Ever been in a meeting where someone confidently said “we need to use AI for our SEO,” and you nodded along while secretly thinking, “Wait… isn’t that machine learning? Or is it deep learning? Are these even different things?”
You’re not alone. These terms get tossed around like confetti at a tech conference, often interchangeably and almost always confusingly. But here’s the kicker: understanding the machine learning vs AI distinction actually matters for your SEO strategy—not just for sounding smart in meetings.
Let me break down these buzzwords into plain English and show you exactly how each one impacts your search rankings differently.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat’s the Actual Difference Between AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning?
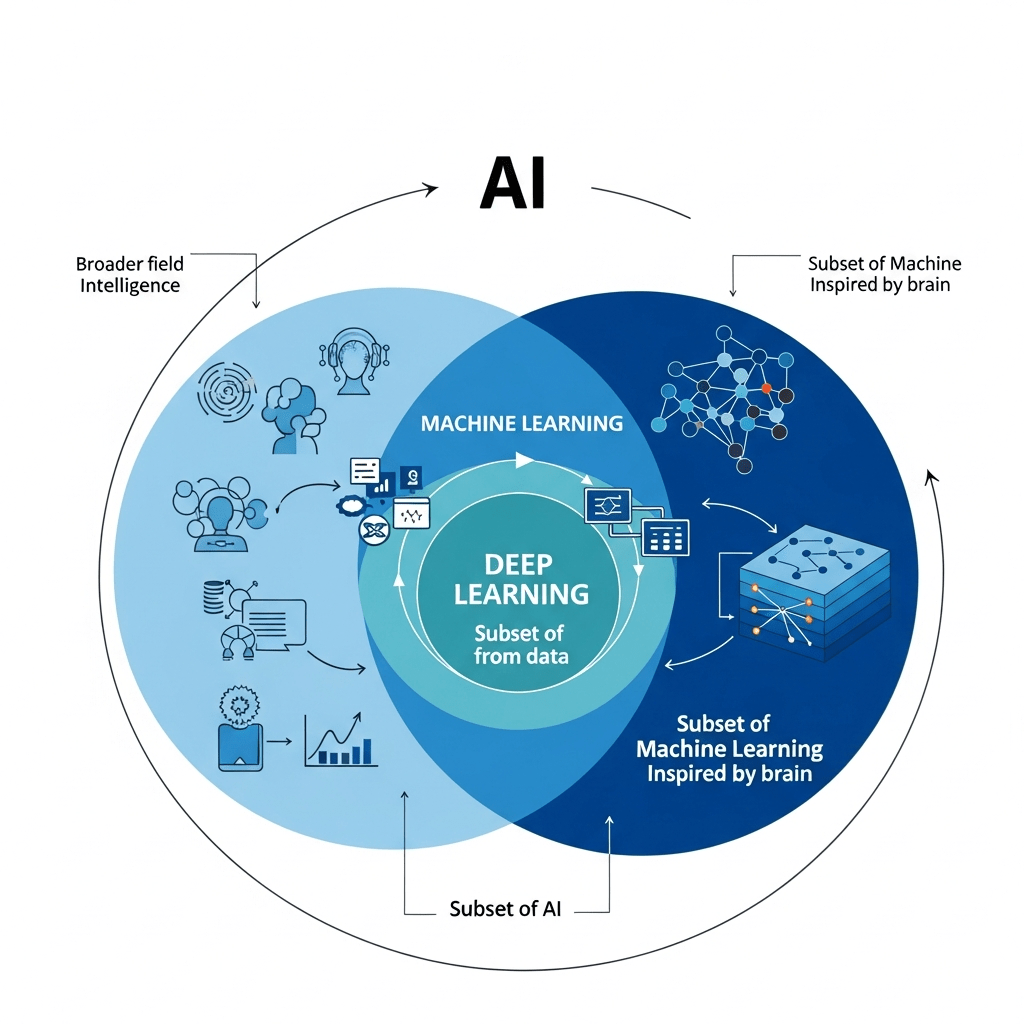
Think of these three concepts like Russian nesting dolls—each one fits inside the other, but they’re not the same thing.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the big daddy—the outermost doll. It’s any computer system that can perform tasks normally requiring human intelligence. This includes everything from your smartphone’s autocorrect to self-driving cars.
