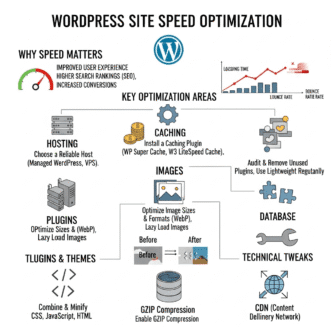
You wake up Monday morning, grab your coffee, and check your site analytics. Zero traffic. Zero. You frantically type your domain into Google and… nothing. Your site has vanished from search results entirely.
Then the email hits your inbox: “Google Search Console Alert: Security Issue Detected.” Your WordPress site was hacked over the weekend, infected with malware, and Google blacklisted you completely. Three years of SEO work, gone in 48 hours.
Sound like a nightmare? It happens to thousands of WordPress sites every single day.
Here’s what most site owners don’t realize: WordPress security SEO isn’t just about protecting your data—it’s about protecting your rankings, traffic, and revenue. A single security breach can obliterate your search visibility faster than any algorithm update ever could.
I’ve seen established WordPress sites lose 100% of their organic traffic overnight due to hacks. I’ve watched business owners cry as they explain how a malware infection tanked their rankings so badly that even after cleaning the site, they never recovered their positions.
The cruel irony? Most of these disasters were completely preventable with basic security measures that take maybe an hour to implement.
WordPress security and SEO are inseparable. Google explicitly states that hacked sites get demoted or removed from search results. Malware warnings decimate click-through rates even if you’re not blacklisted. Slow loading from cryptominers kills your Core Web Vitals. Spam injections destroy your site’s authority.
But here’s the good news: securing your WordPress site doesn’t require a computer science degree or a massive budget. In this guide, I’ll show you exactly how WordPress security affects SEO rankings, which vulnerabilities put you at highest risk, and the specific steps to protect your traffic from security disasters.
Let’s make sure your site never becomes one of those horror stories.
Table of Contents
ToggleHow Does WordPress Security Directly Impact SEO Rankings?
WordPress security SEO is a direct ranking factor in multiple ways that most site owners completely overlook. Google doesn’t just prefer secure sites—they actively punish insecure ones.
Google’s Security Signals as Ranking Factors
Google has explicitly confirmed that website security influences rankings through several mechanisms:
HTTPS as a ranking signal – Since 2014, Google has used HTTPS encryption as a lightweight ranking factor. Sites with SSL certificates get a small boost over non-HTTPS competitors.
According to Google’s 2014 announcement: “We’d like to encourage all website owners to switch from HTTP to HTTPS to keep everyone safe on the web.
Mobile-first indexing security – Google’s mobile-first crawler prioritizes secure connections. Insecure sites get crawled less frequently and indexed less thoroughly.
Safe Browsing API integration – Google maintains a blacklist of compromised sites. If your site appears on it, you’re effectively de-indexed until cleaned and reviewed.
Core Web Vitals impact – Security compromises often degrade site performance (malware, cryptominers, spam scripts), which tanks Core Web Vitals scores and rankings.
User experience signals – Hacked sites trigger browser warnings that create massive bounce rates, sending negative engagement signals to Google.
Real data from research:
According to a 2023 study by Sucuri, hacked WordPress sites experience an average 95% drop in organic traffic within 72 hours of being blacklisted. Recovery takes an average of 4-6 months even after cleaning, and 43% of sites never fully recover their previous traffic levels.
Pro Tip: Google’s John Mueller has stated: “Security is part of our quality guidelines. If your site is hacked, we’ll show warnings in search results, which dramatically impacts click-through rates. In severe cases, we’ll remove the site entirely from our index.”
The Cost of Security Breaches on Search Visibility
Let’s talk numbers. What does a security breach actually cost in SEO terms?
Immediate impacts:
| Security Issue | Traffic Loss | Recovery Time | Permanent Damage Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Blacklist | 95-100% | 3-6 months | 43% never fully recover |
| Malware Warning | 70-95% | 1-3 months | 25% permanent impact |
| Spam Injection | 30-60% | 2-4 months | Low if caught early |
| Site Defacement | 85-100% | 2-5 months | Moderate |
| Cryptomining Malware | 20-40% (gradual) | 1-2 months | Low |
| Data Breach | 50-80% | Variable | High (trust loss) |
Secondary SEO damage from hacks:
Link profile destruction – Hackers inject spammy links that trigger manual penalties
Content manipulation – Hidden spam text tanks content quality scores
Redirect chains – Malicious redirects create technical SEO nightmares
Duplicate content – Spam pages created by hackers cause duplicate content issues
Crawl budget waste – Thousands of malware-generated pages consume crawl budget
Real case study:
A WordPress e-commerce site with \$120K monthly revenue was hacked with pharma spam injection. They discovered it after 12 days (thanks to monitoring). Here’s what happened:
Week 1-2 (undetected):
- Google indexed 2,800+ spam pages
- Manual penalty triggered
- Rankings started dropping
Week 3-4 (cleaning):
- Site cleaned, malware removed
- Disavow file submitted for spam links
- Reconsideration request filed
Month 2-3 (partial recovery):
- Google lifted manual penalty
- Only 60% of previous traffic returned
- Revenue dropped to $45K/month
Month 4-6 (ongoing recovery):
- Gradual traffic improvements
- 85% recovery achieved after 6 months
- Still hadn’t fully recovered to pre-hack levels
Total cost: $340K+ in lost revenue, $8K in security/cleanup services, $15K in additional SEO recovery work. All from a security vulnerability that could have been prevented with a $200/year security plugin.
For comprehensive WordPress protection strategies, check the complete WordPress SEO guide.
What Are the Biggest Security Threats to WordPress SEO?
Understanding what you’re protecting against helps prioritize your security efforts. Not all vulnerabilities equally impact SEO.
Malware and Its Effect on Search Rankings
Malware is malicious software that infects your WordPress site. Different malware types impact SEO differently:
SEO spam malware – Most common, most damaging to rankings:
- Injects hidden spam links (pharma, gambling, adult content)
- Creates thousands of spam pages that get indexed
- Manipulates your legitimate content with invisible spam
- Triggers Google manual penalties
Backdoor malware – Provides hackers ongoing access:
- Allows repeated infections even after cleaning
- Often undetected for months
- Enables installation of other malware types
- Gradually degrades site performance
Cryptominers – Uses your server to mine cryptocurrency:
- Severely slows page load times
- Tanks Core Web Vitals (LCP, FID)
- Increases bounce rate
- Reduces rankings through performance impact
Redirect malware – Sends visitors to malicious sites:
- Creates massive bounce rate
- Google detects and flags quickly
- Can get you blacklisted in days
- Destroys user trust permanently
Database injections – Modifies your WordPress database:
- Hardest to detect and clean
- Can manipulate all content at once
- Often includes admin user creation
- Requires deep technical cleanup
How Google detects infected sites:
Google’s Safe Browsing system crawls over 4 billion URLs daily looking for malware. When they detect infections, they:
- Add your site to their blacklist
- Display warnings in search results: “This site may be hacked”
- Show interstitial warnings in Chrome: “Deceptive site ahead”
- Dramatically reduce or eliminate your search visibility
Real example of malware impact:
A WordPress blog ranked #1-3 for multiple keywords (30K monthly organic traffic) was infected with JavaScript redirect malware that only affected mobile users. Desktop visitors saw nothing wrong.
Timeline:
- Day 0: Infected (unnoticed)
- Day 3: Google’s mobile crawler detected redirects
- Day 5: “This site may be hacked” warning appeared in mobile SERPs
- Day 7: Mobile traffic dropped 97%
- Day 10: Desktop traffic started declining (reputation damage)
- Day 14: Site removed from mobile index entirely
They caught it on day 14, cleaned it immediately, and submitted reconsideration. It took 68 days to fully remove warnings and 4 months to recover 80% of previous traffic.
Pro Tip: According to Wordfence’s 2024 security report, WordPress sites are attacked an average of 44 times per day. That’s not a typo. Your site is under constant attack attempts, whether you realize it or not.
Brute Force Attacks and Login Security
Brute force attacks are automated attempts to guess your admin password by trying thousands of combinations. They’re the #1 entry point for WordPress hacks.
Why they matter for SEO:
Successful breaches lead to:
- Admin account takeover
- Installation of malware
- Content manipulation
- Spam link injection
- User data theft
Failed attempts still cause damage:
- Server resource exhaustion
- Increased load times
- Higher hosting costs
- Potential site crashes during attacks
Common brute force tactics:
Dictionary attacks – Try common passwords:
- “password123”
- “admin”
- “wordpress”
- Site name variations
- Industry-specific terms
Credential stuffing – Use leaked passwords from other sites:
- Hackers buy leaked databases
- Try username/password combos across millions of sites
- Exploits password reuse
Distributed attacks – Use botnets to avoid detection:
- Thousands of IPs attacking simultaneously
- Harder to block with simple IP bans
- Overwhelms basic security measures
The “admin” username problem:
Default WordPress installations used “admin” as the username for years. Hackers know this and target it relentlessly. If your username is still “admin,” you’re making their job ridiculously easy.
