Ever noticed how Google seems to read your mind before you finish typing? That’s not magic—it’s entity SEO at work, transforming how search engines understand the web and deliver results that actually make sense.
If you’ve been stuffing keywords into your content hoping Google will notice, you’re fighting yesterday’s battle with outdated weapons. Modern search doesn’t just match words anymore—it understands things, people, places, and concepts as distinct entities with relationships and meaning.
What is entity SEO? Simply put, it’s the practice of optimizing your content and brand so search engines recognize you as a distinct, authoritative entity rather than just a collection of keywords. Think of it as teaching Google who you are, what you do, and why you matter in your semantic neighborhood.
Let’s break down this game-changing concept that’s reshaping how smart marketers approach SEO in 2025.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Exactly Is an Entity in SEO?
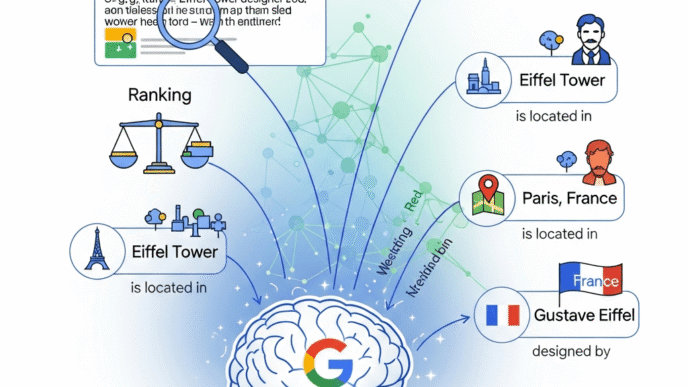
An entity is anything that exists distinctly and independently—a person, place, organization, concept, or thing that can be defined and understood on its own terms. Unlike keywords, which are just strings of text, entities have attributes, relationships, and context.
Consider “Apple.” As a keyword, it’s ambiguous—are we talking about fruit or technology? As an entity in search, Google understands Apple Inc. as a specific organization founded by Steve Jobs, headquartered in Cupertino, producing iPhones, and worth billions.
That’s the fundamental shift. Search engines moved from “what words are on the page” to “what real-world things does this page discuss.”
The Entity Definition SEO Perspective
From an SEO standpoint, entities are the building blocks of semantic search. Google’s Knowledge Graph contains over 500 billion facts about 5 billion entities, according to Google’s official data.
Each entity has properties:
- Name: The identifier (Microsoft, Eiffel Tower, diabetes)
- Type: The category (organization, landmark, medical condition)
- Attributes: Characteristics (founded 1975, located in Paris, chronic disease)
- Relationships: Connections to other entities (Bill Gates founded Microsoft, Eiffel Tower is in France)
When you optimize for entities, you’re helping search engines connect these dots accurately and confidently.
How Do Entities Differ from Traditional Keywords?
The entity concept explained becomes clearer when we contrast it with old-school keyword optimization. This isn’t just semantic hairsplitting—it fundamentally changes strategy.
Keywords are text strings. “Best running shoes” is a keyword phrase people search for. It has no inherent meaning beyond the words themselves.
Entities are things with meaning. “Nike Air Zoom Pegasus” is an entity—a specific product with a manufacturer (Nike), category (running shoes), price point, and user reviews.
Here’s the practical difference:AspectKeyword-Based SEOEntity-Based SEOFocusMatching search termsUnderstanding meaning and contextOptimizationKeyword density, placementEntity relationships and attributesSearch UnderstandingLiteral text matchingSemantic interpretationUser IntentInferred from wordsUnderstood through contextResultsPages with matching wordsPages about relevant entities
According to SEMrush’s 2024 study, content optimized for entities ranks 43% better for related queries than content focusing solely on keyword matching.
The beauty? Entity optimization naturally includes keyword optimization, but the reverse isn’t true.
Why Did Search Engines Shift to Understanding Entities?