Machine Learning (ML) sits inside AI. It’s a specific approach where computers learn from data without being explicitly programmed for every scenario. Instead of saying “if X happens, do Y,” you feed it thousands of examples and it figures out the patterns itself.
Deep Learning (DL) is the innermost doll—a specialized subset of machine learning using neural networks with multiple layers. It’s particularly good at handling complex patterns in massive datasets, like recognizing faces in photos or understanding natural language.
Here’s a simple analogy: If AI is “teaching a computer to recognize cats,” then machine learning is “showing it 10,000 cat photos until it figures out what makes a cat a cat,” and deep learning is “using brain-inspired networks to understand cats at multiple levels—whiskers, pointy ears, fur texture, and typical cat poses.”
Machine Learning vs AI: The Core Differences That Matter for SEO
Let’s get tactical. The difference between AI and machine learning in SEO isn’t just academic—it changes how you optimize.
AI in SEO: The Broad Umbrella
When Google says they use “AI,” they’re typically referring to the entire intelligent system that:
- Understands search queries (what you really mean, not just what you typed)
- Ranks billions of web pages in milliseconds
- Personalizes results based on your location, device, and history
- Detects spam and low-quality content
- Generates featured snippets and AI Overviews
Real example: Google’s Knowledge Graph is an AI system that connects entities (people, places, things) to answer questions directly. When you search “how tall is the Eiffel Tower,” you get an instant answer—that’s AI at work.
Machine Learning in SEO: The Pattern Recognition Engine
Machine learning algorithms power specific components of search engines. They’re the workhorses analyzing patterns in:
- User behavior signals (which results people click, how long they stay)
- Content quality indicators (expertise signals, freshness, comprehensiveness)
- Link quality assessment (which backlinks actually indicate authority)
- Query-content matching (connecting search intent with relevant pages)
Google’s RankBrain is the most famous machine learning application in SEO. Launched in 2015, it specifically handles ambiguous queries by learning from patterns in how users interact with results.
Pro Tip: RankBrain doesn’t replace Google’s algorithm—it’s one ranking signal among hundreds. But it’s a BIG one, especially for queries Google hasn’t seen before.
The Practical Difference for Your SEO Strategy
Here’s where rubber meets road:
AI optimization means: Creating content that serves human needs so well that intelligent systems recognize its value across multiple signals.
Machine learning optimization means: Understanding which specific patterns and signals the learning algorithms prioritize, then ensuring your content exhibits those patterns.
Bottom line: You’re always optimizing for AI (the full system), but understanding machine learning helps you focus on the specific signals that matter most.
Deep Learning vs Machine Learning: Why This Distinction Matters for Search
Now let’s tackle deep learning vs machine learning—a distinction that’s becoming increasingly important as search engines evolve.
Traditional Machine Learning: Rule-Based Pattern Recognition
Traditional machine learning algorithms need humans to identify which features matter. For spam detection, engineers might specify: “Look at sender reputation, number of links, all-caps usage, and certain trigger words.”
The algorithm learns how to weigh these features, but humans decide what features to examine.
In SEO context: Early Google algorithms used traditional ML for things like:
- Identifying duplicate content (comparing known features)
- Detecting paid links (analyzing specific link characteristics)
- Classifying page types (using predefined content signals)
Deep Learning: Discovering Patterns Humans Miss
Deep learning SEO applications use neural networks with multiple layers that discover their own features. You don’t tell the system what to look for—it figures it out.
Google’s BERT (2019) and MUM (2021) are deep learning models. They don’t just analyze predetermined features—they understand language at multiple levels simultaneously: word meanings, sentence structure, context, intent, and even subtle implications.
Real example: Pre-BERT, Google struggled with queries like “can you get medicine for someone pharmacy.” The algorithm didn’t understand that “for someone” was the critical context (picking up someone else’s prescription).
Post-BERT: The deep learning model grasps the nuanced meaning and returns relevant results about pharmacy pickup policies for other people.