Statistics that should scare you:
According to Wordfence’s analysis of 4+ billion attacks:
- 90% of attacks target the login page (wp-login.php and xmlrpc.php)
- 61% of compromised sites had weak passwords
- 8% of attacks succeed within the first 1,000 attempts
- Sites with username “admin” are 3.7x more likely to be compromised
Real breach example:
A small business WordPress site (local plumber) was using username “admin” and password “Plumbing2020!”. Not terrible, but predictable.
A botnet ran a dictionary attack overnight trying industry-specific passwords. “Plumbing2020!” was attempt #847. They got in.
The hackers:
- Installed a backdoor
- Injected pharma spam (150+ spam pages)
- Added malicious redirects for mobile users
- Created spam links across all blog posts
The business owner noticed when customers mentioned the site “looked weird.” By then:
- Google had indexed 89 spam pages
- Site was flagged for malware
- Organic traffic dropped 78%
- 3 customers reported credit card fraud (unrelated but blamed the site)
Cleanup cost: $2,400 professionally. Lost business during downtime: ~$15,000. Recovery time: 3 months.
All because of username “admin” and a predictable password.
Plugin and Theme Vulnerabilities
Outdated plugins and themes are the second most common entry point for WordPress hacks (after weak passwords).
Why plugins are risky:
Code quality varies wildly:
- Free plugins may lack security audits
- Abandoned plugins never get security patches
- Even popular plugins have occasional vulnerabilities
- Theme builders often include bloated, insecure code
Plugin vulnerabilities discovered constantly: According to WPScan’s vulnerability database, new WordPress plugin vulnerabilities are discovered every single day. In 2023 alone, over 3,800 plugin vulnerabilities were documented.
Common plugin vulnerabilities:
SQL injection – Allows database access:
- Hackers can read, modify, or delete data
- Can extract user information
- Often undetected for months
Cross-site scripting (XSS) – Injects malicious scripts:
- Can steal admin sessions
- Redirects users to malware sites
- Manipulates content
File inclusion – Allows file uploads:
- Hackers upload backdoors or malware
- Can execute arbitrary code
- Hard to trace and remove
Authentication bypass – Skips login requirements:
- Direct admin access
- Complete site takeover
- Often combined with other attacks
Abandoned plugins are ticking time bombs:
When a plugin developer stops updating their plugin, known vulnerabilities never get patched. Hackers specifically target sites using abandoned plugins because they know the vulnerabilities won’t be fixed.
Real-world plugin vulnerability impact:
In 2021, a critical vulnerability was discovered in a popular form builder plugin with 5+ million active installations. The vulnerability allowed unauthenticated users to upload malicious files.
The fallout:
- Exploit published publicly within 48 hours
- Mass automated attacks began within a week
- Estimated 1.6 million sites potentially vulnerable
- Thousands of sites compromised before updating
- Many compromised sites saw rankings drop within days
Sites that updated immediately: No impact. Sites that delayed updates: Many were compromised and suffered SEO consequences.
The update dilemma:
“But updates break my site!” – Yes, occasionally. But here’s the risk analysis:
Risk of updating:
- 2-5% chance of minor conflict/breakage
- Usually fixable in minutes to hours
- Can test on staging site first
- Worst case: Site looks wrong temporarily
Risk of NOT updating:
- 100% certainty that known vulnerabilities exist
- Hackers actively exploit known vulnerabilities
- Can lead to complete site compromise
- Recovery takes weeks to months
- Potential complete traffic loss
The math isn’t even close. Always update.
Pro Tip: Keep a list of your installed plugins. Every quarter, check if they’re still actively maintained (recent updates in last 6 months). If not, find alternatives. Using abandoned plugins is like leaving your front door unlocked with a “Please Rob Me” sign.
For comprehensive WordPress maintenance including security, visit the WordPress SEO guide.
How Does SSL/HTTPS Impact WordPress SEO?
SSL certificates encrypt data between users and your server. But beyond security, they’re a confirmed Google ranking factor and critical trust signal.
Why Google Requires HTTPS for SEO
Google has been pushing HTTPS adoption aggressively since 2014, and for good reason: user safety.
Google’s official position:
“HTTPS protects the integrity and confidentiality of data between users and your site. We use HTTPS as a ranking signal, and it’s particularly important for sites that collect sensitive user data.”
How HTTPS affects rankings:
Direct ranking boost – Small but meaningful:
- Google confirmed HTTPS is a lightweight ranking factor
- Acts as a tiebreaker between similar quality sites
- More important in competitive SERPs
Trust signals – Browsers display security indicators:
- Green padlock in address bar
- “Secure” label next to URL
- Absence creates “Not Secure” warning (scary for users)
Mobile-first indexing preference – Google’s mobile crawler prioritizes HTTPS:
- Faster indexing of new content
- Better crawl budget allocation
- Preferred in mobile rankings
HTTP/2 and HTTP/3 benefits – Only work with HTTPS:
- Significantly faster page loading
- Better Core Web Vitals scores
- Improved user experience signals
The “Not Secure” warning problem:
Chrome (70%+ of browsers) shows “Not Secure” for HTTP sites, especially when entering data. This creates:
- Massive trust issues
- Higher bounce rates
- Lower conversion rates
- Negative SEO signals from poor engagement
Statistics on HTTPS adoption:
According to Google’s Transparency Report:
- Over 95% of Chrome traffic uses HTTPS on Android and Windows
- 99 of the top 100 sites use HTTPS by default
- Sites without HTTPS are increasingly rare and penalized
Real impact example:
An e-commerce WordPress site delayed HTTPS migration because “it seemed complicated.” They ranked #4 for their main product keyword.
After Google strengthened HTTPS preference in mobile-first indexing:
- Competitors with HTTPS overtook them
- They dropped to #7
- Traffic decreased 34%
- Conversions dropped even more (48%) due to “Not Secure” warnings
After finally migrating to HTTPS:
- Recovered to position #5 in 45 days
- Eventually climbed back to #3
- Conversions increased 67% vs pre-HTTPS levels
Cost of delaying: ~$80K in lost revenue. Cost of implementing HTTPS: $0 (free Let’s Encrypt certificate) plus 2 hours of setup time.
Installing and Configuring SSL Certificates
Setting up SSL certificates on WordPress is dramatically easier than most people think. Here’s the complete process:
Step 1: Choose an SSL certificate type
| Type | Cost | Best For | Validation Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Let’s Encrypt | Free | Most sites, blogs, small business | Domain validation (DV) |
| Standard SSL | $50-100/yr | Business sites wanting paid support | Domain validation (DV) |
| Wildcard SSL | $100-200/yr | Sites with many subdomains | DV, covers *.domain.com |
| EV SSL | $150-300/yr | E-commerce, banks, high-trust needs | Extended validation (EV) |
For 95% of WordPress sites: Use Let’s Encrypt (free). It’s trusted by all browsers, automatically renews, and works perfectly for SEO purposes.
Step 2: Install SSL certificate
Option A: Through your hosting (easiest)
Most modern WordPress hosts offer one-click SSL installation:
- SiteGround: Security → SSL Manager → Let’s Encrypt → Install
- Cloudways: SSL Certificate → Install Let’s Encrypt
- WP Engine: Built-in, automatic for all sites
- Kinsta: Automatic, included free
- Bluehost: Security → SSL/TLS Status → Install
Takes literally 2 clicks and 3 minutes.
Option B: Through a plugin (alternative)
Really Simple SSL plugin:
- Install and activate Really Simple SSL
- Click “Go ahead, activate SSL!”
- Done.
The plugin handles all configuration automatically.
Step 3: Force HTTPS site-wide
After installing SSL, force all traffic to use HTTPS:
In WordPress (using Really Simple SSL):
- Plugin does this automatically
- Fixes mixed content warnings
- Updates internal links
Manual method (.htaccess): Add to your .htaccess file:
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} off
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ https://%{HTTP_HOST}%{REQUEST_URI} [L,R=301]
Step 4: Update Google Search Console
- Add the HTTPS version as a new property
- Both http:// and https:// need to be added separately
- Submit your sitemap to the HTTPS property
Step 5: Update internal links
Use “Better Search Replace” plugin:
- Replace http://yoursite.com with https://yoursite.com
- Run in “dry run” mode first to preview changes
- Executes the replacement across database
Step 6: Check for mixed content warnings
Use “Why No Padlock” tool or Chrome DevTools:
- Open site in Chrome
- Press F12 → Console tab
- Look for “Mixed Content” warnings
- Fix any http:// resources (images, scripts, etc.)