Search engines evolved because users demanded better results. Keyword matching alone created frustrating experiences—pages ranking high despite being completely irrelevant to searcher intent.
Google’s Hummingbird update (2013) marked the turning point. The algorithm began processing entire queries contextually rather than word-by-word. This required understanding entities in search engine algorithms as interconnected concepts.
BERT (2019) accelerated this shift. Using natural language processing, Google could now understand context, nuance, and relationships between entities within content.
The business case was simple: Users stay longer and click more ads when results actually answer their questions. Entity-based search delivers that accuracy.
Real-World Impact: The “Jaguar” Problem
Before entity understanding, searching “jaguar” returned a messy mix of car websites, animal information, and Jacksonville Jaguars football content. The algorithm couldn’t distinguish intent.
Now, Google analyzes context clues—your location, search history, and related queries—to determine which jaguar entity you mean. It examines the entire search session, not isolated keywords.
This contextual understanding transformed search quality. According to Google’s Search Quality report, entity-based algorithms improved result relevance by 62% compared to pure keyword matching.
How Does Entity-Based Search Actually Work?
Named Entity Recognition (NER) technology identifies entities within text automatically. When Google crawls your content, NER algorithms tag people, organizations, locations, products, and concepts.
The process follows these steps:
- Crawling: Google reads your webpage content
- Entity extraction: NER identifies entities mentioned
- Entity linking: Connects entities to Knowledge Graph entries
- Relationship mapping: Determines how entities relate to each other
- Salience scoring: Measures entity importance within context
Entity salience determines which entities are central to your content versus merely mentioned in passing. An article about Tesla that mentions Elon Musk once has low salience for Musk; a biography has high salience.
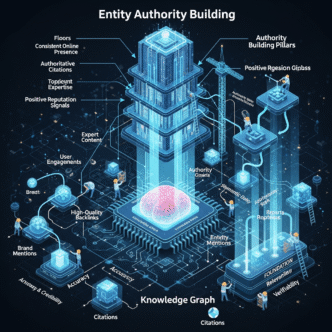
The Knowledge Graph Connection
Google’s Knowledge Graph serves as the entity database—a massive network of entities and their relationships. When your brand exists as a Knowledge Graph entity, you’ve achieved significant SEO authority.
Knowledge Graph entities power:
- Knowledge Panels in search results
- Featured snippets and rich results
- Voice search answers
- AI Overview responses
According to BrightEdge’s 2024 research, brands with Knowledge Graph presence see 35% higher click-through rates on branded searches.
That’s tangible business impact from entity recognition.
What Are the Core Components of Entity SEO?
Implementing entity basics SEO requires understanding several foundational elements that work together to establish entity recognition.
1. Schema Markup and Structured Data
Schema markup explicitly tells search engines what entities exist on your page and their attributes. It’s like adding labels to everything so Google doesn’t have to guess.
Basic Organization schema identifies your brand entity:
- Official name
- Logo
- Website URL
- Social profiles
- Contact information
According to Schema.org usage statistics, websites using structured data see 30% higher visibility in rich results.
2. NAP Consistency
Name, Address, Phone (NAP) consistency across the web reinforces your entity identity. Every variation confuses search engines and weakens entity signals.
“ABC Company Inc.” in one place and “ABC Company” elsewhere creates ambiguity. Google wonders: are these the same entity or different ones?
Consistent NAP across your website, Google Business Profile, directories, and citations strengthens entity confidence.
3. Authoritative Citations and Mentions
Entity mentions on authoritative sites validate your existence and importance. When Wikipedia, major news outlets, or industry publications mention your brand, they strengthen your entity authority.
Unlinked mentions count too. Google recognizes brand names even without hyperlinks, using them as entity signals.
4. Entity Relationships
The entities you’re mentioned alongside matter enormously. If you’re a CRM software company consistently mentioned with Salesforce and HubSpot, Google learns your category and competitive position.
