, let’s understand the game we’re playing.
Google uses over 200 ranking factors, but they fall into three main buckets:
1. Technical SEO (Can Google Crawl Your Site?)
This includes site speed, mobile-friendliness, SSL certificates, and XML sitemaps. If Google’s bots can’t access your content, you won’t rank. Period.
2. On-Page SEO (Is Your Content Relevant?)
This covers keyword optimization, title tags, meta descriptions, header tags, and internal linking. It’s about telling Google exactly what your page is about.
3. Off-Page SEO (Do Others Trust You?)
Backlinks are the currency here. When reputable sites link to you, Google sees it as a vote of confidence. More quality backlinks = higher rankings.
Pro Tip: Don’t obsess over gaming the algorithm. Focus on creating genuinely helpful content, and the technical stuff will amplify your results. Google’s getting smarter—it rewards value, not tricks.
What’s the Best WordPress SEO Plugin in 2025?
Let me save you hours of research: you absolutely need an SEO plugin.
Why? Because managing meta descriptions, XML sitemaps, schema markup, and breadcrumbs manually would be insane. These plugins do the heavy lifting for you.
Here are your top three options:
| Plugin | Best For | Price | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yoast SEO | Beginners | Free / $99/year | Content analysis, readability checker, XML sitemaps, snippet preview |
| Rank Math | Advanced users | Free / $59/year | Google Search Console integration, schema markup, 404 monitor, advanced analytics |
| All in One SEO (AIOSEO) | eCommerce sites | Free / $49.50/year | WooCommerce SEO, local SEO, video sitemap, social media integration |
My Recommendation?
Start with Rank Math if you’re comfortable with technology. It’s free, powerful, and doesn’t hold features hostage behind a paywall like some competitors.
Go with Yoast SEO if you’re brand new. The interface is friendly, the tutorials are everywhere, and the traffic light system (red/orange/green) makes optimization foolproof.
How to Install Your SEO Plugin
- Go to Plugins > Add New in your WordPress dashboard
- Search for your chosen plugin
- Click Install Now, then Activate
- Follow the setup wizard (usually 5 minutes max)
Done. You’ve just unlocked 80% of WordPress’s SEO potential.
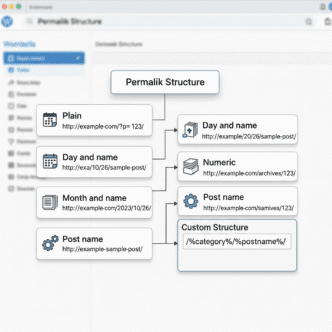
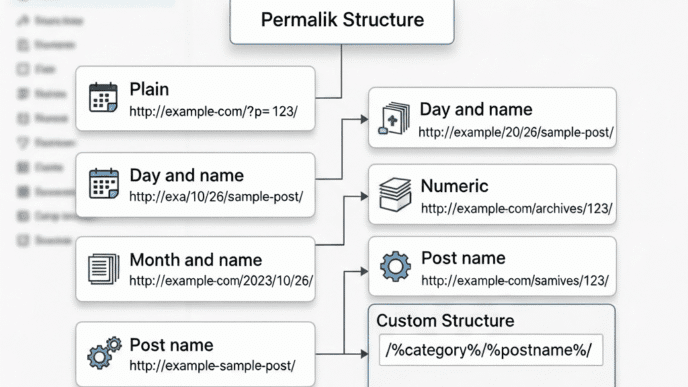
How Do I Choose the Perfect Permalink Structure for SEO?
Your permalink structure is your URL format. And yes, it matters more than you think.
Bad URL: yoursite.com/?p=123
Good URL: yoursite.com/wordpress-seo-guide
See the difference? The second one tells both humans and Google exactly what the page is about.
Setting Up SEO-Friendly Permalinks
- Go to Settings > Permalinks in WordPress
- Select Post name (recommended)
- Click Save Changes
Warning: If you change permalinks on an established site, you’ll break existing links. Set up 301 redirects using a plugin like Redirection to avoid tanking your rankings.
Best Practices for WordPress Permalinks
- Keep URLs short (under 60 characters is ideal)
- Include your focus keyword
- Use hyphens, not underscores (Google treats hyphens as spaces)
- Remove stop words (a, the, and, or) when possible
- Avoid dates in URLs unless you run a news site
Real example: Instead of yoursite.com/2025/01/10/how-to-do-wordpress-seo-optimization-for-beginners-guide, use yoursite.com/wordpress-seo-beginners-guide.
Short. Sweet. Scannable.
What Are the Most Important On-Page SEO Elements in WordPress?
On-page SEO is where you tell Google, “Hey, this post is about WordPress SEO optimization, and here’s why it’s valuable.
Let’s break down the essential elements:
1. Title Tags (The Most Important HTML Element)
Your title tag appears in search results and browser tabs. It’s your first impression.
Formula: Primary Keyword + Benefit/Hook + Year (if relevant)
Examples:
- “WordPress SEO: Complete Guide to Rank #1 in 2025”
- How to Optimize WordPress Sites for Search Engines (2025 Update)
Pro Tip: Keep titles under 60 characters or Google will cut them off with an ellipsis. Use numbers and power words like “Complete,” “Ultimate,” “Proven,” or “Step-by-Step.”
2. Meta Descriptions (Your Sales Pitch)
This is the 155-character snippet that appears below your title in search results. It doesn’t directly affect rankings, but it impacts click-through rates (CTR)—which do affect rankings.
Example: “Learn WordPress SEO optimization from scratch. This complete guide covers plugins, speed, keywords, and link building—everything you need to rank higher in 2025.”
Include your focus keyword, a benefit, and a call-to-action.
3. Header Tags (H1, H2, H3)
Headers structure your content and help Google understand your page hierarchy.
- H1: Your main title (only one per page)
- H2: Major section headings
- H3: Subsections under H2s
Naturally include related keywords in headers. Google pays attention here.
4. Content Quality and Length
Here’s a dirty secret: longer content tends to rank higher. Studies show the average first-page result is 1,400+ words.
But don’t just inflate word count. Focus on comprehensive value. Answer every question your reader might have about the topic.