Common SSL implementation mistakes:
❌ Installing SSL but not forcing HTTPS site-wide (some pages stay HTTP) ❌ Mixed content warnings (HTTP images on HTTPS pages) ❌ Not updating Google Search Console ❌ Forgetting to update internal links in content ❌ Not setting up automatic renewal (Let’s Encrypt expires every 90 days) ❌ Linking to HTTP version in external directories ❌ Not redirecting HTTP to HTTPS (both versions accessible, duplicate content)
Pro Tip: After installing SSL, use Screaming Frog to crawl your entire site and identify any remaining HTTP resources. Fix them before Google discovers the mixed content issues.
What Are the Essential WordPress Security Measures for SEO?
Let’s get practical. Here are the security implementations that directly protect your WordPress security SEO.
Implementing Strong Authentication and Access Control
Authentication security is your first line of defense against the most common attack vector—compromised logins.
1. Change the default “admin” username
If you’re still using “admin,” change it immediately:
- Create a new admin user with a different username
- Log in as the new admin
- Delete the old “admin” account
- Reassign all content to the new user
Never use:
- admin
- administrator
- Your site name
- Your first name
Better options:
- Random combinations
- Unrelated words
- Nothing obvious or guessable
2. Use strong, unique passwords
Bad passwords hackers crack instantly:
- password123
- admin2024
- yoursite2024
- CompanyName123
Good passwords:
- 16+ characters
- Mix of uppercase, lowercase, numbers, symbols
- Completely random or passphrase
- Generated by password manager
Use 1Password, Bitwarden, or LastPass to generate and store complex passwords. Don’t reuse passwords across sites.
3. Enable two-factor authentication (2FA)
2FA adds a second verification step beyond passwords. Even if hackers guess your password, they can’t access your site without the second factor.
Best 2FA plugins for WordPress:
| Plugin | Method | Free/Paid | Ease of Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wordfence Login Security | Authenticator app, email | Free | Easy |
| Two-Factor | Multiple methods | Free | Moderate |
| WP 2FA | Authenticator app, email, SMS | Free/Pro | Easy |
| Google Authenticator | Google Authenticator app | Free | Easy |
How to set up 2FA (using Wordfence):
- Install Wordfence Security plugin
- Go to Wordfence → Login Security
- Enable two-factor authentication
- Scan QR code with Google Authenticator or Authy app
- Enter verification code
- Save backup codes securely
Now every login requires: password + time-based code from your phone.
4. Limit login attempts
Brute force attacks try thousands of password combinations. Limiting login attempts stops them cold.
Methods:
Using Wordfence:
- Wordfence → All Options → Brute Force Protection
- Set max login failures: 5 attempts
- Lockout duration: 20 minutes
- Blocks IP after repeated failures
Using Limit Login Attempts Reloaded:
- Free plugin, lightweight
- Configurable attempt limits
- IP blocking
5. Change wp-login.php URL
Rename your login page so automated bots can’t find it:
Using WPS Hide Login plugin:
- Install WPS Hide Login
- Settings → WPS Hide Login
- Change login URL from wp-login.php to something unique
- Save
Now login is at yoursite.com/secret-login-page instead of the default wp-login.php that bots hammer constantly.
Pro Tip: According to Sucuri’s research, sites with 2FA enabled are 99.9% less likely to be compromised via brute force attacks. It’s the single most effective security measure you can implement.
Installing Security Plugins and Firewalls
Security plugins provide multiple layers of protection. Think of them as your site’s security system.
Top WordPress security plugins compared:
| Plugin | Key Features | Performance Impact | Price | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wordfence | Firewall, malware scan, 2FA, blocking | Light | Free/Premium $119/yr | Most comprehensive |
| Sucuri Security | Malware scan, hardening, monitoring | Very light | Free/Pro $199/yr | Professional sites |
| iThemes Security | 50+ ways to secure, brute force protection | Light | Free/Pro $199/yr | User-friendly |
| All In One WP Security | Firewall, login security, database security | Light | Free | Budget-conscious |
| MalCare | Fast malware scan, automatic cleaning | Light | $99+/yr | Malware-focused |
My recommendation: Wordfence for most WordPress sites. The free version is extremely powerful, and premium adds real-time threat intelligence.
Essential Wordfence setup:
1. Install and activate Wordfence
- Enable the firewall:
- Wordfence → Firewall → Optimize Firewall
- Choose “Extended Protection” (requires .htaccess modification)
- Enable “Rate Limiting” to block aggressive bots
3. Configure scan settings:
- Wordfence → Scan → Scan Options
- Enable “High Sensitivity” scanning
- Schedule automatic daily scans
4. Set up email alerts:
- Get notified of:
- Failed login attempts
- Blocked attacks
- File changes
- Malware detections
5. Enable brute force protection:
- Wordfence → Login Security
- Turn on 2FA for all admin accounts
- Enable CAPTCHA on login and registration
Web application firewall (WAF) benefits:
A firewall filters malicious traffic before it reaches your WordPress site:
Blocks:
- SQL injection attempts
- Cross-site scripting (XSS)
- Malware payloads
- Known attack patterns
- Malicious bots
Cloudflare WAF (alternative/additional):
Cloudflare offers a free WAF that sits in front of your site:
- Filters traffic at DNS level
- Blocks attacks before hitting your server
- Reduces server load
- Improves performance (bonus SEO benefit)
Using both Wordfence + Cloudflare = maximum protection.
Real protection example:
A WordPress news site enabled Wordfence after suffering a hack. In the first 30 days, Wordfence blocked:
- 4,700+ malicious login attempts
- 120 SQL injection attempts
- 87 XSS attempts
- 2,300 requests from known malicious IPs
Without Wordfence, any one of these could have compromised the site. Total cost of protection: $0 (free version).
For comprehensive WordPress security implementation, explore the WordPress SEO guide.
Regular Backups and Disaster Recovery
Backups don’t prevent hacks, but they’re your safety net when security fails. They’re also critical for SEO recovery.
Why backups matter for SEO:
Faster recovery = less traffic loss:
- With backups: Restore in hours
- Without backups: Rebuild in weeks/months
- Every day offline = more ranking damage
Clean version restoration:
- Restore to pre-infection state
- No manual malware removal needed
- Preserve SEO structure and content
Confidence to update:
- Test updates knowing you can rollback
- Reduces fear of “breaking” the site
- Enables proactive security patching
Backup strategy essentials:
Frequency:
- Daily backups for active sites (new content daily)
- Weekly backups for static sites (rarely updated)
- Before any major change (theme/plugin updates, design changes)
What to backup:
- Complete WordPress files
- Entire database
- Uploads folder (images, media)
- Theme and plugin files
Storage locations:
- Offsite storage (not on same server)
- Multiple locations (cloud + local)
- Encrypted backups for sensitive data
Best WordPress backup plugins:
| Plugin | Storage Options | Automation | Price | Best Feature |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UpdraftPlus | Cloud, FTP, email | Scheduled | Free/Premium $70 | Most popular, reliable |
| BackWPup | Multiple destinations | Scheduled | Free/Pro $75 | Detailed control |
| BlogVault | Cloud, automated | Real-time | $89+/yr | Staging, malware scan |
| Jetpack Backup | Cloud, automated | Real-time | $10/mo | Automatic, hassle-free |
| Duplicator | Manual, cloud | Manual/scheduled | Free/Pro $69 | Site migration tool |
Setting up UpdraftPlus (most popular):
1. Install UpdraftPlus
2. Configure backup schedule:
- Settings → UpdraftPlus Backups
- Files backup: Daily (or weekly for static sites)
- Database backup: Daily
- Retain: 7 backups minimum
3. Choose remote storage: Options:
- Google Drive (free 15GB)
- Dropbox (free 2GB)
- Amazon S3 (pay-as-you-go)
- OneDrive (free 5GB)
Connect your chosen storage, test the connection.
4. Run manual backup immediately:
- Click “Backup Now”
- Verify backup completes successfully
- Check files appear in remote storage
5. Test restoration:
- Crucial step most people skip
- Restore backup to staging environment
- Verify everything works
- Now you know restoration works when you need it
Backup testing schedule:
- Test restoration quarterly
- Verify backups are actually being created
- Confirm backup files aren’t corrupted
Pro Tip: According to WordPress.org statistics, only 3 out of 10 site owners have working backups. Of those, less than half have ever tested restoration. Don’t be part of the 70% who discover their backups don’t work during an emergency. Test your backups.
How to Recover from a Security Breach Without Losing SEO Value
Despite best efforts, breaches happen. Here’s how to minimize SEO damage during recovery.
Detecting and Cleaning Malware Quickly
Speed is everything in malware cleanup. Every hour your site stays infected causes more SEO damage.
Signs your WordPress site is infected:
Obvious indicators:
- Google displays “This site may be hacked” warning
- Visitors report seeing pop-ups or ads
- Site redirects to spam/malware sites
- Google Search Console security warning
Subtle indicators:
- Unexpected drop in traffic or rankings
- Slow page load times (cryptominers)
- Unknown admin users in dashboard
- Files or pages you didn’t create
- Unexplained changes to content
- Server CPU/RAM usage spikes
Immediate response checklist:
Step 1: Take site offline (maintenance mode)
- Prevents further visitor exposure
- Stops malware spreading
- Protects your reputation
Use a maintenance plugin:
- WP Maintenance Mode
- Coming Soon Page
- Display simple message: “Temporarily offline for maintenance”
Step 2: Change all passwords immediately
- WordPress admin accounts
- FTP/SFTP access
- Hosting control panel
- Database credentials
Use strong, unique passwords. Assume all old passwords are compromised.