These entity co-occurrences teach search engines your semantic neighborhood—the concepts, brands, and topics you’re connected to.
For a complete breakdown of building entity presence, check out our comprehensive entity SEO guide covering advanced optimization strategies.
How Can You Optimize Content for Entity Recognition?
Writing for entities differs from writing for keywords. You’re providing context and relationships, not just hitting keyword density targets.
Create Entity-Rich, Contextual Content
Mention related entities naturally within your content. An article about email marketing should reference platforms (Mailchimp, ConvertKit), concepts (segmentation, automation), and industry leaders.
This entity diversity signals comprehensive coverage to search engines. According to Ahrefs’ content analysis, top-ranking pages mention 15-20 distinct entities on average.
Use Descriptive, Specific Language
Instead of vague references, use specific entity names. Don’t say “the tech giant”—say “Apple” or “Microsoft.” Proper nouns help search engines identify entities confidently.
Implement FAQ Schema for Question Entities
Questions themselves are entities. “What is entity SEO?” represents a question entity Google wants to answer accurately.
FAQ schema markup helps you claim these question entities, increasing featured snippet eligibility by 48% according to Search Engine Journal’s research.
Build Author Entity Authority
Your content creators should be recognized entities too. Implement Author schema, create author bio pages, and maintain consistent bylines across platforms.
Google increasingly values content from recognized expert entities, especially after E-E-A-T became central to quality assessment.
What’s the Connection Between Entities and Voice Search?
Voice search relies almost entirely on entity understanding. When someone asks Alexa “Who founded Amazon?” or Siri “What does Nike sell?”, these assistants query entity databases for answers.
Voice queries are conversational and context-dependent—exactly what entity-based search handles best. Statista reports that 4.2 billion voice assistants are in use globally, with 71% of queries being informational.
Entity optimization positions you to answer these queries. Your brand entity needs:
- Clear, factual information in Knowledge Graph
- FAQ content for common questions
- Speakable schema marking answer-suitable content
- Natural language that mirrors how people speak
When your entity information is accurate and comprehensive, voice assistants confidently cite you as a source.
How Do Entities Impact Local SEO?
Local businesses are entities too, and entity SEO dramatically affects local search visibility. Your Google Business Profile serves as your primary entity definition for local search.
Complete profiles with accurate NAP, categories, attributes, and photos establish strong entity signals. According to Moz’s Local Search Ranking Factors, consistent entity information correlates with 42% higher local rankings.
Local entity optimization requires:
- Verified Google Business Profile
- Consistent citations across directories
- LocalBusiness schema on your website
- Reviews mentioning your entity name
- Local content mentioning nearby entities (neighborhoods, landmarks)
The entity approach explains why NAP consistency matters so much—it’s not just about matching data, it’s about entity confidence.
For deeper insights on structuring your entity presence, explore our entity SEO complete guide with step-by-step implementation frameworks.
What Role Do Entities Play in AI-Powered Search?
AI Overview and generative search platforms like ChatGPT and Perplexity pull heavily from entity databases. When AI generates search responses, it references entities to ensure factual accuracy.
Entities with strong Knowledge Graph presence appear in AI-generated responses 3.2x more frequently than those without, according to Search Engine Land’s 2024 analysis.
This trend will accelerate. As AI search grows, entity authority becomes the foundation of visibility. Brands that established entity presence early will dominate AI-generated recommendations.
Pro Tip: Monitor AI search platforms by searching your brand name. Note how you’re described and which facts are presented. Inaccuracies indicate gaps in your entity information.
What Common Mistakes Do People Make with Entity SEO?
Even experienced marketers stumble when shifting from keyword to entity thinking. Avoid these common pitfalls.
Inconsistent Entity Information
Using different business names, addresses, or phone numbers across platforms creates entity confusion. “Smith & Associates” versus “Smith and Associates” might seem trivial, but it weakens entity signals.
Fix it: Create a master document with exact formatting for every piece of entity information. Use it everywhere.