The SEO Impact Comparison Table
| Aspect | Traditional Machine Learning | Deep Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Data Requirements | Works with smaller datasets | Needs massive data volumes |
| Feature Engineering | Humans define what to examine | Self-discovers important features |
| Interpretability | Can understand why decisions made | “Black box”—hard to explain decisions |
| SEO Application | Link analysis, spam detection, basic ranking | Language understanding, image recognition, complex intent |
| Optimization Approach | Target known ranking signals | Create genuinely valuable content (patterns emerge naturally) |
| Examples in Search | PageRank, early Penguin/Panda | BERT, MUM, Google Lens |
| What It Means for You | Can reverse-engineer signals | Must focus on authentic quality |
| Update Frequency | Periodic retraining | Continuous learning |
The trend is clear: Search is moving from traditional ML toward more deep learning applications. This means less “gaming the system” and more “genuinely serving users.”
How Does Google Actually Use AI vs Machine Learning vs Deep Learning?
Let’s pull back the curtain on what’s happening when you hit “search.”
The Complete Search Journey
Stage 1: Query Understanding (Deep Learning)
When you type “best headphones under $100,” Google’s deep learning models (like BERT) instantly:
- Understand “best” implies reviews and comparisons
- Recognize “$100” as a price constraint, not just a number
- Grasp that “headphones” could mean wireless, wired, gaming, or studio—but context suggests consumer products
- Consider your location, language, and device
This happens in milliseconds using neural networks trained on billions of queries.
Stage 2: Content Matching (Machine Learning + AI)
Google’s machine learning algorithms then:
- Identify pages mentioning headphones in that price range
- Analyze user engagement patterns (which results satisfied similar queries)
- Evaluate page quality signals (E-E-A-T factors, freshness, comprehensiveness)
- Consider your personalization factors
Stage 3: Ranking (Traditional ML + Deep Learning + Rules)
The final ranking blends:
- Traditional ML signals (PageRank-style link analysis, spam detection)
- Deep learning assessments (content quality, intent matching)
- Hard-coded rules (safe search filters, local preferences, diversity)
Stage 4: Result Presentation (AI Orchestration)
The full AI system decides:
- Should we show a featured snippet?
- Does this need a local pack?
- Should AI Overview generate a summary?
- What related questions should appear?
Real-World Example: The Evolution of “Near Me” Searches
2010 (Basic Rules): “Pizza near me” → Show pages with “pizza” near user’s IP location
2015 (Machine Learning – RankBrain): Learn that “near me” actually means “currently open” and “within 10 minutes” for most users
2019 (Deep Learning – BERT): Understand that “near me” at 10 PM prioritizes differently than at noon, and “pizza” might mean “pizza delivery” at night
2023 (Advanced Deep Learning – MUM): Connect queries across languages, understand that someone searching “pizza near me” after searching “gluten-free restaurants” wants GF pizza options
See the progression? Each evolution required more sophisticated AI vs ML capabilities—and demanded different SEO approaches.
Which Ranking Factors Use Machine Learning vs Deep Learning?
Not all ranking factors are created equal. Some use traditional signals, others leverage machine learning, and the newest use deep learning. Understanding this helps you prioritize optimization efforts.
Traditional Machine Learning Ranking Factors
These factors use pattern recognition from clear, defined features:
Link Analysis:
- PageRank-style authority calculations
- Anchor text relevance matching
- Link velocity and pattern detection
- Spam link identification
Technical SEO Signals:
- Page load speed metrics
- Mobile-friendliness scoring
- Structured data validation
- Crawlability assessment
On-Page Elements:
- Keyword presence and positioning (yes, still matters!)
- Content length and formatting
- Internal linking structure
- Meta tag optimization
Pro Tip: These traditional ML factors are more “hackable” because they’re based on defined features. But don’t be fooled—Google’s machine learning algorithms are sophisticated enough to detect manipulation.
Deep Learning Ranking Factors
These require neural networks to assess and can’t be easily reverse-engineered:
Natural Language Understanding:
- Semantic topic coverage and depth
- Content quality and expertise signals
- Writing style and readability
- Intent satisfaction (matching what users actually want)
User Experience Signals:
- Engagement patterns (dwell time, pogo-sticking)
- Navigation behavior
- Conversion completion
- Repeat visit patterns
Content Comprehension:
- Image relevance and quality (Google Lens)
- Video content understanding
- Multimedia integration value
- Cross-format consistency
Contextual Relevance:
- Personalization factors
- Temporal relevance (freshness when it matters)
- Geographic appropriateness
- Device-specific optimization
The key difference? Traditional ML factors can be checked with tools and optimized directly. Deep learning SEO factors require genuinely good content—the system evaluates holistic quality in ways that can’t be faked.