Step 3: Scan with multiple tools
Wordfence scan:
- Wordfence → Scan
- Run full scan
- Review all flagged files
- Document suspicious files
Sucuri SiteCheck (free online scanner):
- Visit sitecheck.sucuri.net
- Enter your domain
- Reviews external blacklists
- Checks for malware signatures
MalCare (alternative):
- Deep server-side scanning
- Detects hidden backdoors
- Automatic cleaning option
Google Search Console:
- Security & Manual Actions → Security Issues
- Shows what Google detected
- Lists infected URLs
Step 4: Clean infected files
Option A: Automatic cleaning (easiest)
- Wordfence Premium: One-click cleaning
- MalCare: Automatic malware removal
- Sucuri: Professional cleaning service
Option B: Manual cleaning (if you know what you’re doing)
- Delete malicious files
- Clean infected files (remove malicious code)
- Reset file permissions
- Update core WordPress files
- Reinstall plugins and themes
Option C: Restore from clean backup (fastest)
- If you have recent clean backup
- Restore files and database
- Update all software immediately
- Change all passwords
Step 5: Harden security post-cleanup
- Install security plugin (if not already)
- Enable 2FA
- Update everything
- Change all passwords
- Review user accounts (delete suspicious ones)
- Check file permissions
Step 6: Request malware review from Google
- Google Search Console
- Security Issues section
- Click “Request Review”
- Explain what was infected and how you fixed it
- Google reviews in 3-5 days typically
How long SEO recovery takes:
| Infection Severity | Detection Time | Cleanup Time | Google Review | Full SEO Recovery |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minor (caught early) | 1-3 days | 2-6 hours | 3-7 days | 2-4 weeks |
| Moderate (spam injection) | 1-2 weeks | 1-2 days | 7-14 days | 2-3 months |
| Severe (blacklisted) | 2-4 weeks | 2-5 days | 14-30 |
Real cleanup example:
A WordPress blog was infected with SEO spam that injected pharmaceutical links into all posts. They caught it after 18 days.
Cleanup process:
- Day 1: Detected via Google Search Console warning
- Day 1: Took site offline, changed passwords
- Day 2: Hired Sucuri for professional cleaning ($299)
- Day 3: Site cleaned, back online with hardened security
- Day 4: Submitted reconsideration request to Google
- Day 11: Google removed warnings
- Week 3: Rankings started recovering
- Month 2: Traffic back to 70%
- Month 4: Full recovery achieved
Total damage: ~$8,000 in lost ad revenue, $299 cleanup cost, countless stress hours.
Pro Tip: If you can’t afford professional cleanup ($200-500 typically), use MalCare’s automatic cleaning feature ($99/year). It removes most common malware automatically without manual file editing. For severe infections, professional services like Sucuri are worth every penny—trying to clean severe infections yourself often makes it worse.
Communicating with Google After a Breach
Proper communication with Google speeds up recovery and restores trust.
Using Google Search Console for security issues:
Step 1: Verify the breach in GSC
- Open Google Search Console
- Navigate to Security & Manual Actions → Security Issues
- Review detected problems:
- Hacked content
- Malware
- Deceptive pages
- Harmful downloads
Step 2: Document what was compromised Google wants specifics:
- Which files were infected
- What type of malware (spam injection, redirects, etc.)
- When you discovered it
- Which pages were affected
Step 3: Clean thoroughly Don’t request review until you’re 100% confident the site is clean:
- All malware removed
- Backdoors closed
- Vulnerabilities patched
- Security hardened
Step 4: Write a detailed reconsideration request
Good request example:
We discovered our WordPress site was compromised on [date] with [malware type].
The malware [describe what it did].
Steps taken to clean:
1. Took site offline immediately
2. Hired [professional service] to clean all files
3. Restored from clean backup dated [date]
4. Updated WordPress core, all plugins, and themes
5. Changed all passwords
6. Installed Wordfence security plugin
7. Enabled two-factor authentication
8. Removed [X] spam pages from Google's index
Security measures implemented:
- Wordfence Premium with firewall enabled
- Daily automated backups to offsite location
- Two-factor authentication for all admin accounts
- Login page renamed
- Strong password policy enforced
- Automatic security updates enabled
We have verified no malicious code remains and have hardened security
to prevent future compromises.
Bad request example:
My site was hacked. I cleaned it. Please remove the warning.
Google wants evidence you’ve actually fixed the problem and won’t get reinfected immediately.
Step 5: Submit and wait
- Click “Request Review” in Google Search Console
- Typical review time: 3-14 days
- Google emails when review is complete
- If approved: Warnings removed within 72 hours
- If denied: More issues found, clean again and resubmit
Manual penalty vs security issue:
These are different and handled differently:
Security issue:
- Triggered by malware/hacks
- Automatic detection
- Request review through Security Issues
- Usually resolved quickly once cleaned
Manual penalty:
- Human reviewer flagged your site
- Often for spam links (from hacks or otherwise)
- Request review through Manual Actions
- May require disavow file for spam links
Pro Tip: While waiting for Google’s review, submit your sitemap again and use the URL Inspection tool to request re-indexing of cleaned pages. This can speed up Google’s re-crawl and verification process.
Restoring Rankings and Traffic Post-Hack
Cleaning the infection is only half the battle. Recovering SEO momentum requires proactive effort.
Immediate post-cleanup actions:
1. Rebuild trust signals
- Add security badges to homepage
- Update “About” page mentioning security measures
- Consider publishing a transparency post (for severe breaches affecting users)
- Display SSL certificate prominently
- Add trust seals (Norton, McAfee, BBB if applicable)
2. Re-engage your audience
- Email subscribers explaining the issue (brief, professional)
- Post on social media confirming site is secure
- Monitor brand mentions and respond to concerns
- Update Google Business Profile if applicable
3. Monitor rankings closely
- Use Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Rank Math to track rankings daily
- Document recovery progress
- Identify pages that lost rankings most
- Prioritize recovery efforts on those pages
4. Fix technical SEO issues caused by hack
- Remove spam pages from Google’s index (use Removals tool in GSC)
- Disavow toxic backlinks (if hackers built spam links)
- Fix any broken internal links
- Verify redirects work correctly
- Check for duplicate content issues
- Ensure proper canonical tags
5. Refresh and improve affected content
- Update compromised pages with fresh content
- Add new value (more depth, examples, images)
- Update publish dates (if content is actually improved)
- Build internal links to recovered pages
- Share updated content on social media
6. Build new quality signals
- Publish fresh, high-quality content consistently
- Earn new backlinks from reputable sites
- Increase social engagement
- Improve Core Web Vitals
- Enhance user experience
Advanced recovery tactics:
Disavow toxic backlinks:
If hackers injected spam links, you need to tell Google to ignore them:
- Compile list of all spam backlinks (use Ahrefs or GSC)
- Create disavow file (text file listing bad domains)
- Submit via Google’s Disavow Tool
- Document in reconsideration request
Remove hacked pages from Google’s index:
Google may have indexed thousands of spam pages:
- Identify spam URLs (use site:yourdomain.com in Google)
- Verify they’re deleted from your server
- Use GSC Removals tool to expedite removal
- Submit updated sitemap without spam pages
- Return 404 or 410 status codes for deleted URLs
Rebuild positive user signals:
Google tracks engagement metrics:
- Reduce bounce rate: Improve page load speed, add compelling intro
- Increase dwell time: Better internal linking, engaging content
- Boost CTR: Rewrite meta descriptions emphasizing safety/quality
- Encourage social shares: Add prominent share buttons
- Generate positive reviews: Request reviews from happy customers
Recovery timeline expectations:
Week 1-2:
- Warnings removed from Google
- Initial ranking stabilization
- Traffic still significantly down
Week 3-6:
- Gradual ranking recovery begins
- Traffic increases 10-30%
- User trust starts rebuilding
Month 2-3:
- Steady ranking improvements
- Traffic recovers to 50-80%
- New positive signals accumulate
Month 4-6:
- Most rankings recovered
- Traffic returns to 80-95%
- Site authority largely restored
Month 6+:
- Full recovery (if all done correctly)
- Sometimes exceeds pre-hack traffic (if you improved content during recovery)
Case study – successful recovery:
An e-commerce WordPress site was hacked with credit card skimmer malware. Customer complaints alerted them after 5 days.