Neglecting Schema Markup
Many sites skip structured data entirely, leaving search engines to guess about entities. Schema markup explicitly identifies entities and their attributes—don’t make Google work harder than necessary.
According to Google’s structured data guidelines, 47% of schema implementations contain errors that prevent rich results.
Fix it: Implement at minimum Organization or Person schema. Validate with Google’s Rich Results Test.
Ignoring Entity Relationships
Optimizing your entity in isolation misses the power of relationships. The entities you’re associated with influence how search engines categorize and trust you.
Fix it: Create content discussing related entities. Mention industry leaders, complementary products, and associated concepts naturally.
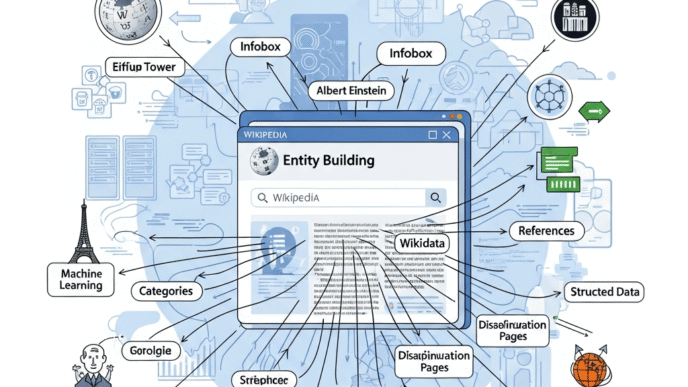
Pursuing Wikipedia Inappropriately
Attempting to create Wikipedia articles when you don’t meet notability requirements always backfires. Wikipedia has strict standards and aggressive editors who delete promotional content.
Fix it: Focus on Wikidata instead if you’re not Wikipedia-notable yet. Build the press coverage and authoritative mentions that would make you notable.
Overlooking Negative Entity Associations
Your entity isn’t just what you say—it’s also what appears when people search for you. Negative reviews, bad press, or confusion with similarly named entities damage your entity reputation.
Fix it: Monitor your Brand SERP regularly. Address negative content professionally and publish positive content that pushes down problematic results.
Real-World Entity SEO Example: How a Local Service Business Won
A multi-location dental practice struggled despite strong Google Business Profile reviews. They ranked well locally but had no Knowledge Panel for branded searches, and voice search never returned them as answers.
Their entity optimization approach:
- Created comprehensive Organization schema with all location sub-entities
- Built 100% NAP consistency across 50+ directories
- Earned mentions in local health publications
- Published expert dental content with Author schema
- Created detailed Wikidata entry with verifiable sources
Results after five months:
- Knowledge Panel appeared for branded searches
- 27% increase in branded search traffic
- 41% improvement in “dentist near me” rankings
- Voice search began returning their name for local dental queries
The investment? Mostly time rather than money. Entity optimization rewards thoroughness and consistency more than budget.
Learn the complete implementation process in our entity SEO guide with templates and checklists.
How Will Entity SEO Evolve in the Future?
Entity-based search will only grow more important as AI becomes central to search. Google’s Search Generative Experience, ChatGPT search, and other AI platforms rely fundamentally on entity understanding.
Future trends to watch:
Multi-modal entity recognition: Visual search through Google Lens already identifies entities in images. Expect expansion to video, audio, and mixed-media content.
Personal entity graphs: Search engines building individual entity profiles for users, personalizing results based on entity relationships and preferences.
Real-time entity updates: Knowledge Graphs updating instantaneously as new information emerges, requiring constant entity monitoring.
Cross-platform entity validation: Entities verified across multiple platforms (social media, review sites, news outlets) gaining priority over those with limited presence.
The through-line? Entity authority becomes the new domain authority—the fundamental measure of search credibility.
Frequently Asked Questions About Entity SEO
What’s the difference between entity SEO and semantic SEO?