Machine Learning vs Deep Learning for Search Optimization: Which Should You Focus On?
Here’s the million-dollar question: which is better AI or machine learning for SEO?
The answer: It’s not an either/or situation, but understanding the distinction helps you allocate effort effectively.
When to Optimize for Traditional Machine Learning Signals
Focus here when:
- You’re in a competitive, established niche where technical excellence matters
- You’re building topical authority (internal linking, content clusters)
- You need quick wins (technical ML factors improve faster)
- Your industry has clear expertise markers (credentials, certifications)
Action items for ML optimization:
- Build strategic internal linking connecting related content (traditional ML loves clear topical relationships)
- Earn quality backlinks from relevant, authoritative domains
- Optimize Core Web Vitals (speed, interactivity, visual stability)
- Structure content with clear hierarchy (H tags, lists, tables)
- Use schema markup to help ML algorithms understand content type
When to Optimize for Deep Learning Signals
Focus here when:
- You’re creating new content or entering emerging topics
- Search intent is complex or ambiguous in your niche
- User satisfaction makes the biggest difference (e-commerce, local, YMYL)
- You need sustainable, long-term rankings (harder to displace once deep learning recognizes quality)
Action items for deep learning optimization:
- Create genuinely comprehensive content that thoroughly answers user questions
- Write naturally and conversationally (BERT and MUM reward natural language)
- Focus on user engagement (make content so good people stay and explore)
- Add unique insights and expertise (neural networks detect originality)
- Update content regularly with fresh perspectives and examples
The Hybrid Approach: Best of Both Worlds
The smartest strategy? Combine both:
Example workflow:
- Use ML-friendly structure: Clear H tags, strategic keywords, internal links (traditional ML)
- Fill it with DL-optimized content: Natural language, comprehensive coverage, unique insights (deep learning)
- Add technical excellence: Fast loading, mobile-optimized, schema markup (traditional ML)
- Optimize for engagement: Compelling introduction, scannable format, clear CTAs (deep learning via user signals)
This is exactly what the AI and machine learning foundations for SEO approach recommends—don’t choose between them.
Understanding AI ML DL in Search Engines: Real Examples You Can Learn From
Theory is great, but let’s look at actual implementations so you can see AI vs ML differences in action.
Example 1: Product Review Queries
Search query: “best running shoes for flat feet”
Traditional ML processing:
- Identifies “running shoes” as product category
- Recognizes “flat feet” as specification
- Matches against pages with these terms
- Checks basic relevance signals
Deep learning processing (BERT/MUM):
- Understands “flat feet” is a medical condition requiring specific shoe features
- Knows “best” implies comparison and expert recommendations
- Recognizes implicit intent: probably wants reviews from runners with flat feet, not just manufacturer specs
- Considers related concepts: arch support, pronation, heel drop
What wins in rankings:
- Pages with expert reviews from podiatrists or experienced runners (E-E-A-T)
- Content explaining why certain shoes work for flat feet (comprehensive expertise)
- Real user experiences and testimonials (engagement signals)
- Clear product comparisons with specific flat-feet-relevant features (structured, valuable content)
Your takeaway: Don’t just list products—explain the why behind recommendations with genuine expertise.
Example 2: Local Service Queries
Search query: “emergency plumber”
Traditional ML factors:
- Location proximity
- Business hours/open now status
- Review ratings and count
- NAP (Name, Address, Phone) consistency
Deep learning factors:
- Understanding “emergency” implies urgent need, after-hours service
- Analyzing review sentiment beyond star ratings (mentions of “came quickly,” “available Sunday,” “fixed immediately”)
- Image recognition of actual work photos vs. stock images
- Detecting business legitimacy through multiple signals
What wins in rankings:
- Google Business Profiles with 24/7 availability clearly stated
- Reviews specifically mentioning emergency response and speed
- Photos of actual work and team members
- Clear pricing for emergency services (transparency)
Your takeaway: For local SEO, deep learning evaluates the meaning behind your signals, not just their presence.