Immediate actions:
- Took site offline within 2 hours of discovery
- Hired forensic security firm ($1,200)
- Notified affected customers (as required by law)
- Notified credit card processors
SEO recovery plan:
- Cleaned malware professionally
- Implemented enterprise-grade security (Sucuri firewall + monitoring)
- Requested Google review (approved in 6 days)
- Published transparency blog post
- Offered affected customers 20% discount
- Improved site speed (Core Web Vitals)
- Added trust badges and security certifications
- Built 15 new quality backlinks through PR outreach
- Published 2 new helpful blog posts weekly
Results:
- Week 1: Traffic down 89%
- Week 4: Traffic recovered to 45%
- Week 8: Traffic at 78%
- Week 14: Traffic exceeded pre-hack levels by 12%
- Trust signals: Positive reviews increased, bounce rate improved
- Sales: Actually increased 8% over pre-hack (better trust signals + improved UX)
They turned a disaster into an opportunity by implementing proper security, being transparent, and improving user experience during recovery.
Pro Tip: Recovery is your opportunity to improve. Don’t just restore to previous state—make your site better, faster, and more secure than before. Many sites that implement comprehensive improvements during recovery actually end up performing better than before the hack.
For complete post-hack recovery strategies, visit the WordPress SEO guide.
What Security Mistakes Kill WordPress SEO?
Even security-conscious site owners make critical errors. Avoid these common pitfalls.
Common Security Misconfigurations That Hurt Rankings
Mistake #1: Blocking Googlebot with security measures
The problem: Overly aggressive security settings accidentally block Google’s crawlers, preventing indexing.
Common causes:
- Firewall blocking Google’s IP ranges
- CAPTCHA on all pages (including for bots)
- Rate limiting too strict for crawler activity
- Country blocking that includes Google’s servers
How to verify:
- Google Search Console → Settings → Crawl Stats
- Check for crawl errors
- Use “Fetch as Google” in URL Inspection tool
- Review Wordfence/Cloudflare logs for Googlebot blocks
How to fix:
- Whitelist Googlebot user agents
- Whitelist Google’s IP ranges
- Don’t use CAPTCHA on content pages
- Test thoroughly after security changes
Real example:
A WordPress site enabled aggressive DDoS protection that limited requests to 5 per minute per IP. Google’s crawler triggered this limit immediately.
Result: Site stopped being crawled. New content wasn’t indexed for 3 weeks before they discovered the issue. Lost rankings for 47 keywords.
Fix: Whitelisted Googlebot IPs. Full re-crawl took 2 weeks. Rankings recovered in 6 weeks.
Mistake #2: Security plugins slowing site to a crawl
The problem: Some security plugins are resource hogs that destroy page speed and Core Web Vitals.
Performance impact comparison:
| Security Plugin | Page Load Impact | Resource Usage | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wordfence | +0.1-0.3s | Light-moderate | ✅ Recommended |
| Sucuri | +0.05-0.15s | Very light | ✅ Recommended |
| All In One Security | +0.1-0.2s | Light | ✅ Good |
| iThemes Security | +0.15-0.3s | Light-moderate | ✅ Good |
| Outdated security plugins | +1-3s | Heavy | ❌ Avoid |
How to test impact:
- Baseline: Test site speed (GTmetrix, PageSpeed Insights)
- Activate security plugin
- Re-test site speed
- Compare results
If plugin adds more than 0.5s to load time, consider alternatives or optimize settings.
Optimization tips:
- Disable unnecessary features (if plugin has modules, only enable what you need)
- Schedule scans during low-traffic times
- Use caching effectively
- Consider server-level security (less plugin reliance)
Mistake #3: Not updating “for stability”
The myth: “If it ain’t broke, don’t update it.”
The reality: Outdated WordPress = massive security vulnerabilities = SEO disaster waiting to happen.
Why people avoid updates:
- Fear of breaking the site
- “I’ll do it later” procrastination
- Don’t want to test after updates
- Previous bad experience with updates
The actual risk analysis:
Risk of updating:
- 2-5% chance of minor compatibility issue
- Usually fixable in minutes
- Can test on staging first
- Temporary visual bugs at worst
Risk of NOT updating:
- 100% certainty of exploitable vulnerabilities
- Hackers actively target known vulnerabilities
- Can lead to complete site compromise
- Recovery takes weeks/months
- Potential permanent traffic loss
Statistics that should terrify you:
According to WPScan’s research:
- 73% of WordPress installations have known vulnerabilities
- Outdated plugins are responsible for 52% of hacks
- Vulnerabilities are exploited within 48 hours of public disclosure
When a vulnerability is announced, hackers immediately start mass-scanning for vulnerable sites. If you wait even a few days to update, you’re at serious risk.
Safe update process:
- Backup first (non-negotiable)
- Test on staging (if possible)
- Update one thing at a time (easier to troubleshoot)
- Check site after each update
- Have rollback plan (your backup)
Mistake #4: Using nulled/pirated premium plugins or themes
The problem: “Free” pirated versions of premium plugins often contain backdoors, malware, or malicious code.
Why nulled themes/plugins are dangerous:
- Backdoors pre-installed
- Hidden malware injections
- Spam link injections
- No security updates (obviously)
- Impossible to clean thoroughly
Real statistics: According to Sucuri’s analysis, 4 out of 5 nulled WordPress themes contain malicious code. That’s an 80% infection rate.
Common malware in nulled themes:
- Base64 encoded backdoors
- Hidden admin users
- Spam link generators
- Redirect scripts
- Data harvesting code
The math:
- Nulled theme: “Free” (but costs you $10K+ when hacked)
- Legitimate theme: $59 (protects your $10K+ in traffic value)
Just buy the legitimate version. The “savings” aren’t worth the risk.
Mistake #5: Ignoring file permission warnings
The problem: Incorrect file permissions allow hackers to modify core WordPress files, themes, and plugins.
Correct WordPress file permissions:
- Directories: 755 (or 750)
- Files: 644 (or 640)
- wp-config.php: 440 or 400 (most secure)
Dangerous permissions:
- 777 – Anyone can read, write, execute (huge security hole)
- 666 – Anyone can read and write files
How to check: Most security plugins (Wordfence, Sucuri) scan for incorrect permissions and alert you.
How to fix: Via FTP/SSH:
find /path/to/wordpress -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \;
find /path/to/wordpress -type f -exec chmod 644 {} \;
chmod 440 wp-config.php
Or use your hosting control panel’s file manager.
Pro Tip: After fixing permissions, some plugins may complain they can’t update automatically. This is fine—manual updates via FTP are more secure anyway for critical sites.
The False Sense of Security Problem
Mistake #6: “I installed a security plugin, I’m protected”
The reality: A security plugin is one layer. It’s not complete protection.
Comprehensive security requires:
✅ Security plugin (Wordfence, Sucuri) ✅ Strong authentication (passwords, 2FA) ✅ Regular backups (tested restoration) ✅ Software updates (core, plugins, themes) ✅ SSL/HTTPS (proper configuration) ✅ Firewall (plugin or Cloudflare) ✅ Monitoring (real-time alerts) ✅ Regular security audits ✅ Hardening (file permissions, .htaccess) ✅ Limited user access (principle of least privilege)
Security is a system, not a single tool.
Mistake #7: Assuming free security plugins are enough
The truth: Free security plugins provide basic protection. For serious sites, premium features matter:
Free version limitations:
- No real-time threat intelligence
- No automatic malware cleaning
- Limited scanning frequency
- No priority support
- No country blocking
- Basic firewall rules
Premium features that prevent disasters:
- Real-time threat defense – Blocks attacks as they emerge
- Automatic malware removal – Cleans infections without manual work
- Country blocking – Block entire regions you don’t serve
- Two-factor authentication – Additional login security
- Premium support – Expert help when you need it
Cost-benefit analysis:
Free plugin:
- Cost: $0
- Protection: Basic
- Risk: Moderate
Premium plugin:
- Cost: $100-200/year
- Protection: Comprehensive
- Risk: Low
Cost of being hacked:
- Lost traffic value: $5,000-50,000
- Cleanup costs: $300-2,000
- Recovery time: 2-6 months
- Reputation damage: Priceless
Investing $100/year to protect $20,000+ in annual traffic value is a no-brainer.
Mistake #8: No monitoring or alerts
The problem: Many hacks go unnoticed for weeks or months, maximizing damage.
Average detection time:
- With monitoring: 2-7 days
- Without monitoring: 30-90 days
What to monitor:
- Failed login attempts
- File changes
- Blacklist status
- Uptime/downtime
- Traffic anomalies
- Server resource usage
Free monitoring options:
- Google Search Console (security alerts)
- Wordfence email alerts
- UptimeRobot (free uptime monitoring)
- Jetpack (basic security scanning)
Premium monitoring:
- Sucuri ($199/yr) – Comprehensive security monitoring
- Jetpack Premium ($10/mo) – Real-time backup + monitoring
- ManageWP (free-$99/mo) – Multi-site monitoring
Pro Tip: Enable email alerts for everything security-related. Yes, you’ll get false positives occasionally. But the one time it’s a real hack, early detection saves your traffic and rankings.