5. Keyword Optimization (Without Keyword Stuffing)
Use your primary keyword:
- In the first 100 words
- In at least one H2 heading
- In your title and meta description
- Naturally throughout the content (aim for 0.5-1% keyword density)
Also sprinkle in LSI keywords (Latent Semantic Indexing)—related terms like:
- WordPress search engine optimization
- On-page SEO for WordPress
- WordPress ranking factors
- SEO best practices for WordPress blogs
Google’s smart. It understands synonyms and context. Write for humans first, then optimize.
6. Internal Linking
Link to other relevant posts on your site. This:
- Keeps visitors on your site longer
- Distributes page authority across your content
- Helps Google discover and index pages
Pro Tip: Use descriptive anchor text instead of “click here.” Instead of “Read this article about plugins,” write “Check out our guide to the best WordPress SEO plugins.”
7. External Links
Link to authoritative sources (think: major publications, government sites, research studies). This builds trust with Google and provides value to readers.
Don’t be afraid of linking out. It won’t hurt your rankings—it actually helps.
How Do I Optimize Images for WordPress SEO?
Images make content scannable and engaging. But unoptimized images are the #1 cause of slow WordPress sites.
Image SEO Checklist
1. Compress Before Uploading
Use tools like:
- TinyPNG (free online compression)
- ShortPixel (WordPress plugin)
- Imagify (automatic compression)
Aim for images under 100KB without sacrificing quality.
2. Use Descriptive File Names
Bad: IMG_4829.jpg
Good: wordpress-seo-dashboard-settings.jpg
Include keywords when relevant.
3. Write Alt Text
Alt text describes images for visually impaired users (and Google). It’s an accessibility requirement and an SEO opportunity.
Formula: Brief description + keyword (if natural)
Example: “WordPress SEO plugin settings dashboard showing meta description editor”
4. Choose the Right Format
- WebP: Best compression and quality (use this in 2025)
- JPEG: Photos and complex images
- PNG: Logos, icons, transparent backgrounds
5. Enable Lazy Loading
This delays loading images until users scroll to them. WordPress has built-in lazy loading since version 5.5, but plugins like WP Rocket enhance it further.
Pro Tip: Add schema markup for images using your SEO plugin. This can get your images featured in Google Image Search, driving additional traffic.
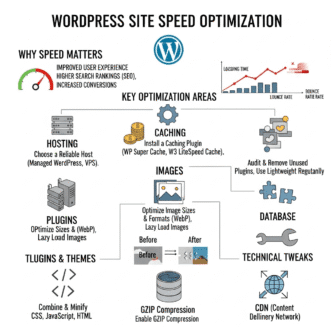
Why Is Site Speed Critical for WordPress SEO?
Page speed is a direct ranking factor. Google confirmed this. Plus, 53% of mobile users abandon sites that take over 3 seconds to load.
Slow site = bad rankings + high bounce rates = even worse rankings. It’s a death spiral.
How to Check Your WordPress Site Speed
Use these free tools:
- Google PageSpeed Insights
- GTmetrix
- Pingdom Website Speed Test
Aim for a load time under 3 seconds.
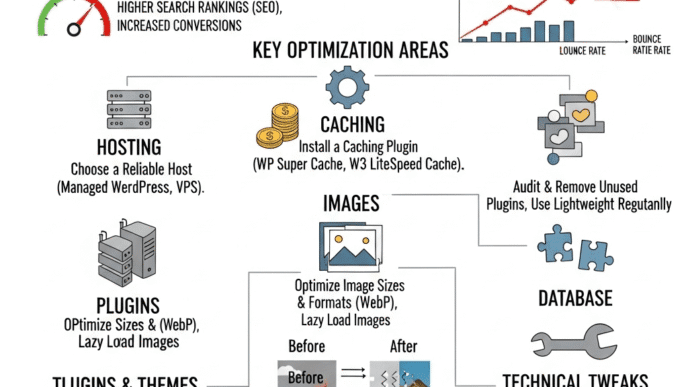
12 Ways to Speed Up Your WordPress Site
1. Choose Fast WordPress Hosting
Cheap shared hosting ($3/month) is slow. Invest in quality:
- Kinsta (managed WordPress hosting)
- SiteGround (excellent performance)
- WP Engine (premium, but blazing fast)
2. Use a Caching Plugin
Caching creates static HTML versions of your pages, reducing server load.
Top options:
- WP Rocket (paid, easiest)
- W3 Total Cache (free, powerful)
- WP Super Cache (free, simple)
3. Enable GZIP Compression
This reduces file sizes sent to browsers. Most caching plugins enable this automatically.
4. Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML
Remove unnecessary characters from code. Again, caching plugins handle this.
5. Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
CDNs store copies of your site on servers worldwide, delivering content from the closest location.
Try:
- Cloudflare (free plan available)
- BunnyCDN (affordable, fast)
6. Optimize Your Database
Over time, WordPress databases get bloated with revisions, spam, and trash. Use WP-Optimize to clean it up monthly.
7. Limit Plugins
Every plugin adds code. Delete unused plugins and choose lightweight alternatives.
8. Disable Pingbacks and Trackbacks
Go to Settings > Discussion and uncheck these. They’re outdated and slow your site.
9. Choose a Fast Theme
Bloated themes kill speed. Stick with lightweight options like:
- GeneratePress
- Astra
- Neve
10. Defer JavaScript Loading
This prevents JavaScript from blocking page rendering. Your caching plugin can handle this.
11. Reduce External HTTP Requests
Every external font, script, or stylesheet adds load time. Minimize what you embed from third-party sources.
12. Upgrade PHP Version
Outdated PHP slows down WordPress. Check with your host to upgrade to PHP 8.0 or higher.
Pro Tip: Don’t chase a perfect 100 score on PageSpeed Insights. Aim for 85+ on mobile and 90+ on desktop. Obsessing over tiny improvements wastes time better spent creating content.
How Do I Make My WordPress Site Mobile-Friendly?
Google uses mobile-first indexing. This means it primarily uses your mobile site to determine rankings—even for desktop searches.
If your site isn’t mobile-friendly, you’re invisible.