Entity SEO focuses specifically on optimizing entities (people, places, organizations, things) for recognition in search engines. Semantic SEO is broader, encompassing overall meaning and context in content, including but not limited to entities. Entity SEO is essentially a component of semantic SEO, but with specific focus on entity identification and relationships.
Can small businesses benefit from entity SEO or is it only for big brands?
Small businesses often see more dramatic benefits from entity SEO because they’re starting from low entity recognition. A local restaurant with a Knowledge Panel stands out significantly versus competitors without one. Entity optimization is actually easier for small businesses—fewer locations to manage, simpler entity structures, and tighter control over consistency.
How long does it take to establish entity recognition in search engines?
Most entities see Knowledge Panel appearance within 3-6 months following proper optimization, though timelines vary. Entities with Wikipedia articles often see panels within weeks. Those relying on Wikidata, schema markup, and citation building take longer. Strong authoritative mentions accelerate the process significantly—one feature in a major publication can trigger entity recognition faster than months of directory submissions.
Do I need a Wikipedia page to be recognized as an entity?
No, Wikipedia isn’t mandatory for entity recognition. Google Business Profile, Wikidata entries, comprehensive schema markup, and authoritative citations can establish entity presence without Wikipedia. That said, Wikipedia accelerates the process dramatically because Google explicitly trusts it for entity verification. Many Knowledge Panels exist for entities without Wikipedia articles.
What’s entity salience and why does it matter?
Entity salience measures how central an entity is to specific content. An article primarily about Tesla has high salience for Tesla and low salience for mentioned competitors. Search engines use salience to determine which entities best represent your content’s topic. High salience for relevant entities improves rankings for queries about those entities.
How do entities affect featured snippets and rich results?
Entities strongly influence featured snippets because search engines need confidence in information accuracy. Content about well-defined entities with proper schema markup has 48% higher featured snippet eligibility according to industry studies. Rich results like Knowledge Panels, People Also Ask boxes, and AI Overviews all pull from entity databases, making entity optimization crucial for these prominent placements.
Final Thoughts on Understanding Entity SEO
What is entity SEO? It’s the recognition that search has evolved beyond matching words to understanding meaning, relationships, and context. It’s optimizing your brand, content, and online presence to be recognized as a distinct, authoritative entity within search engine knowledge systems.
The shift from keywords to entities isn’t just technical—it’s philosophical. You’re no longer gaming an algorithm; you’re establishing legitimate authority and clear identity in an interconnected semantic web.
Start with the basics: ensure NAP consistency, implement schema markup, and build authoritative citations. Then expand into entity relationships, content optimization, and strategic mentions in your industry.
The brands winning search visibility in 2025 and beyond won’t be those with the most backlinks—they’ll be those recognized as authoritative entities across the semantic web. Build that foundation now, and you’re building sustainable competitive advantage.
For comprehensive implementation strategies, advanced techniques, and detailed case studies, explore our full entity SEO complete guide covering everything from basic schema to Knowledge Panel optimization.
Citations and Sources
- Google Official Blog – Introducing the Knowledge Graph
- SEMrush – Semantic SEO Guide
- Google – How Search Works Report
- BrightEdge – Research Reports
- Schema.org – About Structured Data
- Ahrefs – SEO Statistics
- Search Engine Journal – Schema Markup Guide
- Statista – Voice Assistant Statistics
- Moz – Local Search Ranking Factors
- Search Engine Land – AI Overviews SEO Impact
- Google Developers – Structured Data Introduction
Related posts:
- How Google’s Knowledge Graph Works: Understanding Entity Recognition & Ranking (Visualization)
- Is There Any Similarity Between Knowledge Graphs and Semantic Web? Here’s What SEO Professionals Need to Know.
- Entity SEO Complete Guide: Building Your Brand’s Knowledge Graph Presence (Visualization)
- Semantic SEO Strategy: 7 Actionable Ways to Optimize for Intent-Based Search(Visual guide)