Security Tools and Resources Comparison
Let’s compare the top security solutions to help you choose what’s right for your site.
Best WordPress Security Plugins Compared
Here’s an honest, comprehensive comparison based on actual usage:
| Plugin | Free/Premium | Key Strengths | Limitations | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wordfence | Free + Premium ($119/yr) | Most comprehensive, firewall, malware scanner, 2FA, real-time threat intelligence (premium) | Can be resource-intensive on shared hosting | Most WordPress sites, serious protection |
| Sucuri | Free + Pro ($199-$299/yr) | Website firewall, malware removal, DDoS protection, best performance | Premium required for key features | Professional sites, high-value sites |
| iThemes Security Pro | Free + Pro ($199/yr) | 50+ security features, user-friendly, good documentation | Can be overwhelming for beginners | Power users, agencies |
| All In One WP Security | Free | Completely free, comprehensive features, lightweight | Limited advanced features, basic UI | Budget-conscious, smaller sites |
| Solid Security | Free + Pro ($99/yr) | Good balance of features and performance | Fewer features than Wordfence | Mid-size sites |
| MalCare | Premium ($99/yr) | Automatic malware cleaning, very fast scanner | No free version | Sites prioritizing malware protection |
Recommendation by site type:
Personal blogs / Small sites:
- All In One WP Security (free) + CloudFlare (free)
- Cost: $0
- Protection: Adequate for low-risk sites
Business sites / Medium traffic:
- Wordfence Premium + Daily backups
- Cost: $119/yr + backup solution
- Protection: Comprehensive
E-commerce / High-value sites:
- Sucuri Pro + MalCare + Premium hosting security
- Cost: $299-500/yr
- Protection: Enterprise-level
For absolute maximum security (overkill for most):
- Cloudflare Pro ($20/mo)
- Sucuri Website Firewall ($199/yr)
- Wordfence Premium ($119/yr)
- Daily remote backups
- Security monitoring service
Hosting Security Features Comparison
Your hosting provider is your first line of defense. Not all hosting is equally secure.
| Hosting Provider | Security Features | Auto-Updates | Firewall | Malware Scanning | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WP Engine | Excellent | ✅ Core auto-updates | ✅ EverCache (CDN + WAF) | ✅ Daily | $30-290/mo |
| Kinsta | Excellent | ✅ Core auto-updates | ✅ Cloudflare integration | ✅ Daily | $35-1,650/mo |
| Cloudways | Very Good | ✅ Optional | ✅ With Cloudflare | ⚠️ Add-on | $11-442/mo |
| SiteGround | Good | ✅ Core + plugin updates | ✅ Basic | ⚠️ Daily (GoGeek plan) | $3-15/mo |
| Bluehost | Basic | ⚠️ Core only | ⚠️ SiteLock (paid add-on) | ❌ Add-on only | $3-30/mo |
| HostGator | Basic | ⚠️ Core only | ❌ None | ❌ Add-on only | $3-14/mo |
What managed WordPress hosting provides:
- Automatic WordPress core updates
- Server-level security hardening
- DDoS protection
- Malware scanning and removal
- Daily backups
- Staging environments (test security changes safely)
- Expert WordPress support
Budget hosting security gaps:
- Shared server resources (one infected site can affect others)
- Minimal security hardening
- No automatic updates beyond core
- No malware scanning
- Basic or no backups
- Generic support (not WordPress experts)
The hosting security upgrade is worth it:
Moving from $5/month shared hosting to $30/month managed WordPress hosting costs $300/year extra.
But you get:
- Professional malware scanning ($200/yr value)
- Daily backups ($100/yr value)
- Better performance (SEO benefit)
- Expert support (time savings)
- Peace of mind (priceless)
Pro Tip: If you can’t afford managed WordPress hosting, at minimum choose a host with:
- Free SSL certificates (Let’s Encrypt)
- Daily automated backups
- Server-level caching
- Good uptime record (99.9%+)
- SSH access (for manual security hardening)
SiteGround and Cloudways meet these requirements at reasonable prices ($11-15/mo).
For comprehensive hosting recommendations, explore the WordPress SEO guide.
How to Build a WordPress Security Maintenance Schedule
Ongoing maintenance prevents most security disasters. Here’s your systematic schedule.
Daily Security Tasks
Automated (set and forget): ✅ Security plugin monitoring (Wordfence sends email alerts) ✅ Uptime monitoring (UptimeRobot checks every 5 minutes) ✅ Automated backups (UpdraftPlus daily schedule) ✅ Security scan (Wordfence daily scan at 3 AM)
Manual (5 minutes/day): ✅ Check security alert emails (respond to any issues) ✅ Glance at Google Search Console (any new warnings?) ✅ Quick traffic check (any sudden unexplained drops?)
Weekly Security Tasks
Every Monday (15 minutes):
✅ Review failed login attempts
- Check Wordfence → Tools → Live Traffic
- Look for patterns (same IPs trying repeatedly?)
- Block suspicious IPs if needed
✅ Check for available updates
- Dashboard → Updates
- Note what needs updating
- Schedule update time this week
✅ Review Google Search Console
- Security & Manual Actions
- Coverage (any indexing issues?)
- Performance (traffic trends normal?)
✅ Check backup success
- Verify last backup completed
- Spot-check backup files exist in storage
Monthly Security Tasks
First Monday of each month (30-60 minutes):
✅ Apply all available updates
- Backup first (always!)
- Update plugins one at a time
- Update themes
- Update WordPress core if available
- Test site after updates
✅ Review user accounts
- Users → All Users
- Remove inactive accounts
- Verify all users still need access
- Check for suspicious new users
✅ Run comprehensive security scan
- Wordfence → Scan
- Review all warnings and issues
- Fix any problems found
✅ Review security logs
- Check Wordfence traffic logs
- Look for attack patterns
- Adjust firewall rules if needed
✅ Test backup restoration
- At least quarterly, test full restoration
- Restore to staging environment
- Verify everything works
✅ Check SSL certificate
- Verify SSL is working
- Check expiration date (Let’s Encrypt renews every 90 days)
- Test HTTPS redirects
✅ Review file changes
- Wordfence shows all file modifications
- Investigate any unexpected changes
- Verify theme/plugin updates are legitimate
Quarterly Security Tasks
Every 3 months (2-3 hours):
✅ Comprehensive security audit
- Run Wordfence premium scan (or hire audit)
- Review all security settings
- Check file permissions site-wide
- Verify .htaccess security rules
✅ Plugin and theme cleanup
- Delete unused plugins/themes
- Check if installed plugins are still maintained
- Replace abandoned plugins with alternatives
- Document all active plugins
✅ Password rotation
- Change all admin passwords
- Update FTP/SFTP credentials
- Update database password
- Update hosting control panel password
✅ Review hosting security
- Check hosting account for updates/changes
- Review server logs for anomalies
- Verify backups are being stored offsite
- Test backup restoration fully
✅ Security education
- Review latest WordPress security news
- Update security procedures if needed
- Train team on new threats
- Review this checklist and update
Annual Security Tasks
Once per year (4-6 hours):
✅ Professional security audit
- Consider hiring professional audit ($500-2,000)
- Penetration testing
- Code review
- Infrastructure review
✅ SSL certificate renewal (if not auto-renewing)
- Renew before expiration
- Test new certificate
- Update any hardcoded HTTPS references
✅ Review and update security documentation
- Incident response plan
- Recovery procedures
- Contact information
- Access credentials (stored securely)
✅ Security budget review
- Evaluate security tool costs
- Consider upgrades (free → premium?)
- Budget for next year’s security
- Calculate ROI of security investments
✅ Disaster recovery drill
- Simulate site compromise
- Practice full recovery from backup
- Time the recovery process
- Document lessons learned
Pro Tip: Create a checklist document (Google Docs, Notion, etc.) and literally check boxes as you complete tasks. Set calendar reminders for each schedule. What gets scheduled gets done.
WordPress Security SEO Checklist
Let’s consolidate everything into an actionable implementation checklist.