Quick Mobile SEO Checklist
1. Use a Responsive WordPress Theme
Most modern themes are responsive by default (they adapt to screen sizes). Test yours by resizing your browser window.
2. Test Mobile Usability
Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool. Just enter your URL and Google will tell you if there are issues.
3. Optimize Touch Elements
Buttons and links should be easy to tap (minimum 48×48 pixels). Avoid tiny clickable elements bunched together.
4. Avoid Intrusive Pop-Ups
Google penalizes sites with pop-ups that cover content on mobile. If you use them, make sure they’re easy to dismiss.
5. Improve Mobile Page Speed
Mobile users are impatient. Follow the speed optimization tips above, with extra focus on image compression and eliminating render-blocking resources.
What Is Schema Markup and Do I Need It?
Schema markup (structured data) is code that helps search engines understand your content better. It can get you rich snippets—those enhanced search results with star ratings, images, prices, or FAQ accordions.
Rich snippets = higher click-through rates = more traffic.
Types of Schema for WordPress Sites
- Article schema: Blog posts and news
- Product schema: eCommerce listings with prices and reviews
- FAQ schema: Question-and-answer sections
- Recipe schema: Cooking sites with ingredients and times
- Local Business schema: Contact info, hours, location
How to Add Schema Markup to WordPress
Option 1: Use Rank Math or Yoast SEO (both have schema features built-in)
Option 2: Use a dedicated plugin like Schema Pro
Option 3: Manually add JSON-LD code (not recommended unless you’re technical)
Most SEO plugins handle schema automatically. Just enable the relevant schema types in settings.
Pro Tip: Use Google’s Rich Results Test to verify your schema is working correctly. Not all schema types are eligible for rich snippets, but it’s worth implementing for the ones that are.
How Do I Create an XML Sitemap in WordPress?
An XML sitemap is a file that lists all your important pages, making it easier for Google to crawl your site.
Good news: WordPress automatically generates sitemaps (since version 5.5). Your sitemap is likely already live at yoursite.com/wp-sitemap.xml.
But default WordPress sitemaps are basic. For more control, use your SEO plugin.
Setting Up a Better XML Sitemap
With Rank Math:
- Go to Rank Math > Sitemap Settings
- Enable sitemap (usually on by default)
- Choose which post types to include
- Exclude low-value pages (tags, archives, etc.)
With Yoast SEO:
- Go to SEO > General > Features
- Enable XML sitemaps
- Customize in SEO > Search Appearance
Submitting Your Sitemap to Google
- Open Google Search Console
- Select your property
- Go to Sitemaps in the left menu
- Enter your sitemap URL (usually
yoursite.com/sitemap_index.xml) - Click Submit
Do the same in Bing Webmaster Tools (yes, Bing matters—it powers 33% of US searches).
What Is Google Search Console and Why Do I Need It?
Google Search Console (GSC) is a free tool that shows you how Google sees your WordPress site. It’s like getting direct feedback from Google itself.
You’ll see:
- Which keywords you’re ranking for
- How many clicks and impressions you’re getting
- Indexing issues that need fixing
- Mobile usability problems
- Manual penalties (hopefully none)
Setting Up Google Search Console
Click Start Now and sign in with your Google account
Add your property (choose URL prefix)
Verify ownership using one of these methods:
- HTML file upload
- HTML tag (easiest—just paste code in your SEO plugin)
- Google Analytics (if already connected)
- Domain name provider
Submit your sitemap (as described above)
Pro Tip: Check GSC weekly. Look for pages with impressions but low click-through rates—those are quick wins for rewriting titles and meta descriptions.
How Do I Do Keyword Research for WordPress Content?
Keywords are the bridge between what people search and what you write. Get this wrong, and even great content goes unseen.
The Keyword Research Process
Step 1: Brainstorm Seed Keywords
What would your ideal reader type into Google? Start broad.
Examples for a WordPress SEO site:
- WordPress SEO
- WordPress optimization
- SEO plugins
- Improve WordPress rankings
Step 2: Use Keyword Research Tools
Free options:
- Google Keyword Planner (in Google Ads)
- Ubersuggest (limited free searches)
- AnswerThePublic (question-based keywords)
Paid options (worth it):
- Ahrefs ($99/month)
- SEMrush ($119.95/month)
- Mangools KWFinder ($29/month)
Look for:
- Search volume: How many monthly searches?
- Keyword difficulty: How hard to rank? (aim for lower competition)
- Search intent: What does the searcher want?
Step 3: Find Long-Tail Keywords
Long-tail keywords are specific 3-5 word phrases with lower search volume but higher intent.
Example:
- “SEO” (too broad, super competitive)
- “WordPress SEO” (better, but still tough)
- “WordPress SEO plugin for beginners” (specific, easier to rank)
Long-tail keywords convert better because they match specific user intent.
Step 4: Analyze Competitor Content
Google your target keyword. What are the top 5 results doing well? What can you do better?
Look at:
- Content depth
- Unique angles they’re missing
- Questions they didn’t answer
Step 5: Match Search Intent
Google rewards content that matches what users actually want.
| Search Intent | User Goal | Content Type |
|---|---|---|
| Informational | Learn something | Blog post, guide, tutorial |
| Navigational | Find a specific site | Homepage, branded content |
| Commercial | Compare options before buying | Reviews, comparisons, “best of” lists |
| Transactional | Buy something now | Product pages, service pages |
Pro Tip: Don’t keyword-stuff. Use your primary keyword naturally in key places, then use variations and related terms throughout. Google understands context—write for humans.
How Do I Write SEO-Optimized Content in WordPress?
You’ve got your keywords. Now let’s create content Google and readers both love.
The SEO Content Writing Formula
1. Hook Readers Immediately
Your first 100 words determine if people stay or bounce. Start with:
- A relatable pain point
- A surprising statistic
- A bold promise
- A compelling question
2. Structure for Scannability
Online readers skim. Make it easy:
- Short paragraphs (2-3 sentences max)
- Subheadings every 200-300 words
- Bullet lists for steps or features
- Bold important points
3. Use the Bucket Brigade Technique
These are phrases that keep readers scrolling:
- “Here’s the thing…”
- “But wait, there’s more.”
