Your online store looks beautiful. Your products are amazing. Your prices are competitive. But somehow, you’re invisible on Google while your competitors are raking in organic traffic.
Here’s the brutal reality: you could have the best products in the world, but if your technical SEO for ecommerce is broken, Google can’t crawl, index, or rank your pages properly. It’s like having a Ferrari with a faulty engine—looks great, goes nowhere.
This guide will walk you through how to fix technical SEO issues on ecommerce sites that are silently killing your rankings. No confusing jargon, no unnecessary complexity—just the essential fixes that actually move the needle.
Let’s turn your technical SEO from a roadblock into a rocket booster.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhy Technical SEO for Ecommerce Is More Critical Than You Think
Picture this: you’ve spent thousands on product photography, written perfect descriptions, and built a gorgeous site. Then Google’s crawlers show up and can’t find half your pages because of technical issues you didn’t even know existed.
Technical SEO is the foundation everything else sits on. According to SEMrush, technical issues affect 74% of ecommerce websites, with the average site having 20+ critical errors. These aren’t minor problems—they’re actively preventing you from ranking.
Think of ecommerce technical optimization as the plumbing in your house. When it works, nobody notices. When it breaks, everything backs up and nothing functions properly. The difference? Most people notice broken plumbing immediately. Broken technical SEO silently costs you thousands in lost traffic.
The good news? Most technical issues are fixable once you know what to look for. And since most online stores ignore this stuff, fixing it gives you an instant competitive advantage.
What Are the Most Common Technical SEO Issues Killing Ecommerce Sites?
Before we dive into solutions, let’s identify the usual suspects. These are the technical problems that plague most online stores:
Site Speed Problems: Your pages load slower than molasses in January, causing visitors (and Google) to bounce.
Crawlability Issues: Google’s bots can’t access important pages because of robots.txt problems, broken links, or messy site structure.
Duplicate Content: Multiple URLs showing the same content (product variations, pagination, filters) confuse search engines.
Mobile Issues: Your site looks terrible or doesn’t function on phones, where 60%+ of traffic happens.
Indexing Problems: Important pages aren’t in Google’s index, or useless pages are wasting your crawl budget.
Broken Structured Data: Schema markup is missing, incorrectly implemented, or outdated.
HTTPS and Security Issues: Mixed content warnings, expired certificates, or lack of SSL entirely.
The average ecommerce site has 3-7 of these issues simultaneously. Let’s fix them systematically.
How Do You Conduct an Ecommerce SEO Audit to Find Technical Issues?
You can’t fix what you can’t see. An ecommerce SEO audit reveals exactly what’s broken and how to fix it.
Step 1: Crawl Your Site Like Google Does
Use crawling tools to see your site through Google’s eyes:ToolBest ForPriceScreaming Frog SEO SpiderComprehensive technical auditsFree (500 URLs) / $259/yearAhrefs Site AuditAll-in-one technical analysis$99+/monthSEMrush Site AuditTechnical health monitoring$119+/monthGoogle Search ConsoleGoogle’s actual crawl dataFree
Pro Tip: Start with Screaming Frog’s free version for stores under 500 pages. Export the data and prioritize fixing critical errors (red flags) before warning issues (yellow flags). I’ve found that fixing just the top 10 critical errors can boost rankings by 20-30% within weeks.
Step 2: Check Google Search Console
Google Search Console shows you exactly what Google sees:
- Coverage report: Which pages are indexed vs. excluded
- Core Web Vitals: Speed and user experience metrics
- Mobile Usability: Phone-specific issues
- Security Issues: Malware or hacking problems
Set aside 30 minutes weekly to review Search Console. Catching issues early prevents disasters.
Step 3: Test Mobile Experience
Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test on key pages:
- Homepage
- Top 5 category pages
- Top 10 product pages
- Checkout flow
If any fail, that’s costing you rankings AND sales.
Step 4: Analyze Site Speed
Run Google PageSpeed Insights on the same pages. Target these benchmarks:
- Desktop: 90+ score
- Mobile: 75+ score (harder to achieve)
- LCP: Under 2.5 seconds
- INP: Under 200ms
- CLS: Under 0.1
For comprehensive strategies on technical optimization, check our complete ecommerce SEO guide.
How to Fix Site Speed Issues on Ecommerce Websites
Site speed optimization is the #1 technical issue affecting ecommerce sites. Research from Portent shows conversion rates drop 0.3% for every second of load time.
If your site takes 5 seconds to load instead of 2, you’re losing massive amounts of revenue. Every. Single. Day.
Optimize Images (The Biggest Culprit)
Images typically account for 50-70% of page weight. Here’s improving site speed for ecommerce websites 101:
Compression:
- Use tools like TinyPNG or Squoosh
- Target: Under 200KB per image
- Maintain quality: 80-85% JPEG compression
Format:
- Switch to WebP (20-30% smaller than JPEG)
- Keep PNG fallbacks for older browsers
- Avoid GIFs for animations (use MP4 instead)
Lazy Loading:
- Load images only as users scroll to them
- Saves bandwidth and improves initial load time
- Built into modern platforms, or use plugins
Proper Sizing:
- Don’t serve 4000px images when displaying 400px
- Use responsive images with srcset attribute
- Generate multiple sizes for different devices
Pro Tip: Implement a CDN (Content Delivery Network) like Cloudflare or Amazon CloudFront. This serves images from servers closest to your visitors, dramatically reducing load times globally. I’ve seen CDNs cut load times by 40-60% for international traffic.