Example 3: Informational Content Rankings
Search query: “how to train for a marathon”
Traditional ML evaluation:
- Keyword matching: “marathon,” “training,” “how to”
- Content length (comprehensive guides rank better)
- Backlink profile from running/fitness sites
- Page structure and formatting
Deep learning evaluation:
- Does content cover beginner, intermediate, and advanced runners? (comprehensive intent)
- Are there specific, actionable training plans? (practical value)
- Does it address common concerns (injuries, nutrition, rest days)? (holistic coverage)
- Is the writing style appropriate for the audience? (readability and engagement)
What wins in rankings:
- Content from experienced runners with credentials (E-E-A-T)
- Detailed, customizable training plans (high practical value)
- Coverage of related topics without being asked (anticipating user needs)
- Personal stories and realistic expectations (engagement and trust)
Your takeaway: Deep learning SEO rewards content that anticipates and satisfies the complete user journey, not just the immediate query.
Common Myths About Machine Learning vs AI in SEO (Debunked)
Let’s clear up some dangerous misconceptions floating around:
Myth #1: “AI SEO means just using AI writing tools”
Reality: Using ChatGPT or Jasper doesn’t make your strategy “AI-optimized.” You’re optimizing for Google’s AI systems, not necessarily with AI tools.
Plenty of successfully ranked content is written entirely by humans. Conversely, pure AI-generated content often fails because it lacks the genuine expertise that deep learning models detect.
Myth #2: “Machine learning optimization means keyword stuffing is back”
The truth: Some marketers think because machine learning algorithms look for patterns, stuffing keywords creates those patterns. Wrong.
Modern neural networks easily detect unnatural language patterns. Google’s spam algorithms (also using ML) specifically target this manipulation.
What actually works: Natural keyword inclusion that emerges from comprehensive topic coverage.
Myth #3: “Deep learning is too complex to optimize for, so just create good content”
Half right, half wrong: Yes, you can’t directly manipulate deep learning signals. But understanding how these systems evaluate quality helps you create strategically good content.
For instance, knowing that BERT values conversational question-answering should influence your content structure. Understanding that MUM connects concepts across formats should inform your multimedia strategy.
Myth #4: “Traditional ML factors don’t matter anymore with deep learning”
Wrong: Google uses a blended approach. A site with terrible technical SEO (traditional ML factors) won’t rank well, even with amazing content that deep learning loves.
Think of it like this: Traditional ML gets you in the game. Deep learning helps you win.
Myth #5: “Understanding AI vs machine learning is only for enterprise sites”
Not true: Small businesses and individual bloggers benefit even more from understanding these distinctions. Large brands can brute-force some success with massive content volume and budgets.
Smaller players need strategic precision—knowing which machine learning vs deep learning signals to prioritize with limited resources.
Practical Tools for Leveraging Machine Learning and Deep Learning in SEO
You don’t need to build your own neural networks to benefit from these technologies. Here are accessible tools that put AI power in your hands:
Machine Learning-Powered SEO Tools
Semrush Keyword Magic Tool
- Uses ML to cluster related keywords semantically
- Predicts keyword difficulty based on competitive patterns
- Identifies question-based queries (perfect for deep learning optimization)
Ahrefs Content Gap Analysis
- ML algorithms identify topics your competitors rank for that you don’t
- Pattern recognition in competitor success factors
- Predictive ranking difficulty
Screaming Frog SEO Spider
- ML-based duplicate content detection (beyond exact matches)
- Pattern recognition for identifying template issues
- Automated categorization of page types
Deep Learning-Assisted Content Tools
Surfer SEO & Clearscope
- Analyze top-ranking content using NLP (natural language processing)
- Suggest semantic terms and topic coverage based on neural network analysis
- Reverse-engineer what deep learning algorithms reward
MarketMuse
- Deep learning models assess content comprehensiveness
- Topic modeling to identify coverage gaps
- Content briefs based on AI-driven competitive analysis
Frase.io
- Uses deep learning to understand search intent
- Generates content outlines matching what ranks
- Answer-engine optimization for featured snippets
AI-Powered Writing Assistants (Use Wisely!)
ChatGPT, Claude, Jasper
- Useful for: Research, outlining, drafting initial content
- Dangerous for: Publishing unedited AI content without expertise
- Best practice: AI for efficiency, human for expertise and authenticity
Pro Tip: Use AI tools to identify what to write about and structure your content, then add the unique insights, examples, and expertise that only you can provide. This is the sweet spot for understanding AI ML DL in search engines—combining machine efficiency with human authority.