- “Let me explain…”
- “Here’s why that matters…”
4. Answer Questions Thoroughly
Don’t leave readers hanging. If you raise a question, answer it completely before moving on.
5. Add Visuals
Break up text with:
- Screenshots
- Infographics
- Charts or graphs
- Videos
6. Include a Clear Call-to-Action (CTA)
What should readers do next? Comment? Download something? Read another post? Tell them.
Pro Tip: Write like you talk. Contractions, sentence fragments, and conversational tone make content more engaging. Formal, stiff writing doesn’t rank—or convert—as well.
What Is Internal Linking and How Do I Use It?
Internal links connect pages on your own site. They’re SEO gold.
Benefits:
- Keeps visitors engaged longer (lower bounce rate)
- Distributes link equity (page authority) across your site
- Helps Google understand site structure
- Boosts rankings for linked pages
Internal Linking Best Practices
1. Link to Relevant Content
Don’t force it. Only link when it genuinely adds value for the reader.
2. Use Descriptive Anchor Text
Bad: “Click here for more info”
Good: “Learn how to optimize images for WordPress SEO”
3. Link to Older Posts
New content naturally gets links. Don’t forget older, valuable posts that need a boost.
4. Create Hub Pages
These are comprehensive guides (like this one) that link to related subtopics. Those subtopics link back to the hub.
5. Don’t Overdo It
3-5 internal links per 1,000 words is a good target. More than that feels spammy.
Pro Tip: Regularly audit your site for broken internal links using a plugin like Broken Link Checker. Broken links hurt user experience and SEO.
How Do I Build High-Quality Backlinks to My WordPress Site?
Backlinks are links from other websites to yours. They’re Google’s #1 ranking factor (along with content quality).
Think of backlinks as votes of confidence. The more quality sites that link to you, the more Google trusts you.
Types of Backlinks
Good Backlinks:
- From high-authority sites (think: Forbes, HuffPost, industry leaders)
- From relevant sites in your niche
- With natural anchor text
- From diverse domains
Bad Backlinks:
- From spammy, low-quality sites
- From link farms
- With over-optimized anchor text (exact match keywords every time)
- Site-wide footer links
White-Hat Link Building Strategies
1. Create Link-Worthy Content
This is the foundation. Content worth linking to includes:
- Original research and data
- Comprehensive guides (like this one)
- Unique case studies
- Helpful tools or calculators
- Controversial opinions (backed by evidence)
2. Guest Posting
Write content for other blogs in your niche. Include a natural link back to your site in the author bio or content.
Find opportunities: Google "your niche" + "write for us" or "guest post guidelines"
3. Resource Page Link Building
Many sites have “resources” or “helpful links” pages. If your content fits, email the site owner and suggest adding your link.
Find broken links on other sites using tools like Ahrefs or browser extensions. Contact the site owner, point out the broken link, and suggest your content as a replacement.
5. HARO (Help A Reporter Out)
Journalists need expert quotes for articles. Sign up at helpareporter.com, respond to relevant queries, and get featured (with a backlink) in major publications.
6. Create Infographics
Visual content gets shared and linked to more than text. Create an infographic, embed it on your site, then provide an embed code so others can share it (with a link back to you).
7. Podcast Interviews
Appear as a guest on podcasts in your niche. Most podcasts link to guests in show notes.
8. Collaborate with Other Bloggers
Roundup posts, joint webinars, or co-authored content naturally generate cross-links.
Pro Tip: One link from a high-authority site beats 100 links from spammy directories. Focus on quality over quantity. And never, ever buy links—Google penalizes this harshly.
What Are the Technical SEO Must-Haves for WordPress?
Technical SEO is the foundation. If it’s broken, no amount of great content will save you.
Technical SEO Checklist
1. Install an SSL Certificate (HTTPS)
Google confirmed HTTPS is a ranking signal. Plus, browsers mark non-HTTPS sites as “Not Secure,” scaring visitors away.
Most hosts offer free SSL certificates through Let’s Encrypt. Check with your hosting provider.
2. Fix Broken Links (404 Errors)
Broken links frustrate users and waste Google’s crawl budget. Use a plugin like Broken Link Checker to find and fix them.
3. Create a Robots.txt File
This tells search engines which pages to crawl (or not crawl). Your SEO plugin likely creates one automatically.
Check it at yoursite.com/robots.txt.
Google only crawls a limited number of pages per visit. Don’t waste it on:
- Admin pages
- Duplicate content
- Low-value tag/category pages
Use your robots.txt file or noindex tags to exclude these.
5. Fix Duplicate Content Issues
WordPress can create duplicate content through:
- Tag and category archives
- Paginated archives
wwwvsnon-wwwversions
Your SEO plugin handles most of this. Just make sure you’ve set a preferred domain in Search Console.
6. Implement Breadcrumb Navigation
Breadcrumbs show users (and Google) where they are on your site.
Example: Home > Blog > WordPress SEO Guide
Enable breadcrumbs in your SEO plugin under schema settings.
Google measures:
- LCP (Largest Contentful Paint): Loading speed
- FID (First Input Delay): Interactivity
- CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift): Visual stability
Check these in Google Search Console > Core Web Vitals.
Pro Tip: Use Google’s Lighthouse (built into Chrome DevTools) to audit your site’s technical health. It gives actionable recommendations.
How Do I Optimize WordPress for Local SEO?
If you run a local business—restaurant, dentist, plumber, boutique—local SEO is your goldmine.
Local SEO Strategy for WordPress
1. Claim Your Google Business Profile
This is the #1 local SEO factor. Your listing appears in Google Maps and local search results.
Steps:
- Go to google.com/business
- Enter your business info
- Verify via postcard, phone, or email
- Optimize your profile (photos, hours, description, posts)
2. Use Local Keywords
Include your city/region in:
- Page titles
- Meta descriptions
- Content
- Headers
Example: “Best WordPress SEO services in Austin, Texas“
3. Create Location-Specific Pages
If you serve multiple cities, create separate pages for each.