Minimize JavaScript and CSS
Bloated code slows everything down. Most ecommerce platforms load unnecessary scripts.
JavaScript fixes:
- Defer non-critical scripts (load after page content)
- Remove unused plugins and integrations
- Minify code (compress file sizes)
- Use async loading for third-party scripts
CSS optimization:
- Inline critical CSS (styles needed immediately)
- Defer non-critical stylesheets
- Remove unused CSS rules
- Minify and compress
Real example: An online furniture store removed 7 unused plugins, minified their CSS, and deferred non-critical JavaScript. Page load time dropped from 6.2 seconds to 2.1 seconds. Organic traffic increased 34% within 8 weeks.
Upgrade Your Hosting
Cheap shared hosting kills site speed. If you’re doing $10k+/month, you’ve outgrown budget hosting.
Hosting progression:
- Shared hosting: $5-20/month (for new stores under $1k/month)
- VPS/Cloud hosting: $50-200/month (for $5k-50k/month stores)
- Managed ecommerce hosting: $200-500/month (for $50k+ stores)
- Enterprise solutions: Custom pricing (for large operations)
Pro Tip: Don’t upgrade hosting unless you’ve optimized images and code first. Bad code will be slow on any server. Fix the basics, then upgrade if needed.
What’s the Optimal Ecommerce Site Structure for SEO?
Ecommerce site structure determines how easily Google crawls your store and how quickly customers find products. Get this wrong and you’re fighting an uphill battle.
The Ideal Site Architecture
Follow this hierarchy for crawlability for online stores:
Homepage
├── Category 1
│ ├── Subcategory 1A
│ │ ├── Product 1
│ │ ├── Product 2
│ │ └── Product 3
│ └── Subcategory 1B
├── Category 2
└── Category 3
Golden rules:
- Every page accessible within 3 clicks from homepage
- Logical groupings (by product type, use case, or audience)
- Consistent URL structure
- Clear parent-child relationships
URL Structure Best Practices
Your URLs should be clean, descriptive, and hierarchical:
❌ Bad: yourstore.com/products?id=12345&cat=8 ✅ Good: yourstore.com/mens-shoes/running-shoes/nike-air-zoom-pegasus
URL optimization rules:
- Include primary keywords naturally
- Use hyphens, not underscores
- Keep it short (3-5 words ideal)
- Show hierarchy (category/subcategory/product)
- Avoid unnecessary parameters
Internal Linking Strategy
Strategic internal links help Google discover and understand your pages:
From Homepage:
- Link to main categories
- Feature bestsellers or seasonal products
- Include navigation menu
From Category Pages:
- Link to subcategories
- Feature products within category
- Cross-link related categories
From Product Pages:
- Link to related products
- Link back to parent category
- Cross-sell complementary items
Pro Tip: Use descriptive anchor text with keywords. Instead of “click here,” use “shop waterproof hiking boots” or “explore organic cotton t-shirts.” This gives Google context about the linked page.
Learn more about building an effective site structure in our ecommerce SEO ultimate guide.
How to Handle Duplicate Content Issues on Ecommerce Sites
Duplicate content is the plague of ecommerce. Product variations, filters, pagination, and sorting options create dozens of URLs with identical content.
The Canonical Tag Solution
Canonical tags tell Google which version of similar pages is the “master” copy.
When to use canonicals:
- Product variations (different colors, sizes)
- Filtered category pages (price ranges, brands)
- Paginated pages (page 2, 3, 4 of results)
- HTTP vs HTTPS versions
- WWW vs non-WWW versions
Example: Your blue shirt exists at:
/mens-shirts/cotton-tshirt-blue/mens-shirts/cotton-tshirt?color=blue/sale-items/cotton-tshirt-blue
Add this to the variation pages:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://yourstore.com/mens-shirts/cotton-tshirt-blue" />
Parameter Handling in Search Console
Tell Google which URL parameters to ignore:
Common ecommerce parameters to configure:
?color=(product variations)?sort=(sorting options)?page=(pagination)?sessionid=(tracking codes)
In Search Console → Settings → URL Parameters, specify how Google should handle each parameter.
Product Variation Strategy
You have a shirt in 5 colors and 4 sizes. That’s 20 potential combinations. Do you create 20 pages?
Option 1: Single Page with Selectors (Recommended)
- One URL for base product
- Dropdowns/swatches for variations
- Canonical tags if variations have separate URLs
- Less duplicate content risk
Option 2: Separate Pages with Canonicals
- Individual URLs for major variations (colors)
- Canonical tags pointing to primary version
- Unique content highlighting each variation
- More work but can target more keywords
Pro Tip: For minor variations (sizes), always use Option 1. For significantly different products (colors that appeal to different audiences), Option 2 works if you write genuinely unique content. Never create separate pages with identical descriptions.
What Are the Most Critical Mobile SEO Issues for Ecommerce?
Over 60% of ecommerce traffic is mobile. If your mobile experience sucks, you’re literally turning away the majority of potential customers.
Mobile-First Indexing
Google now primarily uses your mobile site for rankings. Desktop performance matters less than it used to.