How to Future-Proof Your SEO Strategy for Advancing AI
Here’s what we know: AI, machine learning, and deep learning in search will only get more sophisticated. How do you stay ahead?
The Principles That Won’t Change
Despite technological evolution, these fundamentals remain constant:
1. User satisfaction always wins Whether it’s traditional ML or advanced deep learning, every system ultimately measures user satisfaction. Create content that genuinely helps people, and you’re future-proofed.
2. Expertise cannot be faked (for long) Neural networks get better at detecting shallow vs. deep knowledge. Build genuine expertise in your niche—it’s your competitive moat.
3. Technical excellence is table stakes As deep learning gets better at evaluating content quality, technical SEO becomes the differentiator between equals. Fast, accessible, well-structured sites win.
4. Natural language beats optimization tricks Every Google update moves toward rewarding natural, helpful content. Write for humans first—the machine learning algorithms will follow.
Emerging Trends to Watch
Multimodal AI integration Google’s MUM can understand information across text, images, and video simultaneously. Future optimization: Create content ecosystems across formats, not just blog posts.
Conversational AI search Voice search and AI assistants like ChatGPT are changing how people search. Preparation: Focus on question-based content and conversational language patterns.
Predictive personalization Machine learning will increasingly predict what individual users want before they search. Strategy: Build topical authority so you’re the answer regardless of how the question is asked.
Zero-click search evolution AI Overviews and featured snippets mean more answers without clicks. Adaptation: Become the cited source in AI-generated answers through authoritative, well-structured content.
For more on staying current with these changes, check out how machine learning is transforming SEO practices.
The Bottom Line: Machine Learning vs AI vs Deep Learning for Your SEO
Let’s bring this home with what actually matters for your Monday morning strategy session.
Artificial Intelligence in SEO is the full ecosystem—the intelligent systems orchestrating search. You’re always optimizing for AI, whether you think about it explicitly or not.
Machine learning powers specific components—link analysis, spam detection, user signal interpretation. Optimize here through clear technical signals, strategic structure, and defined quality markers.
Deep learning handles the complex stuff—language understanding, intent matching, content quality assessment. Optimize here through genuine expertise, comprehensive coverage, and authentic user satisfaction.
The winning formula isn’t choosing one over the other—it’s understanding that modern difference between AI and machine learning in SEO means you need a layered approach:
- Foundation layer (Traditional ML): Technical excellence, clear structure, strategic linking
- Content layer (Deep Learning): Natural language, comprehensive expertise, user engagement
- Orchestration layer (Full AI): Everything working together to serve user needs
Think of it like building a house: Traditional machine learning is your solid foundation and framing. Deep learning is your interior design and user experience. AI is the entire home functioning as a comfortable living space.
Stop worrying about which technology to “optimize for” and start thinking about creating content that works at every level—technically sound, comprehensively helpful, and genuinely valuable.
The marketers winning with AI and ML applications in modern SEO aren’t the ones who can explain backpropagation in neural networks. They’re the ones who understand that whether it’s machine learning, deep learning, or some future AI technology, the goal stays the same: connect the right users with the right information at the right time.
And honestly? If you do that well, the specific technology behind it becomes less important than the results you drive.
Ready to dive deeper into specific implementations? Explore advanced neural network applications in SEO or learn about practical machine learning tools for everyday optimization.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Is machine learning more important than AI for SEO? Machine learning is part of AI, not separate from it. ML is one methodology within the broader AI ecosystem. For SEO, you’re optimizing for the complete AI system, which includes machine learning, deep learning, and other technologies. Focus on the outcome (satisfying users) rather than the specific technology.
Q: Can I optimize for deep learning specifically? Not directly. Deep learning systems evaluate holistic content quality across hundreds of implicit signals. Your optimization is indirect: create genuinely expert, comprehensive content that naturally exhibits quality signals. Unlike traditional ML factors (which can be checked with tools), deep learning optimization requires authentic excellence.
Q: Do neural networks replace Google’s traditional ranking factors? No. Google uses a hybrid approach combining traditional signals (PageRank-style link analysis, technical factors), machine learning (pattern recognition in user behavior), and deep learning (language understanding, intent matching). All three layers work together. Ignore any layer at your peril.