Example:
- yoursite.com/seo-services-austin
- yoursite.com/seo-services-dallas
4. Get Local Citations
List your business on:
- Yelp
- Yellow Pages
- Industry-specific directories
- Local chamber of commerce sites
Ensure your NAP (Name, Address, Phone) is identical everywhere.
5. Encourage Customer Reviews
Reviews boost rankings and build trust. Ask happy customers to leave reviews on Google, Yelp, and Facebook.
6. Add Local Business Schema
Use your SEO plugin to add Local Business schema markup with your address, phone, hours, and service area.
Get links from:
- Local news sites
- Chamber of commerce
- Local bloggers
- Community organizations
Pro Tip: Post regularly on your Google Business Profile. Google favors active, engaged businesses in local search results.
What Are the Biggest WordPress SEO Mistakes to Avoid?
Let’s talk about what NOT to do. These mistakes tank rankings fast.
10 WordPress SEO Mistakes That Kill Rankings
1. Using Cheap, Slow Hosting
You can’t out-optimize bad hosting. Invest in quality from the start.
2. Ignoring Mobile Optimization
Mobile-first indexing means mobile matters most. Test your site thoroughly on phones and tablets.
3. Keyword Stuffing
Repeating your keyword 50 times doesn’t help—it hurts. Google’s smarter than that. Write naturally.
4. Thin, Low-Quality Content
300-word posts rarely rank anymore. Create comprehensive, valuable content.
5. Not Using an SEO Plugin
Trying to manage meta tags, sitemaps, and schema manually is a nightmare. Use a plugin.
6. Neglecting Alt Text on Images
Every image should have descriptive alt text for accessibility and SEO.
7. Forgetting to Submit Your Sitemap
Google will eventually find you, but why wait? Submit your sitemap to Search Console.
8. Blocking Search Engines in Settings
Double-check Settings > Reading and ensure “Discourage search engines from indexing this site” is unchecked. (This is on by default for new sites!)
9. Not Fixing Broken Links
Broken links waste crawl budget and frustrate users. Fix them.
10. Buying Backlinks
Google’s spam filters are insanely good now. Bought links will get you penalized, not ranked.
Pro Tip: Set up Google Search Console alerts. You’ll get notified of critical issues like indexing problems or manual penalties before they tank your traffic.
How Often Should I Update My WordPress SEO Strategy?
SEO isn’t “set it and forget it.” Google updates its algorithm constantly (reportedly 500-600 changes per year).
SEO Maintenance Schedule
Weekly:
- Check Google Search Console for errors
- Monitor rankings for key pages
Monthly:
- Audit site speed
- Update old content with fresh info
- Fix broken links
- Check for new backlink opportunities
Quarterly:
- Review keyword rankings
- Update SEO plugin and WordPress core
- Analyze competitor strategies
- Refresh top-performing content
Annually:
- Comprehensive SEO audit
- Review and update your keyword strategy
- Assess hosting performance
Pro Tip: Set reminders. SEO maintenance is boring, but neglecting it for 6 months can cost you dearly.
What’s Next? Your WordPress SEO Action Plan
Feeling overwhelmed? Don’t be. You don’t have to do everything at once.
Here’s your 30-day WordPress SEO roadmap:
Week 1: Foundation
- [ ] Install an SEO plugin (Rank Math or Yoast)
- [ ] Set up SEO-friendly permalinks
- [ ] Install an SSL certificate
- [ ] Submit sitemap to Google Search Console
Week 2: On-Page Optimization
- [ ] Optimize your 5 most important pages (title tags, meta descriptions, headers)
- [ ] Add alt text to images
- [ ] Improve internal linking between posts
Week 3: Technical SEO
- [ ] Test and improve site speed (install caching plugin, compress images, enable CDN)
- [ ] Check mobile-friendliness
- [ ] Fix any broken links
Week 4: Content and Links
- [ ] Conduct keyword research for 5 new content ideas
- [ ] Publish one comprehensive, SEO-optimized post
- [ ] Reach out to 3 sites for backlink opportunities (guest posts, HARO, etc.)
Then keep building.
How Do I Track My WordPress SEO Progress?
You can’t improve what you don’t measure. Tracking your SEO performance tells you what’s working (and what’s not).
Essential WordPress SEO Metrics to Monitor
1. Organic Traffic
This is the lifeblood of SEO—visitors from search engines.
Where to check: Google Analytics (GA4)
- Go to Reports > Acquisition > Traffic Acquisition
- Filter by source: Organic Search
What you want to see: Steady upward trend month-over-month.
2. Keyword Rankings
Which keywords are you ranking for? What positions?
Tools to use:
- Google Search Console (free—shows clicks and average position)
- SEMrush (tracks specific keywords)
- Ahrefs Rank Tracker
- Mangools SERPWatcher
What to track: Your top 10-20 target keywords. Don’t obsess over rankings alone—traffic and conversions matter more.
3. Click-Through Rate (CTR)
How many people click your result when they see it in search?
Where to check: Google Search Console > Performance
Average CTR by position:
- Position 1: ~30-40%
- Position 2: ~15-20%
- Position 3: ~10-12%
- Position 10: ~2-3%
Pro Tip: If you have high impressions but low CTR, your title and meta description need work. They’re not compelling enough.
4. Bounce Rate and Dwell Time
Are visitors sticking around or leaving immediately?
Where to check: Google Analytics
- Bounce Rate: Percentage who leave after viewing one page
- Average Engagement Time: How long visitors stay
High bounce rates (70%+) signal your content doesn’t match search intent or isn’t engaging enough.
5. Backlinks
How many sites are linking to you? What’s their quality?
Tools to use:
- Google Search Console (limited data, but free)
- Ahrefs (most comprehensive)
- Moz Link Explorer
- Majestic SEO
What matters: Domain authority of linking sites, not just quantity.
6. Pages Per Session
How many pages do visitors view per visit?
Where to check: Google Analytics
Higher is better—it means your internal linking is working and content is engaging.
7. Conversions
What actions do you want visitors to take?
- Newsletter signups
- Product purchases
- Contact form submissions
- Download requests
Set up Goals in Google Analytics to track these.
Pro Tip: Create a simple spreadsheet or dashboard. Track your top 5-10 metrics monthly. This makes trends obvious and keeps you accountable.