Mobile optimization essentials:
Responsive Design:
- Site adapts to any screen size
- Images scale properly
- Text readable without zooming
- No horizontal scrolling
Touch-Friendly Elements:
- Buttons minimum 44×44 pixels
- Adequate spacing between taps
- Easy-to-use dropdown menus
- No Flash or unsupported plugins
Simplified Navigation:
- Hamburger menus for space
- Sticky “Add to Cart” buttons
- Easy-to-find search
- Streamlined checkout
Common Mobile Technical Issues
Problem 1: Viewport Not Configured Missing or incorrect viewport meta tag makes sites unusable on mobile.
Fix:
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
Problem 2: Content Wider Than Screen Fixed-width elements cause horizontal scrolling.
Fix: Use relative widths (width: 100% instead of width: 1200px)
Problem 3: Unplayable Content Flash, certain videos, or unsupported formats don’t work on mobile.
Fix: Use HTML5 video, avoid Flash entirely
Pro Tip: Test on actual devices, not just Chrome’s device emulator. Real-world testing catches issues simulators miss—like tiny tap targets, forms triggering wrong keyboards, or slow loading on 4G. I keep old phones around specifically for testing.
How to Fix Crawlability and Indexing Issues
Google can’t rank pages it can’t find or access. Common technical SEO mistakes ecommerce stores make revolve around crawlability.
Robots.txt Problems
Your robots.txt file controls what search engines can access. A misconfigured file can block your entire site.
Check your robots.txt: yourstore.com/robots.txt
Common mistakes:
# WRONG - Blocks everything
User-agent: *
Disallow: /
# WRONG - Blocks all Google
User-agent: Googlebot
Disallow: /
# RIGHT - Blocks only admin/cart
User-agent: *
Disallow: /admin/
Disallow: /cart/
Disallow: /checkout/
Pro Tip: Use Google Search Console’s robots.txt Tester to verify your file isn’t blocking important pages. I’ve seen stores accidentally block their entire product catalog because someone added Disallow: /products/ years ago.
XML Sitemap Optimization
Sitemaps tell Google which pages to crawl and how often they change.
Sitemap best practices:
- Include all important pages (products, categories)
- Exclude filtered/parameter URLs (use canonicals instead)
- Update automatically when products added/removed
- Submit to Search Console
- Keep under 50MB or 50,000 URLs (create multiple if needed)
Sitemap structure for ecommerce:
sitemap_index.xml (main sitemap)
├── products.xml (all product pages)
├── categories.xml (category pages)
├── blog.xml (content pages)
└── pages.xml (static pages)
Fixing Crawl Budget Waste
Large ecommerce sites have thousands of pages. Google won’t crawl them all frequently, so prioritize what matters.
Pages wasting crawl budget:
- Filtered category pages with faceted navigation
- Search result pages
- Session ID URLs
- Pagination pages (use rel=”next/prev” or canonical)
- Old blog posts with no traffic
Fix: Use robots.txt, noindex tags, or canonicals to prevent Google from wasting time on low-value pages.
Orphan Page Detection
Orphan pages have no internal links pointing to them. Google struggles to discover them.
Find orphans with Screaming Frog:
- Crawl your site
- Compare to XML sitemap
- Pages in sitemap but not crawl = orphans
Fix: Add internal links from relevant category or product pages.
For more on site structure and crawlability, explore our comprehensive ecommerce SEO guide.
How to Implement Schema Markup for Ecommerce Sites
Structured data (schema markup) helps Google understand your content and display rich results—those eye-catching search results with stars, prices, and availability.
Essential Schema Types for Ecommerce
Product Schema:
{
"@context": "https://schema.org/",
"@type": "Product",
"name": "Nike Air Zoom Pegasus 40",
"image": "https://yourstore.com/images/nike-pegasus.jpg",
"description": "Lightweight running shoes...",
"brand": {
"@type": "Brand",
"name": "Nike"
},
"offers": {
"@type": "Offer",
"price": "139.99",
"priceCurrency": "USD",
"availability": "https://schema.org/InStock"
},
"aggregateRating": {
"@type": "AggregateRating",
"ratingValue": "4.7",
"reviewCount": "234"
}
}
What to include:
- Product name
- Image URL
- Description
- Brand
- Price and currency
- Availability status
- Ratings and reviews (if applicable)
- SKU or product ID
Breadcrumb Schema: Helps Google understand site hierarchy and shows breadcrumbs in search results.
Organization Schema: Business information appearing in knowledge panels.
FAQ Schema: Common questions displayed directly in search results.
Testing Schema Markup
Use Google’s Rich Results Test to validate implementation.
Common schema errors:
- Missing required fields
- Incorrect data types (text instead of number)
- Outdated schema.org vocabulary
- Mismatched information (schema says “in stock” but page says “sold out”)
Pro Tip: Most ecommerce platforms have plugins or apps that add schema automatically (like Yoast for WordPress, or built-in features in Shopify). Don’t code it manually unless necessary. The key is ensuring accuracy—schema data must match visible page content.
What HTTPS and Security Issues Affect Ecommerce SEO?
Security isn’t optional for ecommerce. Google explicitly uses HTTPS as a ranking factor, and customers won’t trust a non-secure checkout.
SSL Certificate Implementation
Every ecommerce site needs an SSL certificate (the padlock icon in the browser).
SSL checklist:
- [ ] Certificate installed and active
- [ ] All pages load via HTTPS
- [ ] HTTP redirects to HTTPS (301 redirects)
- [ ] Update internal links to HTTPS
- [ ] Fix mixed content warnings
- [ ] Update canonical tags to HTTPS
- [ ] Update XML sitemap to HTTPS URLs
Common SSL issues:
Mixed Content Warnings: HTTPS page loading HTTP resources (images, scripts, stylesheets).