Immediate Actions (Do Today)
✅ Install security plugin
- Wordfence (recommended) or alternative
- Run initial scan
- Enable firewall
- Configure email alerts
✅ Enable HTTPS/SSL
- Install SSL certificate (free Let’s Encrypt)
- Force HTTPS site-wide
- Fix mixed content warnings
- Update Google Search Console
✅ Strong authentication
- Change “admin” username if still using
- Generate strong unique password
- Enable two-factor authentication
- Limit login attempts
✅ Install backup plugin
- UpdraftPlus or alternative
- Configure daily backups
- Set up remote storage
- Run immediate manual backup
✅ Update everything
- WordPress core
- All plugins
- All themes
- Test site after updates
✅ Remove unused software
- Delete unused plugins
- Delete unused themes
- Clean up database
This Week Actions
✅ Security hardening
- Change default login URL
- Disable file editing in dashboard
- Protect wp-config.php
- Set proper file permissions
- Disable XML-RPC if not needed
✅ Monitoring setup
- Google Search Console verification
- Uptime monitoring (UptimeRobot)
- Security alert configuration
- Traffic monitoring baseline
✅ User access review
- Audit all user accounts
- Remove unnecessary users
- Enforce strong password policy
- Document who has access
✅ Content security
- Check for existing malware
- Scan for spam injections
- Review recent content changes
- Verify no unauthorized posts
This Month Actions
✅ Advanced security
- Consider Cloudflare (free tier)
- Implement security headers
- Add CAPTCHA to forms
- Enable database security features
- Consider premium security upgrade
✅ Testing and verification
- Test backup restoration
- Verify firewall is working
- Check SSL configuration
- Test all security alerts
✅ Documentation
- Create security contact list
- Document recovery procedures
- Save access credentials securely
- Create incident response plan
Ongoing Maintenance
✅ Daily (automated)
- Security monitoring
- Backup creation
- Uptime checks
- Alert review
✅ Weekly
- Review security logs
- Check for updates
- Monitor Google Search Console
- Review traffic patterns
✅ Monthly
- Apply all updates
- Run comprehensive scans
- Review user accounts
- Test backups
✅ Quarterly
- Full security audit
- Password rotation
- Plugin/theme cleanup
- Security training
✅ Annually
- Professional audit
- Disaster recovery drill
- Security budget review
- Update all documentation
Pro Tip: Print this checklist, check off items as you complete them, and keep it somewhere visible. Security through obscurity doesn’t work—security through systematic implementation does.
For the complete WordPress security and SEO implementation roadmap, visit the comprehensive WordPress SEO guide.
Common WordPress Security Questions Answered
How often should I update WordPress and plugins?
Short answer: As soon as updates are available, especially security updates.
Detailed answer:
Security updates: Immediately (within 24-48 hours)
- These patch known vulnerabilities
- Hackers exploit known vulnerabilities within days
- Delaying security updates is extremely risky
Feature updates: Within 1-2 weeks
- Test on staging first if possible
- Review changelog for breaking changes
- Backup before updating
Major version updates: Within 2-4 weeks
- Wait for X.X.1 release (first bug-fix update)
- Ensure plugin compatibility
- Test thoroughly on staging
- Backup and update during low-traffic period
Update frequency best practices:
- Check for updates weekly minimum
- Enable automatic updates for minor core releases
- Subscribe to security mailing lists for critical updates
- Never delay security patches more than 7 days
Pro Tip: WordPress.org releases security updates for severe vulnerabilities within days of discovery. If you see a WordPress core security update, apply it immediately—hackers are already exploiting it in the wild.
Can security plugins slow down my site and hurt SEO?
Yes, but modern security plugins are well-optimized.
Performance impact reality:
| Activity | Impact | When It Happens |
|---|---|---|
| Firewall checking | 0.05-0.2s | Every page load |
| Malware scanning | High CPU | Scheduled (2-5 AM typically) |
| Log writing | Minimal | Background |
| Blocking attacks | Saves resources | As needed |
Net impact: Well-configured security plugins add 0.1-0.3 seconds to page load typically. But they prevent massive slowdowns from:
- Cryptomining malware (can add 3-10 seconds)
- Spam page generation (wastes server resources)
- DDoS attacks (crashes site entirely)
Optimization tips:
- Schedule scans during low-traffic hours
- Disable unnecessary features
- Use caching effectively
- Choose lightweight plugins (Sucuri, Wordfence)
- Avoid outdated plugins
The trade-off is worth it:
- 0.2s slower from security plugin = minor SEO impact
- Site hack = 100% traffic loss
Real example:
A site worried about Wordfence slowing their site disabled it. Within 3 weeks, they were hacked with cryptomining malware that increased page load time from 1.8s to 9.3s.
After cleaning and re-enabling Wordfence:
- Page load: 2.0s (0.2s slower than before Wordfence)
- But protected from the malware that would have added 7+ seconds
Pro Tip: Use GTmetrix or PageSpeed Insights to measure your site speed before and after installing a security plugin
. The impact should be minimal (under 0.3s). If it’s more, check your plugin settings or consider a lighter alternative.
Do I really need to pay for premium security plugins?
It depends on your site’s value and risk tolerance.
When free plugins are sufficient:
- Personal blogs with minimal traffic
- Hobby sites with no revenue
- Sites with limited sensitive data
- Low-profile sites (not high-value targets)
- You’re willing to manually handle security issues
When premium is worth it:
- Business sites generating revenue
- E-commerce sites
- Sites with customer data
- High-traffic sites (more attractive targets)
- You want automatic malware removal
- You need expert support during emergencies
Cost-benefit analysis:
Free security:
- Cost: $0
- Manual malware cleanup: 5-10 hours + stress
- Downtime during hack: 2-7 days
- Lost revenue during downtime: Variable
- Risk of incomplete cleanup: High
Premium security ($100-200/year):
- Cost: $100-200/year
- Automatic malware removal: Minutes
- Real-time threat blocking: Prevents most attacks
- Expert support: Saves hours of troubleshooting
- Peace of mind: Priceless
Real calculation example:
Small business WordPress site:
- Monthly revenue: $5,000
- Average hack downtime: 5 days
- Lost revenue during downtime: ~$833
- Professional cleanup cost: $500
- Total hack cost: $1,333
vs
- Wordfence Premium: $119/year
- Prevents 99.9% of hacks
- ROI: Paying for itself if it prevents just ONE hack
For sites earning $1,000+/month, premium security is an easy decision.
Pro Tip: Start with free versions to learn the features. Once you understand the value, upgrade to premium for your primary business site. Keep free versions for test/staging sites.
How do I know if my WordPress site has been hacked?
Obvious signs:
- Google displays “This site may be hacked” warning
- Browser shows malware warnings
- Site redirects to spam/adult sites
- Pop-ups appear that you didn’t create
- Site is completely down or defaced
Subtle signs (harder to detect):
- Sudden unexplained traffic drop (check Google Analytics)
- Unknown users in WordPress dashboard (Users → All Users)
- Files modified you didn’t touch (check Wordfence file changes)
- New posts/pages you didn’t create
- Spam in comments or content you don’t recognize
- Slow performance (cryptominers)
- Hosting resource usage spikes
- Unknown plugins or themes installed
Detection tools:
1. Wordfence scan:
- Wordfence → Scan
- Free, thorough scan
- Checks for malware, backdoors, file changes
2. Sucuri SiteCheck (online tool):
- Visit sitecheck.sucuri.net
- Enter your domain
- Checks blacklists and malware signatures
- Free, no account needed
3. Google Search Console:
- Security & Manual Actions → Security Issues
- Google notifies you of detected malware
- Check regularly
4. VirusTotal:
- virustotal.com
- Scans URL with 70+ security scanners
- Shows if any detect malware
5. Google Safe Browsing:
- transparencyreport.google.com/safe-browsing/search
- Check if Google flagged your site
- Free lookup tool
Manual inspection methods:
Check your site:yoursite.com in Google:
site:yoursite.com viagra
site:yoursite.com pharmacy
site:yoursite.com casino
If spam pages appear, you’re infected.
Check recent file modifications: Via FTP, sort by “date modified” and look for:
- Core WordPress files recently changed
- Unknown files in root directory
- Files in /wp-content/uploads/ with .php extension
- Suspicious files in /wp-includes/
Check database for spam: Use phpMyAdmin or plugin:
- Search wp_posts for spam content
- Check wp_users for unknown admin accounts
- Look for unfamiliar entries in wp_options
When in doubt:
- Hire professional malware scan ($50-100)
- Use MalCare or Sucuri premium for deep scan
- Better to be paranoid than compromised
Pro Tip: Don’t wait for obvious signs. Run security scans monthly even if everything seems fine. Many infections stay hidden for months, doing SEO damage the entire time. Early detection is everything.
What should I do immediately after discovering a hack?
Immediate response checklist (first 30 minutes):
1. Stay calm, act fast:
- Don’t panic-delete everything
- Document what you’re seeing
- Screenshot evidence
- Note the date/time discovered
2. Take site offline:
- Enable maintenance mode
- Prevents further damage
- Protects visitors from malware
- Use “WP Maintenance Mode” plugin or .htaccess:
RewriteEngine on
RewriteCond %{REMOTE_ADDR} !^123\.123\.123\.123
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_URI} !/maintenance.html$ [NC]
RewriteRule .* /maintenance.html [R=302,L]
(Replace IP with yours so you can still access)
3. Change all passwords immediately:
- WordPress admin (all accounts)
- FTP/SFTP access
- Hosting control panel
- Database credentials
- Email accounts associated with site
Use strong, unique passwords (password manager generated).