What Advanced WordPress SEO Techniques Should I Know?
You’ve got the basics down. Ready to level up? Here are advanced tactics that separate amateurs from pros.
1. Content Pruning (Delete or Improve Low-Performers)
Not all content deserves to exist. Some pages drag down your site’s overall quality score.
What to prune:
- Thin content (under 300 words with no value)
- Outdated posts with zero traffic
- Duplicate or near-duplicate content
- Posts with high bounce rates and no engagement
How to prune:
- Option A: Delete and 301 redirect to a relevant page
- Option B: Combine similar posts into one comprehensive piece
- Option C: Update and refresh with current info
Pro Tip: Use Google Analytics to find pages with zero traffic in the last 6 months. Those are prime pruning candidates.
2. Topic Clusters and Pillar Pages
This is how modern SEO works. Instead of random posts, you create content hubs.
The structure:
- Pillar page: Comprehensive guide on a broad topic (like this post)
- Cluster posts: Detailed posts on subtopics, all linking back to the pillar
Example:
- Pillar: WordPress SEO (this guide)
- Clusters: WordPress speed optimization, best SEO plugins, image optimization, schema markup, etc.
This signals to Google that you’re an authority on the topic.
3. Update Old Content Regularly
Google loves fresh content. Instead of always creating new posts, update your top performers.
What to update:
- Statistics and data
- Screenshots
- Outdated recommendations
- Links to newer, related content
- Year in title (e.g., “2024” → “2025”)
Pro Tip: Add an “Last Updated: [Date]” notice at the top. Google notices this and may give you a ranking boost.
4. Optimize for Featured Snippets
Featured snippets are the “position zero” results—the answer box at the top of search results.
Types of snippets:
- Paragraph (answers in 40-60 words)
- List (numbered or bulleted steps)
- Table (comparisons or data)
- Video (usually from YouTube)
How to win snippets:
- Identify questions in your niche (use AnswerThePublic or “People Also Ask” in Google)
- Provide clear, concise answers in your content
- Use proper formatting (H2 question + direct answer)
- Add tables or lists where appropriate
5. Implement Advanced Schema Types
Beyond basic Article schema, try:
- FAQ Schema: For question-and-answer sections
- How-To Schema: For step-by-step tutorials
- Video Schema: For embedded videos
- Review Schema: For product reviews (with ratings)
These can get you enhanced search results that attract more clicks.
6. Create “Linkable Assets”
These are resources so valuable that people naturally link to them:
- Original research and surveys
- Industry statistics and data
- Ultimate guides and checklists
- Free tools and calculators
- Templates and swipe files
Example: “50 WordPress SEO Statistics Every Blogger Should Know (2025 Edition)”
7. Build Authority with E-E-A-T
Google’s quality guidelines emphasize:
- Experience: Show you’ve actually done what you’re teaching
- Expertise: Demonstrate deep knowledge
- Authoritativeness: Get recognized by others in your field
- Trustworthiness: Be accurate, cite sources, have an About page
How to improve E-E-A-T:
- Add detailed author bios with credentials
- Include author schema markup
- Get mentioned on reputable sites
- Display trust signals (security badges, testimonials)
- Cite authoritative sources
- Keep content accurate and updated
8. Leverage User-Generated Content
Comments, reviews, and testimonials add fresh content and long-tail keywords naturally.
Enable comments on blog posts and respond to them. It increases dwell time and signals engagement.
9. Optimize for Voice Search
More people are using Alexa, Siri, and Google Assistant. Voice searches are conversational and question-based.
Voice search optimization tips:
- Target long-tail, conversational keywords
- Answer questions directly
- Use FAQ sections
- Focus on local SEO (many voice searches are local)
Example: Instead of optimizing for “WordPress SEO,” also target “How do I optimize my WordPress site for SEO?“
10. Monitor and Fix Core Web Vitals
These are Google’s page experience metrics:
| Metric | What It Measures | Good Score |
|---|---|---|
| LCP (Largest Contentful Paint) | Loading speed of main content | Under 2.5 seconds |
| FID (First Input Delay) | Time until page is interactive | Under 100 milliseconds |
| CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift) | Visual stability (no jumping elements) | Under 0.1 |
How to fix:
- LCP: Optimize images, improve server response time, use lazy loading
- FID: Minimize JavaScript, defer non-critical scripts
- CLS: Set dimensions for images/videos, avoid inserting content above existing content
Check your scores in Google Search Console > Core Web Vitals or PageSpeed Insights.
Pro Tip: Core Web Vitals are a ranking factor, but they’re a tiebreaker, not a game-changer. Focus on content quality first, technical optimization second.
How Do I Handle WordPress SEO for WooCommerce Stores?
Running an eCommerce site on WordPress? WooCommerce SEO has unique challenges.
WooCommerce SEO Best Practices
Treat each product page like a mini landing page:
- Unique product descriptions (never copy from manufacturers)
- Target long-tail buyer keywords (“buy wireless gaming mouse” not just “mouse”)
- High-quality product images with alt text
- Customer reviews (add fresh content and keywords naturally)
- Schema markup for products (price, availability, ratings)
2. Handle Duplicate Content
WooCommerce creates potential duplicates:
- Product variations (different sizes/colors)
- Filter pages
- Paginated category pages
Solutions:
- Use canonical tags to point to main versions
- Set filter pages to
noindex - Implement “View All” pagination or
rel="next"andrel="prev"tags
3. Optimize Category and Tag Pages
Don’t leave these as bare product listings. Add:
- 200-300 words of intro text
- FAQ section
- Buying guide content
Example: Instead of just listing “Running Shoes,” add content about choosing the right running shoe, shoe types, sizing tips, etc.