Fix: Update all resource URLs to HTTPS or use protocol-relative URLs (//example.com/image.jpg)
Expired Certificates: SSL certificates expire annually. Set calendar reminders.
Chain Errors: Incomplete certificate chain causes browser warnings.
Fix: Work with your hosting provider to install the full certificate chain.
Security Best Practices
Regular Updates:
- Keep platform software updated (WordPress, Magento, Shopify, etc.)
- Update plugins and themes
- Patch security vulnerabilities promptly
Strong Passwords:
- Use password managers
- Enable two-factor authentication
- Limit admin access
Regular Backups:
- Daily automated backups
- Store backups off-server
- Test restoration process
Pro Tip: Use Cloudflare (free tier available) for additional security layer, DDoS protection, and CDN benefits. I’ve seen it prevent dozens of attacks on ecommerce stores while also improving load times.
How to Monitor and Maintain Technical SEO Health
Technical SEO checklist for online stores isn’t a one-time project—it requires ongoing monitoring.
Weekly Technical SEO Tasks
Every Monday morning:
- [ ] Check Google Search Console for new errors
- [ ] Review Core Web Vitals trends
- [ ] Monitor uptime (use tools like UptimeRobot)
- [ ] Check recent product pages for technical issues
- [ ] Verify important pages remain indexed
Monthly Technical SEO Tasks
First of each month:
- [ ] Full site crawl with Screaming Frog
- [ ] Analyze crawl budget usage
- [ ] Review mobile usability reports
- [ ] Test site speed on key pages
- [ ] Verify schema markup accuracy
- [ ] Check for broken links (internal and external)
Quarterly Technical SEO Tasks
Every 3 months:
- [ ] Comprehensive technical SEO audit
- [ ] Benchmark against competitors
- [ ] Update XML sitemaps
- [ ] Review and update robots.txt
- [ ] Analyze log files for crawl patterns
- [ ] Review redirect chains
Tools for Ongoing Monitoring
| Tool | Monitors | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Google Search Console | Indexing, errors, Core Web Vitals | Weekly |
| PageSpeed Insights | Site speed, performance | Weekly |
| Screaming Frog | Technical issues, broken links | Monthly |
| Ahrefs/SEMrush Site Audit | Overall technical health | Monthly |
| UptimeRobot | Site uptime and availability | Real-time |
Pro Tip: Set up automated email alerts in Google Search Console for critical issues—indexing problems, security issues, manual actions. Don’t wait to discover problems; get notified immediately so you can fix them before they impact rankings.
Real-World Technical SEO Case Study
Let’s look at a concrete example of how to fix technical SEO issues on ecommerce sites with real results.
The Business: Mid-sized fashion retailer, $5M annual revenue, 2,000 product pages
The Problem: Despite great products and competitive prices, organic traffic was stagnant. Competitors with inferior products were outranking them.
The Technical Audit Revealed:
- Average page load time: 8.3 seconds
- 847 broken internal links
- 312 pages blocked by robots.txt accidentally
- No schema markup on any products
- 1,200+ duplicate content issues from filters
- Mobile usability errors on 67% of pages
The Fix (Over 4 Months):
Month 1:
- Fixed robots.txt blocking issue (immediate 40% traffic increase)
- Implemented image optimization (reduced page size by 65%)
- Fixed 847 broken links
Month 2:
- Added canonical tags to all filtered pages
- Implemented product schema on all 2,000 products
- Upgraded hosting (reduced server response time by 70%)
Month 3:
- Completely redesigned mobile experience
- Fixed all mobile usability errors
- Implemented lazy loading for images
Month 4:
- Created separate XML sitemaps by content type
- Optimized internal linking structure
- Fixed remaining Core Web Vitals issues
The Results:
- Organic traffic increased 287%
- Page load time dropped to 2.1 seconds
- Mobile traffic increased 412%
- Conversion rate improved 23%
- Revenue from organic search grew 356%
Key Takeaway: They didn’t need new products or a site redesign. They fixed technical issues preventing Google from properly crawling, indexing, and ranking their existing pages. Technical SEO was the bottleneck holding everything back.
AI and Technical SEO: What’s Changing in 2025
AI is transforming how we approach technical SEO for ecommerce. Here’s what matters:
AI-Powered Auditing Tools
New tools use machine learning to:
- Predict which technical issues impact rankings most
- Automatically prioritize fixes by potential ROI
- Identify patterns across thousands of pages
- Suggest fixes based on successful implementations
Tools like Oncrawl and Botify now use AI to analyze log files and predict crawl behavior, helping large sites optimize crawl budget more effectively.
Automated Technical Monitoring
AI monitors technical health continuously:
- Detect new issues within minutes
- Alert when critical pages become unindexable
- Track Core Web Vitals trends automatically
- Identify crawl anomalies before they impact traffic
Voice Search Technical Requirements
With voice assistants gaining popularity, technical optimization now includes:
- Structured data for voice search results
- Fast mobile load times (voice users are impatient)
- HTTPS for all pages (voice assistants prioritize secure sites)
- Local business schema for “near me” queries
Pro Tip: While AI tools are powerful, they’re not magic. Use them to identify issues and prioritize fixes, but understand WHY each issue matters before implementing changes. Blindly following AI recommendations without context can create new problems.