Q: Which type of content benefits most from understanding machine learning vs deep learning? Informational/educational content benefits most from deep learning optimization (comprehensive expertise, natural language). Local business and e-commerce benefit from machine learning optimization (structured data, clear signals, technical excellence). Complex queries requiring nuance benefit from understanding how deep learning interprets intent.
Q: Are AI-written articles using machine learning or deep learning? Most AI writing tools (ChatGPT, Claude, Jasper) use deep learning models—specifically, large language models built with transformer neural networks. However, these tools creating content is different from Google’s systems evaluating content. Google’s AI uses multiple technologies to assess whether AI-written content meets quality standards.
Q: How often do machine learning and deep learning algorithms update? Machine learning models typically retrain periodically (days to weeks). Deep learning models can learn continuously or through major updates (like Google’s core updates). The practical takeaway: Focus on evergreen quality rather than chasing algorithm changes. Good content works across updates.
Q: Can small websites compete with big sites in the age of machine learning SEO? Absolutely—sometimes even better. Machine learning and especially deep learning evaluate content quality and expertise, not just domain size. A small site with genuine expertise in a niche often outranks large generic sites. The democratizing effect of AI in search is that authentic expertise beats volume.
Q: What’s the single biggest mistake people make with AI vs ML in SEO? Focusing on the technology instead of the outcome. Marketers waste time debating whether RankBrain is ML or DL, when they should focus on what all these systems reward: content that genuinely satisfies user intent. Understand the concepts, then optimize for results, not for specific technologies.
Q: Will quantum computing change the machine learning vs deep learning equation for SEO? Potentially, but not yet practically. Quantum computing could dramatically accelerate machine learning training and enable more sophisticated deep learning models. For now, focus on optimizing for current AI systems. When quantum-enhanced search arrives, the fundamentals (quality, expertise, user satisfaction) will still apply—just evaluated more sophisticatedly.
AI vs Machine Learning vs Deep Learning in SEO
Interactive Guide to Understanding Search Intelligence
The Nested Relationship
Learning
Learning
Hover over each circle to see the relationship
🤖 Artificial Intelligence
- Broad concept of intelligent machines
- Includes rule-based systems
- Encompasses all smart technologies
- Google's complete search system
🧠 Machine Learning
- Learns from data patterns
- Requires feature engineering
- Powers RankBrain
- Handles link analysis & spam detection
⚡ Deep Learning
- Neural networks with multiple layers
- Self-discovers features
- Powers BERT & MUM
- Understands natural language
| Aspect | Machine Learning | Deep Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Data Requirements | Works with smaller datasets | Needs massive data volumes |
| Feature Engineering | Humans define features | Self-discovers features |
| Training Time | Minutes to hours | Hours to weeks |
| Interpretability | Clear decision paths | "Black box" complexity |
| SEO Applications | Link analysis, spam detection | Language understanding, intent |
| Google Examples | RankBrain, PageRank | BERT, MUM, Neural Matching |
| Optimization Approach | Target specific signals | Create authentic quality |
| Evolution Rate | Periodic updates | Continuous learning |
Ranking Factor Impact by Technology
Evolution of AI in Search Engines
PageRank (Traditional ML)
Google's original algorithm using mathematical link analysis. First major ML application in search.
Hummingbird Update
Semantic search begins. Google starts understanding query meaning, not just keywords.
RankBrain Launch (Machine Learning)
First major AI system using ML to interpret search queries and user satisfaction signals.
Neural Matching (Deep Learning)
DL connects concepts to queries beyond keywords. Understands semantic relationships.
BERT Revolution (Deep Learning)
Transformer-based neural networks understand conversational context. Game-changer for natural language.
MUM Introduction (Advanced DL)
1000x more powerful than BERT. Multimodal understanding across 75+ languages and formats.
AI Overviews (SGE)
Generative AI creates answer summaries directly in search results. New era of search begins.
Helpful Content & AI Detection
Advanced ML/DL systems detect AI-generated content quality and authentic expertise.
Key Statistics & Data Points
Source: seoprojournal.com - AI & SEO Intelligence
Data compiled from Google Research, Search Engine Journal, Backlinko, Semrush & Industry Reports (2024)