4. Improve Product Image SEO
Use:
- Multiple images (different angles, lifestyle shots)
- WebP format for fast loading
- Descriptive filenames:
red-nike-running-shoes.jpg - Alt text: “Red Nike Air Max running shoes for women”
5. Create Comparison Pages
These rank well for commercial intent keywords:
- “Product A vs Product B”
- “Best [product type] for [use case]”
- “Top 10 [products] in 2025”
6. Build Product-Specific Landing Pages
For high-value products, create dedicated SEO landing pages separate from product pages. Include:
- In-depth guides
- Videos and tutorials
- Use cases and benefits
- Comparison tables
7. Optimize for Transactional Keywords
Target keywords with buying intent:
- “Buy [product]”
- “[Product] for sale”
- “Best price [product]”
- “[Product] discount”
- “Where to buy [product]”
Pro Tip: Use the Yoast WooCommerce SEO addon or Rank Math Pro (both have WooCommerce-specific features). They automatically handle product schema, optimize category pages, and more.
What About WordPress Multisite SEO?
Running a WordPress Multisite network? SEO gets trickier with multiple sites under one installation.
Multisite SEO Challenges
1. Duplicate Content Across Sites
If sites share content, Google may penalize you.
Solution: Use canonical tags pointing to the original content source.
2. Subdomain vs Subdirectory Structure
- Subdomains:
site1.yournetwork.com(treated as separate sites by Google) - Subdirectories:
yournetwork.com/site1(link equity flows to main domain)
Recommendation: Use subdirectories when possible. They’re stronger for SEO.
3. Separate SEO Settings Per Site
Most SEO plugins work with Multisite, but settings must be configured individually for each site.
Pro Tip: Use Rank Math Pro Multisite or Yoast SEO Premium—they’re designed for Multisite networks and make management easier.
How Do I Recover from a Google Penalty?
Your traffic dropped off a cliff? You might be penalized.
Types of Google Penalties
1. Manual Penalties
A human reviewer found your site violating guidelines.
Where to check: Google Search Console > Security & Manual Actions
Common causes:
- Unnatural backlinks (spam links)
- Thin content
- User-generated spam
- Cloaking or hidden text
How to recover:
- Identify the issue in Search Console
- Fix it (remove bad links, improve content, etc.)
- Submit a reconsideration request
2. Algorithmic Penalties
Google’s algorithm automatically demoted you (no manual action).
Common causes:
- Panda: Low-quality or duplicate content
- Penguin: Spammy backlinks
- Core Updates: Overall site quality issues
How to recover:
- Identify which update affected you (check dates)
- Improve content quality, remove bad links, fix technical issues
- Wait for the next algorithm refresh (can take months)
Pro Tip: Prevention is easier than recovery. Never buy links, avoid black-hat tactics, and focus on quality over shortcuts.
What Are the Best WordPress SEO Tools and Resources?
You don’t need a massive budget, but the right tools make SEO dramatically easier.
Essential SEO Tools
| Tool | Purpose | Price |
|---|---|---|
| Google Search Console | Monitor search performance, indexing issues | Free |
| Google Analytics 4 | Track traffic, user behavior | Free |
| Rank Math/Yoast SEO | On-page optimization, technical SEO | Free / Premium |
| Ahrefs | Backlink analysis, keyword research, competitor analysis | $99/month |
| SEMrush | All-in-one SEO suite (keywords, audits, tracking) | $119.95/month |
| Ubersuggest | Affordable keyword research and tracking | $29/month |
| Screaming Frog | Technical SEO audits (crawls your site) | Free (500 URLs) / $259/year |
| GTmetrix | Site speed testing | Free / Paid |
| AnswerThePublic | Question-based keyword ideas | Free (limited) / $99/month |
Free WordPress SEO Resources
Blogs to follow:
- Search Engine Journal (searchenginejournal.com)
- Moz Blog (moz.com/blog)
- Ahrefs Blog (ahrefs.com/blog)
- Yoast SEO Blog (yoast.com/seo-blog)
- Backlinko (backlinko.com)
Communities:
- r/SEO on Reddit
- SEO Signals Lab (Facebook group)
- Traffic Think Tank (paid Slack community, but worth it)
YouTube Channels:
- Ahrefs (excellent tutorials)
- Income School (Project 24)
- Matt Diggity (advanced tactics)
Pro Tip: Don’t tool-hop. Pick 3-5 tools, master them, and stick with them. Constantly switching wastes time and money.
Common WordPress SEO Questions Answered
Let’s tackle some questions I hear all the time.
Does Changing Themes Hurt SEO?
Short answer: Not if you do it right.
What can hurt:
- Broken internal links if URL structure changes
- Slower site speed if new theme is bloated
- Lost schema markup if theme included it
How to switch safely:
- Choose a fast, SEO-friendly theme
- Test on a staging site first
- Check for broken links after switching
- Monitor rankings for 2-3 weeks
Should I Use AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages)?
Honestly? AMP is less critical in 2025 than it was a few years ago.
Google no longer gives AMP preferential treatment in search results. Focus on Core Web Vitals and mobile optimization instead.
When to use AMP:
- News sites (AMP can help with Google News)
- Sites with extremely slow mobile performance
Otherwise, skip it.
How Long Until I See SEO Results?
The dreaded question. Here’s the truth:
- New sites: 6-12 months for significant traffic
- Established sites: 2-4 months for noticeable improvements
- Individual posts: 3-6 months to reach full ranking potential
Variables that speed things up:
- Domain age and authority
- Competition level
- Content quality
- Backlink building efforts
Pro Tip: SEO is a marathon, not a sprint. Anyone promising page-one rankings in 30 days is lying or using black-hat tactics that’ll get you penalized.
Can I Do SEO Without an SEO Plugin?
Technically, yes. But why would you?
SEO plugins automate tedious tasks (sitemaps, meta tags, schema) and prevent mistakes. They’re free (or cheap) and save countless hours.
Verdict: Just use a plugin. Seriously.
Do I Need to Hire an SEO Agency?
It depends:
DIY if:
- You have time to learn and implement
- Your budget is tight
- Your site is relatively small (under 100 pages)
- You enjoy the process
Hire an agency if:
- You’re overwhelmed or lack time
- Your site is large or complex
- You’re in a highly competitive niche
- You need advanced technical SEO work
Middle ground: Hire a freelance SEO consultant for an audit and strategy, then implement yourself.
Does Social Media Help SEO?
Directly? No. Social signals aren’t ranking factors.