Common Technical SEO Mistakes Ecommerce Stores Make
Even experienced store owners fall into these traps:
Mistake 1: Ignoring Mobile Completely
Testing only on desktop means you’re blind to issues affecting 60%+ of your traffic.
Fix: Test key pages on actual phones weekly. Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test and Search Console mobile reports.
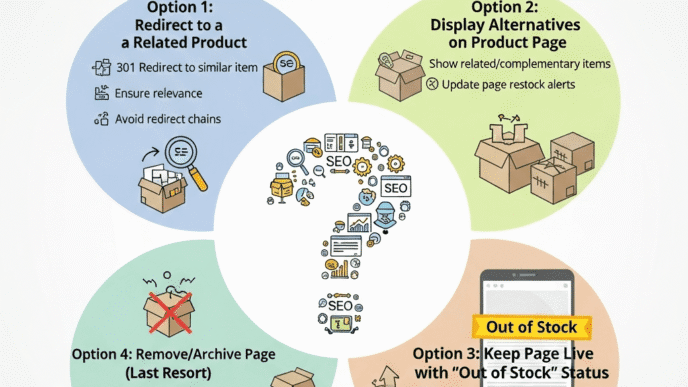
Mistake 2: Deleting Out-of-Stock Products
Removing products that rank well throws away valuable SEO equity.
Fix: Keep pages live with restock notifications and alternative product recommendations. Use 301 redirects only if permanently discontinued.
Mistake 3: Not Using Canonicals for Variations
Product filters and variations create duplicate content nightmares.
Fix: Implement canonical tags on all filtered, sorted, and variation pages pointing to the main version.
Mistake 4: Blocking Important Pages with Robots.txt
Accidentally blocking product catalogs or category pages is more common than you’d think.
Fix: Regularly test your robots.txt file and verify important pages aren’t blocked.
Mistake 5: Neglecting Core Web Vitals
Ignoring Google’s speed and UX metrics directly impacts rankings.
Fix: Monitor Core Web Vitals monthly and prioritize fixes for failing pages.
Mistake 6: Using Noindex Instead of Canonical
Noindex removes pages from Google entirely. Canonical consolidates duplicate signals.
Fix: Use canonical tags for duplicates, noindex only for truly worthless pages (cart, checkout, account pages).
Pro Tip: The biggest mistake is treating technical SEO as a one-time project. It’s ongoing maintenance. Set calendar reminders for regular audits and don’t let technical debt accumulate.
Expert Insights on Ecommerce Technical SEO
John Mueller, Google Search Advocate:
“For ecommerce sites, focus on site speed and mobile usability first. These aren’t just ranking factors—they directly impact conversion rates. A technically perfect site that loads slowly still loses to a fast site with minor technical flaws.”
Lily Ray, SEO Director:
The most overlooked technical SEO issue for ecommerce is internal linking. You could have perfect technical setup but if Google can’t easily discover and understand your page hierarchy through internal links, you’re leaving rankings on the table.
Barry Schwartz, Search Engine Roundtable:
I see ecommerce sites overthink technical SEO while ignoring basics. Fix your broken links, implement HTTPS correctly, ensure mobile works, and optimize speed. These fundamentals matter more than complex technical tweaks.”
These experts agree: ecommerce technical optimization starts with fundamentals. Master the basics before worrying about advanced techniques.
Technical SEO Checklist for Online Stores
Here’s your complete technical SEO checklist for online stores you can implement today:
Site Speed Optimization
- [ ] Compress all images under 200KB
- [ ] Implement lazy loading
- [ ] Enable CDN
- [ ] Minify JavaScript and CSS
- [ ] Remove unused plugins/scripts
- [ ] Upgrade hosting if needed
- [ ] Target Core Web Vitals benchmarks
Mobile Optimization
- [ ] Responsive design implemented
- [ ] All buttons minimum 44×44 pixels
- [ ] No horizontal scrolling
- [ ] Text readable without zooming
- [ ] Mobile-friendly test passes
- [ ] No unsupported content (Flash, etc.)
Site Structure
- [ ] All pages within 3 clicks of homepage
- [ ] Logical URL structure
- [ ] Clean, descriptive URLs
- [ ] Proper internal linking
- [ ] Breadcrumb navigation
Crawlability and Indexing
- [ ] Robots.txt configured correctly
- [ ] XML sitemap created and submitted
- [ ] No orphan pages
- [ ] Canonical tags on duplicate pages
- [ ] Proper parameter handling
- [ ] No broken links
Security
- [ ] SSL certificate installed
- [ ] All pages load via HTTPS
- [ ] HTTP→HTTPS redirects active
- [ ] No mixed content warnings
- [ ] Regular backups configured
Schema Markup
- [ ] Product schema on all products
- [ ] Organization schema
- [ ] Breadcrumb schema
- [ ] Review schema (if applicable)
- [ ] FAQ schema where appropriate
- [ ] Validated with Rich Results Test
Ongoing Monitoring
- [ ] Google Search Console connected
- [ ] Weekly error checks
- [ ] Monthly full site crawls
- [ ] Quarterly comprehensive audits
- [ ] Uptime monitoring active
For comprehensive implementation guidance, reference our ecommerce SEO guide.