4. Contact your host:
- Report the hack
- Ask if they see infection details
- Request server logs
- Check if other sites on account affected
5. Scan with multiple tools:
- Wordfence (if already installed)
- Sucuri SiteCheck online scanner
- Request scan from hosting provider
- Document what’s found
Next 24-48 hours:
6. Choose recovery method:
Option A: Restore from clean backup (fastest if you have one)
- Verify backup is clean (pre-infection date)
- Restore files and database
- Update all software immediately
- Change all passwords again
- Scan restored site
Option B: Professional cleaning (recommended for severe infections)
- Sucuri: $299+ emergency cleanup
- Wordfence: Premium includes removal assistance
- MalCare: $99/year includes automatic cleaning
- Local security firm: $300-1,500
Option C: Manual cleaning (if you know what you’re doing)
- Delete malicious files
- Clean infected files (remove malicious code)
- Remove spam from database
- Close security holes
- Rescan until clean
7. Harden security:
- Install/configure security plugin
- Enable two-factor authentication
- Update everything
- Remove unused plugins/themes
- Set proper file permissions
- Implement security best practices
8. Notify Google:
- Check Google Search Console for warnings
- Clean site thoroughly first
- Submit reconsideration request
- Provide detailed cleanup information
Within first week:
9. Monitor closely:
- Check for reinfection daily
- Review security logs
- Monitor traffic/rankings
- Scan repeatedly
10. Analyze how it happened:
- Review security logs
- Identify entry point
- Patch vulnerability
- Prevent future occurrences
11. Communicate (if necessary):
- Notify users if data was compromised
- Update social media (professionally)
- Maintain transparency
- Rebuild trust
What NOT to do:
❌ Delete everything without backup ❌ Ignore it hoping it goes away ❌ Try complex manual cleanup without expertise ❌ Restore backup without understanding how hack occurred ❌ Bring site back online before thorough cleaning ❌ Skip password changes ❌ Fail to harden security post-cleanup
Pro Tip: Keep a printed emergency response checklist with contact information (hosting support, security service, backup location, etc.) readily accessible. During an emergency, having a clear checklist prevents panic-driven mistakes.
How does website security affect Google rankings beyond blacklisting?
Security impacts SEO in multiple indirect ways:
1. Site performance degradation:
- Cryptominers consume server resources → slow page loads
- Spam scripts add unnecessary code → increased page weight
- DDoS attacks overwhelm server → downtime or extreme slowness
- Impact: Core Web Vitals scores tank, rankings drop
2. User experience destruction:
- Malware warnings create 90%+ bounce rates
- Redirects to spam sites frustrate users
- Pop-ups and spam ads ruin UX
- Slow loading (from security issues) increases bounce
- Impact: Google sees terrible engagement signals
3. Link profile contamination:
- Spam link injection creates toxic backlink profile
- Outbound spam links look like link schemes
- Footer/sidebar spam violates quality guidelines
- Impact: Manual penalties possible, algorithmic devaluation
4. Content quality degradation:
- Hidden spam text violates quality guidelines
- Keyword stuffing from spam injection
- Duplicate content from spam pages
- Content manipulation confuses topical relevance
- Impact: Quality algorithm demotions
5. Indexing issues:
- Spam pages waste crawl budget
- Redirect chains confuse crawlers
- Server errors from attacks prevent crawling
- robots.txt manipulation blocks important pages
- Impact: Important pages don’t get indexed/crawled
6. Trust signal destruction:
- Security warnings destroy click-through rates
- Blacklist status removes site from results entirely
- Browser warnings prevent visitors from accessing
- Reputation damage reduces branded searches
- Impact: Even after cleaning, recovery takes months
Real-world cascading failure example:
Day 1: Site infected with SEO spam malware
- 500 spam pages created
- Hidden spam links added to all posts
- Cryptominer installed
Day 7: Google notices anomalies
- Spam pages getting indexed
- Site speed degraded 60%
- Core Web Vitals failing
Day 14: Algorithm adjusts
- Rankings start dropping
- Traffic down 25%
- Bounce rate increased
Day 21: Manual review triggered
- Site added to blacklist
- “This site may be hacked” warning appears
- Traffic drops 95%
Day 30: Discovery and cleanup
- Malware removed
- Reconsideration submitted
- But damage is done:
- Lost 30 days of traffic
- Spam pages still in Google’s index
- Toxic links need disavowing
- Trust signals destroyed
Recovery takes 4-6 months to approach previous traffic levels.
All of this from inadequate security.
Pro Tip: Security isn’t just about preventing blacklisting—it’s about protecting your entire SEO ecosystem: performance, user experience, content quality, link profile, and trust signals. One security breach can damage all of these simultaneously.
For comprehensive WordPress security and SEO strategies, visit the complete WordPress SEO guide.
Final Thoughts: Your WordPress Security SEO Action Plan
Here’s what most WordPress site owners don’t realize until it’s too late: WordPress security SEO isn’t optional—it’s foundational.
You can have the world’s best content, perfect technical SEO, hundreds of quality backlinks, and flawless Core Web Vitals. But one security breach can obliterate all of it in 72 hours.
The harsh reality:
- 30,000+ websites are hacked daily (University of Maryland study)
- WordPress powers 43% of all websites, making it a massive target
- Average hack goes undetected for 197 days (IBM Security)
- 43% of hacked sites never fully recover their traffic (Sucuri)
But here’s the good news: The vast majority of WordPress hacks are completely preventable.
They’re not sophisticated zero-day exploits by elite hackers. They’re automated bots exploiting:
- Weak passwords (“admin” + “password123”)
- Outdated plugins with known vulnerabilities
- Missing security plugins
- No two-factor authentication
- Absent backups
The sites that get hacked are the ones that thought “it won’t happen to me.”
Your 30-day security implementation roadmap:
Week 1: Foundation
- Install Wordfence or equivalent security plugin
- Enable HTTPS/SSL site-wide
- Install backup plugin with daily schedule
- Change “admin” username if applicable
- Generate strong unique passwords
Week 2: Hardening
- Enable two-factor authentication
- Update WordPress core, plugins, themes
- Delete unused plugins and themes
- Set up uptime and security monitoring
- Test backup restoration
Week 3: Advanced Protection
- Configure firewall settings
- Limit login attempts
- Change default login URL
- Set proper file permissions
- Review and limit user access
Week 4: Maintenance Systems
- Create security maintenance schedule
- Set up automatic updates where possible
- Document security procedures
- Establish recovery plan
- Review and optimize
The investment required:
- Time: 4-6 hours over 30 days
- Money: $0-200 (free tools work, premium better for serious sites)
- Mental energy: Minimal once set up
What you’re protecting:
- Traffic value: $5,000-100,000+ annually
- Brand reputation: Years to build, hours to destroy
- Customer trust: Irreplaceable
- Your sanity: Recovering from hacks is nightmare fuel
- Your business: Some sites never recover
The ROI of security is infinite if it prevents one catastrophic hack.
Remember:
- Security is not a one-time task—it’s an ongoing practice
- Free tools can provide adequate protection for smaller sites
- Premium tools ($100-200/year) are worth it for business sites
- Backups are your safety net—test them quarterly
- Updates are non-negotiable—apply them weekly
- Monitoring catches problems early—set up alerts
Start today. Not tomorrow. Not next week. Today.
Pick one action item from this guide and implement it right now. Then another tomorrow. Small consistent security improvements compound into comprehensive protection.
Your WordPress site is under constant attack. Right now, bots are probing for vulnerabilities. The question isn’t “will my site be targeted?” It’s “will my security stop them?”
Make sure the answer is yes.
Want to master every aspect of WordPress SEO including security, performance, content strategy, and technical optimization? The comprehensive WordPress SEO guide covers everything you need to dominate search results while keeping your site secure.
Your rankings are waiting to be protected. Your traffic is waiting to stay safe. Your business is waiting for you to take security seriously.
Don’t wait for a hack to learn this lesson. Start securing your WordPress site now.
About the Author: This guide was created by SEO and security practitioners who’ve helped hundreds of WordPress sites recover from hacks and, more importantly, prevent them in the first place. We’ve seen the devastation security breaches cause—and the relief proper security provides.
Last Updated: October 2025
Additional Security Resources:
- WordPress.org Security Guide – Official security documentation
- WPScan Vulnerability Database – Track WordPress security issues
- Wordfence Intelligence – Real-time threat intelligence
- Sucuri Blog – Security news and research
- OWASP Top 10 – Web application security risks
Security Tools Referenced:
- Wordfence (Free/Premium $119/yr) – Comprehensive security plugin
- Sucuri Security (Free/Premium $199+/yr) – Website firewall and protection
- UpdraftPlus (Free/Premium $70/yr) – Backup and restoration
- Cloudflare (Free/Pro $20/mo) – CDN and security layer
- MalCare ($99+/yr) – Automatic malware removal
Emergency Security Contacts:
- Sucuri Emergency Response – sucuri.net/website-security/emergency-response
- Wordfence Premium Support – wordfence.com/products/wordfence-care/
- GoDaddy Website Security – godaddy.com/web-security
- SiteLock Emergency Response – sitelock.com/products/emergency-response/
Your WordPress security starts now. Take action before you become another hack statistic.