Indirectly? Yes. Social media:
- Drives traffic to your site
- Increases brand awareness (leading to more branded searches)
- Helps content get discovered (which can lead to backlinks)
Think of social media as an SEO amplifier, not a replacement.
The Future of WordPress SEO: What’s Coming in 2025 and Beyond
SEO never stands still. Here’s what’s shaping the future.
1. AI-Generated Content and Google’s Response
AI writing tools are everywhere. Google’s stance?
They don’t penalize AI content—they penalize low-quality, unhelpful content (regardless of how it’s created).
What this means for you:
- AI can help with research and drafting
- But you must add expertise, experience, and unique insights
- Don’t publish raw AI output—edit, enhance, personalize
Pro Tip: Use AI as a research assistant, not a replacement for your expertise. Google’s getting better at detecting generic, regurgitated content.
2. Search Generative Experience (SGE)
Google’s testing AI-powered answers directly in search results. This means:
- Featured snippets become even more valuable
- Long-tail, specific queries might get answered without clicks
- Expertise and authority matter more than ever
How to adapt:
- Focus on topics requiring human expertise and experience
- Create content AI can’t replicate (personal stories, case studies, original research)
- Target queries where users want multiple perspectives, not just one answer
3. Visual and Video Search Growth
More people are searching with:
- Google Lens (visual search)
- YouTube (video search)
- Voice assistants
What to do:
- Optimize images with proper filenames and alt text
- Create video content (YouTube is the #2 search engine)
- Add video schema markup
- Transcribe videos for text-based searchability
4. Core Web Vitals Evolution
Google will keep refining page experience metrics. Expect:
- New performance signals beyond current Core Web Vitals
- Greater emphasis on mobile experience
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP) replacing FID in 2024/2025
Stay ahead: Regularly test and optimize site speed.
5. E-E-A-T Becomes More Critical
Google’s cracking down on low-quality content. Building Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trust isn’t optional anymore.
How to build E-E-A-T:
- Include detailed author bios
- Cite credible sources
- Show proof of experience (screenshots, results, case studies)
- Get mentioned by authoritative sites
- Maintain an active About page and contact info
Pro Tip: The future of SEO rewards creators who demonstrate genuine expertise and add unique value. Generic content farms won’t survive.
Your WordPress SEO Success Story Starts Now
Congrats—you made it to the end of this massive guide. That’s dedication.
Here’s what you’ve learned:
- WordPress SEO fundamentals (plugins, permalinks, on-page optimization)
- Technical SEO essentials (speed, mobile, schema, sitemaps)
- Content strategies that rank (keyword research, writing, internal linking)
- Link building tactics (guest posts, HARO, linkable assets)
- Advanced techniques (topic clusters, featured snippets, E-E-A-T)
- How to track and improve your SEO performance
But knowledge without action is worthless.
Your Next Steps
Pick three things from this guide and implement them this week. Not ten. Not twenty. Just three.
Maybe it’s:
- Installing an SEO plugin
- Optimizing your five most important pages
- Improving your site speed
Then next week, pick three more.
SEO compounds. Small, consistent improvements add up to massive results over time.
One Final Thought
SEO isn’t about tricking Google. It’s about making your site genuinely better—faster, more useful, easier to navigate, more trustworthy.
Do that, and rankings follow naturally.
So stop overthinking. Start optimizing. Your WordPress site has massive potential—it’s time to unlock it.
Now go build something worth ranking for.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the best SEO plugin for WordPress?
Rank Math and Yoast SEO are the top choices. Rank Math offers more features in the free version, while Yoast is more beginner-friendly with excellent documentation.
How long does WordPress SEO take to work?
New sites typically need 6-12 months to see significant traffic. Established sites can see improvements in 2-4 months with consistent optimization efforts.
Do I need coding skills for WordPress SEO?
No. Modern SEO plugins handle technical elements without code. Basic WordPress skills are enough for most SEO tasks.
Can I do SEO without paying for tools?
Yes. Google Search Console, Google Analytics, free versions of SEO plugins, and Ubersuggest’s limited free plan cover the basics. Paid tools accelerate progress but aren’t mandatory.
How often should I publish new content for SEO?
Quality beats frequency. One comprehensive, well-optimized post per week outperforms five mediocre daily posts. Focus on depth and value over volume.
Does WordPress.com have the same SEO capabilities as WordPress.org?
No. WordPress.org (self-hosted) gives you full control over SEO. WordPress.com has limitations—you can’t install custom plugins on free plans, restricting your optimization options.
Should I focus on SEO or content first?
Content first, SEO second. Create genuinely helpful content, then optimize it for search engines. Great content poorly optimized beats garbage content perfectly optimized.
How do I know if my WordPress site is penalized?
Check Google Search Console > Security & Manual Actions. For algorithmic penalties, look for sudden traffic drops after Google algorithm updates. Compare your drop date with known Google update dates.
Is WordPress better for SEO than other platforms?
WordPress is excellent for SEO due to its flexibility, plugins, and clean code. However, content quality and optimization matter more than platform choice. Great SEO is possible on any platform with proper implementation.
Can I migrate to WordPress without losing SEO rankings?
Yes, but do it carefully. Use 301 redirects for all old URLs, maintain URL structure when possible, and submit your new sitemap to Search Console immediately. Monitor rankings closely for 4-6 weeks after migration.
📊 WordPress SEO Statistics 2025
Interactive Dashboard | Real Data from Industry Research | seoprojournal.com
| Plugin | Active Installations | Rating | Premium Price | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yoast SEO | 10M+ | ⭐ 4.8/5 | $99/year | Beginners |
| Rank Math | 3M+ | ⭐ 5.0/5 | $59/year | Advanced Users |
| All in One SEO | 3M+ | ⭐ 4.7/5 | $49.60/year | eCommerce |
| SEOPress | 300K+ | ⭐ 4.8/5 | $39/year | Budget-Conscious |
📊 All statistics verified from official sources including W3Techs, Google Research, WordPress.org, and industry reports
Created by seoprojournal.com | Data accurate as of October 2025
Sources: W3Techs, Google/SOASTA, WordPress.org, Backlinko, SEMrush, WPZOOM, BuiltWith, Ahrefs