Tools and Resources for Technical SEO
Bookmark these essential resources:
Free Tools:
- Google Search Console – Official crawl and index data
- Google PageSpeed Insights – Speed and Core Web Vitals
- Mobile-Friendly Test – Mobile usability
- Rich Results Test – Schema validation
- Screaming Frog – Free up to 500 URLs
Premium Tools:
- Ahrefs Site Audit – Comprehensive technical analysis
- SEMrush Site Audit – Technical health monitoring
- Sitebulb – Visual technical audits
- DeepCrawl/Lumar – Enterprise-level auditing
Educational Resources:
- Google Search Central – Official SEO documentation
- Web.dev – Performance and best practices
- Technical SEO guides at seoprojournal.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How often should I run a technical SEO audit?
Full comprehensive audit quarterly, but monitor weekly via Google Search Console. Run quick Screaming Frog crawls monthly to catch new issues early.
What’s the most important technical SEO factor for ecommerce?
Site speed and mobile usability. These impact both rankings AND conversions. A slow site loses customers even if it ranks well.
How long do technical SEO fixes take to impact rankings?
Quick wins (fixing robots.txt, broken links) show results in 1-2 weeks. Major improvements (site speed, mobile optimization) take 4-8 weeks. Patience required—Google needs to recrawl and reassess.
Do I need to know coding for technical SEO?
Basic HTML/CSS helps but isn’t required. Most platforms (Shopify, WordPress, BigCommerce) have plugins or apps handling technical optimization. Focus on understanding what needs fixing, then use tools or hire developers for implementation.
Should I noindex paginated category pages?
No. Use rel=”next” and rel=”prev” (though Google now ignores these) or canonical tags back to page 1. Noindexing pagination wastes valuable crawl opportunities.
How do I fix duplicate content from product variations?
Use canonical tags pointing all variations to the main product page. Or create one page with dropdown selectors instead of separate URLs for each variation.
What’s the difference between 301 and 302 redirects?
301 is permanent (passes SEO value), 302 is temporary (doesn’t pass value). For ecommerce, almost always use 301 redirects when products are discontinued or URLs change.
Can technical SEO alone improve rankings?
Yes, especially if technical issues are currently blocking Google from crawling/indexing pages properly. But maximum results come from combining technical SEO with great content and quality backlinks.
Final Thoughts: Your Technical SEO Action Plan
Technical SEO for ecommerce is the invisible foundation that makes everything else possible. You can have perfect products, brilliant content, and aggressive marketing—but if technical issues block Google from crawling, indexing, and understanding your site, you’re building on quicksand.
The good news? Most ecommerce stores completely neglect technical SEO, which means fixing it gives you an immediate competitive advantage. While competitors focus on content and links, you can leapfrog them by ensuring Google can actually access and rank your pages.
Start simple. Don’t try to fix everything at once:
This Week:
- Run a Screaming Frog crawl
- Check Google Search Console for critical errors
- Test your top 5 pages with PageSpeed Insights
- Fix any broken robots.txt issues
- Verify SSL certificate is working correctly
This Month:
- Optimize images on your top 20 product pages
- Implement canonical tags on filtered/variation pages
- Add product schema to your bestselling items
- Fix all broken internal links
- Ensure mobile usability passes on key pages
This Quarter:
- Complete comprehensive technical audit
- Optimize site-wide page speed
- Restructure internal linking if needed
- Implement all schema types
- Set up ongoing monitoring systems
Remember: technical SEO isn’t sexy. It doesn’t feel as exciting as creating content or launching campaigns. But it’s the difference between a site that grows organically and one that stays stuck despite your best efforts.
The stores dominating organic search didn’t get there by accident. They built solid technical foundations that let Google do its job properly. Now it’s your turn.
Stop letting technical issues silently drain your rankings and revenue. Start fixing them today.
Ready to master every aspect of ecommerce SEO? Our comprehensive ecommerce SEO guide covers keyword research, content strategy, link building, and advanced optimization techniques that complement these technical fixes.
Want actionable SEO strategies delivered regularly? Visit seoprojournal.com for expert guides, case studies, and proven tactics that drive real results for online stores.
Advanced Technical SEO Strategies for Large Ecommerce Sites
Once you’ve mastered the fundamentals, these advanced tactics separate good sites from great ones:
Log File Analysis
For stores with 10,000+ pages, analyzing server log files reveals exactly how Google crawls your site.
What log file analysis shows:
- Which pages Google crawls most frequently
- Crawl budget allocation across site sections
- Pages Google ignores completely
- Wasted crawl on low-value pages
- Bot behavior patterns
Tools for log analysis:
- Screaming Frog Log File Analyzer
- Botify (enterprise)
- Oncrawl (enterprise)
Pro Tip: If Google isn’t crawling your new products frequently, it’s a crawl budget issue. Reduce crawl waste by blocking or noindexing low-value pages (filters, search results, old blog posts). Focus Google’s attention on what matters—products and categories.
JavaScript SEO for Modern Frameworks
Many ecommerce platforms now use JavaScript frameworks (React, Vue, Angular). These create unique technical challenges.
Common JavaScript SEO issues:
- Content not rendering for search engines
- Slow rendering blocking indexing
- Important content loaded client-side only
- Navigation links not crawlable
Solutions:
- Implement server-side rendering (SSR)
- Use dynamic rendering for bots
- Ensure critical content in initial HTML
- Test with Google’s JavaScript test in Search Console
Real example: A headless commerce store built on React wasn’t getting product pages indexed. Implementing server-side rendering increased indexed pages by 400% within 2 months.
International SEO Technical Setup
Selling globally requires specific technical implementation:
Hreflang Tags: Tell Google which language/country version to show different users.
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="en-us" href="https://example.com/en-us/" /> <link rel="alternate" hreflang="en-gb" href="https://example.com/en-gb/" /> <link rel="alternate" hreflang="es-es" href="https://example.com/es-es/" />URL Structure Options:
Option Example Pros Cons ccTLD example.co.uk Strongest geo-targeting signal Expensive, complex management Subdomain uk.example.com Easy to set up Weaker domain authority Subdirectory example.com/uk/ Consolidates domain authority Less clear geo-targeting Pro Tip: For most ecommerce stores, subdirectories work best. They keep all SEO value under one domain while clearly organizing by country/language. Use hreflang tags properly and you’re golden.
Faceted Navigation Optimization
Filtering and sorting options create massive duplicate content issues if not handled correctly.
The problem:
/running-shoes/ /running-shoes/?color=blue /running-shoes/?color=blue&size=10 /running-shoes/?color=blue&size=10&brand=nike /running-shoes/?sort=priceEach combination creates a unique URL with similar or identical content.
Solutions:
Option 1: Canonical to Main Category Point all filtered URLs to the unfiltered category page.
Option 2: Noindex Filtered Pages Prevent filtered pages from being indexed entirely.
Option 3: Strategic Indexing Index valuable filters (brand pages) but not combinations.
Pro Tip: Use Search Console URL Parameters to tell Google how to handle filters. For sorting/pagination parameters, choose “No URLs.” For valuable filters like brand, choose “Representative URL.” This prevents crawl budget waste without blocking valuable pages.
Platform-Specific Technical SEO Considerations
Different ecommerce platforms have unique technical challenges:
Shopify Technical SEO
Strengths:
- Excellent mobile optimization out-of-box
- Automatic SSL and security
- Clean URL structure
- Fast hosting infrastructure
Weaknesses:
- Limited URL structure control (/products/ and /collections/ forced)
- Duplicate content from /products/ and /collections/ showing same items
- Blog on subdomain by default
- Limited robots.txt control
Fixes:
- Use canonical tags aggressively
- Implement apps for advanced schema
- Move blog to main domain with Blog customization
- Use Shopify’s built-in sitemap
WooCommerce Technical SEO
Strengths:
- Complete URL control
- Unlimited customization
- Extensive plugin ecosystem
- Full robots.txt and .htaccess access
Weaknesses:
- Speed depends on hosting quality
- Requires manual optimization
- Plugin conflicts can break functionality
- Security responsibility falls on you
Fixes:
- Use dedicated WooCommerce hosting
- Install Yoast SEO or RankMath
- Implement caching (WP Rocket, W3 Total Cache)
- Regular updates and security monitoring
Magento Technical SEO
Strengths:
- Built for large catalogs
- Powerful URL rewrite management
- Advanced caching options
- Native multi-store support
Weaknesses:
- Complex technical setup
- Requires developer knowledge
- Resource-intensive (needs strong hosting)
- Steep learning curve
Fixes:
- Hire Magento specialists for setup
- Implement Varnish caching
- Optimize database regularly
- Use CDN for static assets
Pro Tip: Don’t fight your platform’s limitations. Work within its strengths. If you need complete control, WooCommerce. If you need simplicity and speed, Shopify. If you’re enterprise-scale, Magento. Choose based on your needs, then optimize within those constraints.
Learn platform-specific optimization strategies in our ecommerce SEO ultimate guide.
Measuring Technical SEO Success
How do you know if your technical fixes are working? Track these metrics:
Primary Technical SEO KPIs
Crawl Efficiency:
- Pages crawled per day (Search Console)
- Crawl errors (decreasing over time)
- Crawl budget utilization
- Average time between crawls
Indexing Health:
- Total indexed pages (should increase)
- Index coverage errors (should decrease)
- Important pages indexed (should be 100%)
- Low-value pages excluded (expected)
Site Speed Metrics:
- Core Web Vitals (LCP, INP, CLS)
- PageSpeed Insights scores
- Time to First Byte (TTFB)
- Total blocking time
Mobile Performance:
- Mobile usability errors (should be zero)
- Mobile search traffic percentage
- Mobile conversion rate
- Mobile vs desktop speed scores
Schema Markup:
- Pages with valid schema (increasing)
- Rich result appearances
- Click-through rate on rich results
- Schema validation errors (zero)
Secondary Impact Metrics
Search Visibility:
- Organic traffic trends
- Keyword rankings
- Click-through rates
- Impressions in Search Console
Business Impact:
- Organic conversion rate
- Revenue from organic traffic
- Pages per session
- Bounce rate
Pro Tip: Create a simple dashboard tracking your top 5 technical metrics weekly. I use Google Data Studio (free) to pull data from Search Console, Analytics, and PageSpeed Insights automatically. Review every Monday—consistency beats perfection.
Creating a Technical SEO Maintenance Schedule
Technical SEO checklist for online stores needs regular maintenance to stay effective:
Daily Monitoring (Automated Alerts)
Set up alerts for:
- Site downtime (UptimeRobot)
- Security issues (Search Console)
- Critical errors (Search Console)
- Traffic drops >20% (Google Analytics)
Weekly Tasks (30 minutes)
Every Monday morning:
- Review Search Console coverage report
- Check for new crawl errors
- Monitor Core Web Vitals trends
- Verify recent products are indexed
- Check site uptime report
Monthly Tasks (2-3 hours)
First week of each month:
- Full site crawl with Screaming Frog
- Analyze new broken links
- Review page speed on top 20 pages
- Check mobile usability errors
- Verify schema markup accuracy
- Analyze crawl budget usage
- Update XML sitemaps if needed
Quarterly Tasks (Full day)
Every 3 months:
- Comprehensive technical SEO audit
- Competitive technical analysis
- Log file analysis (large sites)
- Review and update robots.txt
- Audit internal linking structure
- Test checkout flow technically
- Update documentation
Annual Tasks (2-3 days)
Once per year:
- Complete platform update/upgrade
- Full site restructure assessment
- International expansion technical setup
- Comprehensive security audit
- Hosting/infrastructure review
- Historical performance analysis
Pro Tip: Schedule these in your calendar with reminders. Technical SEO fails when it becomes “whenever we have time.” Treat it like any other critical business function—schedule it, do it, repeat.
When to Hire Technical SEO Help
Some issues require expert intervention. Know when to DIY vs hire:
DIY-Friendly Technical SEO:
- Image optimization
- Adding schema markup (with plugins)
- Fixing broken links
- Writing robots.txt
- Creating XML sitemaps
- Basic mobile optimization
- SSL certificate installation
Hire an Expert For:
- JavaScript rendering issues
- Custom platform development
- Large-scale site migrations
- Complex redirect mapping
- Server configuration optimization
- Log file analysis and crawl budget
- International site setup
- Enterprise-level technical issues
What to look for in technical SEO help:
- Platform-specific experience (your ecommerce platform)
- Proven track record with measurable results
- Clear communication (explains technical stuff simply)
- Transparent pricing and timelines
- Ongoing support, not just one-time fixes
Pro Tip: For small fixes, hire on Upwork or Fiverr ($50-500). For comprehensive technical SEO, expect $2,000-10,000+ depending on site size and complexity. For enterprise stores, ongoing retainers ($3,000-15,000/month) make sense. Don’t cheap out on technical SEO—poor implementation can cause more problems than it solves.
The Future of Technical SEO for Ecommerce
What’s coming in the next 2-3 years that you should prepare for:
Core Web Vitals Evolution
Google continues refining user experience metrics. Expect:
- More emphasis on Interaction to Next Paint (INP)
- Stricter thresholds for mobile performance
- Additional UX metrics beyond current Core Web Vitals
- Increased weight in ranking algorithms
Prepare by: Building speed and UX into your development process, not bolting it on afterward.
AI-Generated Content Detection
Google’s algorithms increasingly detect thin AI content. For ecommerce:
- Product descriptions need human expertise
- Category content must demonstrate real knowledge
- Generic AI-written content gets filtered
- Unique insights and testing become crucial
Prepare by: Using AI as a tool, not a replacement for human expertise. Add real product testing, comparisons, and insights AI can’t provide.
Visual Search Optimization
Google Lens and visual search growing rapidly. Technical requirements:
- High-quality product images from multiple angles
- Detailed image alt text and metadata
- Structured data including image properties
- Fast image loading without quality loss
Prepare by: Treating image SEO as seriously as text SEO—it’s not optional anymore.
Privacy and Tracking Changes
Cookie deprecation and privacy regulations affect technical implementation:
- Server-side tracking becoming standard
- First-party data strategies essential
- Analytics getting more complex
- Consent management required
Prepare by: Working with developers to implement privacy-compliant tracking that still provides actionable data.
Pro Tip: Don’t chase every new trend, but stay informed. Follow Google Search Central Blog, attend webinars, and join ecommerce SEO communities. Technical SEO evolves continuously—what works today might be obsolete in 18 months.
Your Technical SEO Success Roadmap
You’ve learned how to fix technical SEO issues on ecommerce sites from foundation to advanced tactics. Now let’s make it actionable:
Phase 1: Emergency Fixes (Week 1) Fix anything actively blocking Google:
- Robots.txt errors
- Site downtime issues
- Major mobile usability problems
- SSL certificate issues
- Critical broken links
Phase 2: Foundation (Weeks 2-4) Build proper technical foundation:
- Optimize site speed basics
- Implement canonical tags
- Add product schema markup
- Fix crawlability issues
- Ensure mobile-friendly
Phase 3: Optimization (Months 2-3) Improve what’s working:
- Advanced speed optimization
- Complete schema implementation
- Optimize internal linking
- Refine URL structure
- Enhance mobile UX
Phase 4: Maintenance (Ongoing) Keep everything healthy:
- Weekly monitoring
- Monthly audits
- Quarterly reviews
- Continuous improvement
The stores that dominate organic search didn’t get there overnight. They systematically built technical foundations, then maintained and improved them continuously.
Your technical SEO journey starts with one fix. Pick the most critical issue from your audit today and fix it. Tomorrow, fix another. Build momentum through consistent action, not overwhelming yourself with everything at once.
Technical perfection is impossible—but technical excellence is absolutely achievable. And it’s the difference between an invisible store and one that grows organically month after month.
Stop letting technical issues hold your store back. Start fixing them today.
Master every aspect of ecommerce SEO: From keyword research to link building, our comprehensive ecommerce SEO guide covers everything you need to dominate organic search in 2025.