You’ve spent months perfecting your product. Your website converts like crazy in your home market. But when you try to expand internationally? Cricket sounds.
Here’s the brutal truth: 67% of companies fail at international SEO simply because they treat it like regular SEO with a translation layer slapped on top. Spoiler alert—Google doesn’t work that way.
This international SEO guide will walk you through everything you need to dominate search results across borders, languages, and cultures. No fluff, no jargon—just actionable strategies that actually work in 2025.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Exactly Is International SEO and Why Should You Care?
International SEO is the process of optimizing your website so search engines can identify which countries you want to target and which languages you use for business.
Think of it like this: You wouldn’t use the same pickup line in Tokyo that you’d use in Texas, right? Same logic applies here.
When done correctly, international SEO helps you:
- Reach customers in multiple countries without building separate websites
- Avoid duplicate content penalties across different language versions
- Show up in local search results even when you’re not physically present
According to Statista’s global e-commerce report, the global e-commerce market hit $6.3 trillion in 2024, and it’s projected to reach $8.1 trillion by 2026. Missing out on international SEO means leaving serious money on the table.
How Does International SEO Differ from Regular SEO?
Regular SEO is like cooking for yourself. International search optimization is like running a restaurant chain across five continents—same core recipe, but you need to adjust for local tastes.
Key differences:
| Regular SEO | International SEO |
|---|---|
| One language, one audience | Multiple languages, multiple audiences |
| Single domain authority | Authority split across regions |
| Local keyword research | Multi-market keyword research |
| Standard hreflang? Not needed | Hreflang tags are critical |
| Cultural context? Less important | Cultural adaptation is everything |
Example: When eBay expanded to China, they simply translated their US site. They failed spectacularly. Taobao (Alibaba’s platform) dominated because they understood Chinese consumers wanted social features, bargaining options, and different payment methods. That’s not just translation—that’s global SEO strategy done right.
What Are the Core Components of a Global SEO Strategy?
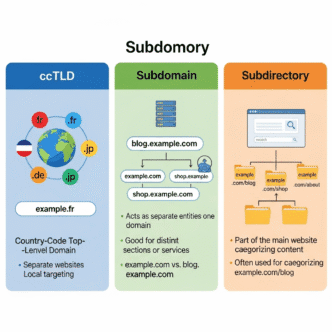
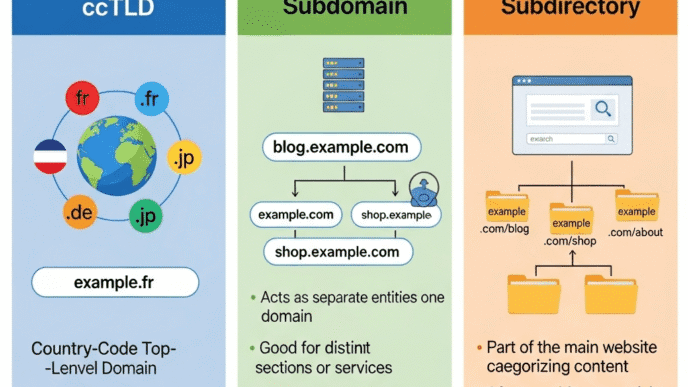
1. URL Structure: Your Foundation
You’ve got three main options for structuring your international website SEO:
Country Code Top-Level Domains (ccTLDs)
- Example: example.de (Germany), example.fr (France)
- Pro: Strongest signal to Google about targeting
- Con: Expensive and requires building authority for each domain
Subdirectories with gTLDs
- Example: example.com/de/, example.com/fr/
- Pro: Consolidates domain authority, easier to manage
- Con: Slightly weaker geo-targeting signal
Subdomains
- Example: de.example.com, fr.example.com
- Pro: Can host on country-specific servers
- Con: Google treats these as separate sites
My honest take? For most businesses, subdirectories are the sweet spot. Companies like Shopify, HubSpot, and Airbnb all use this approach because it balances SEO power with practical management.
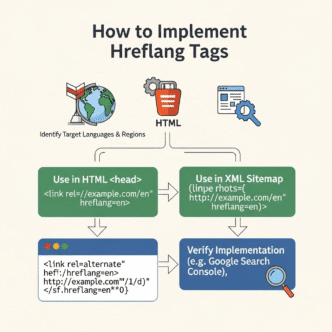
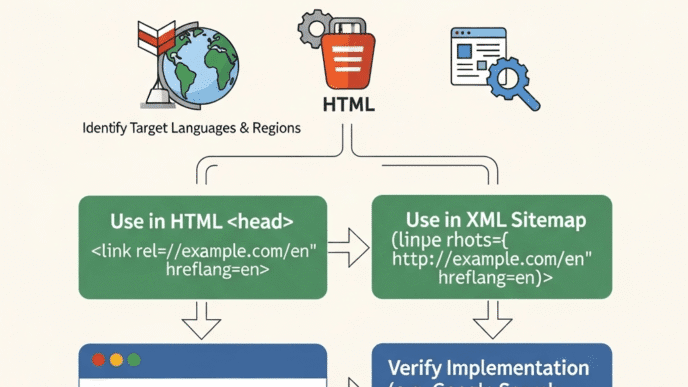
2. Hreflang Tags: The Unsung Hero
If international SEO had a superhero, hreflang would be it. These HTML tags tell Google which language and country version of a page to show users.
Proper implementation looks like this:
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="en-us" href="https://example.com/en-us/" />
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="en-gb" href="https://example.com/en-gb/" />
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="es-es" href="https://example.com/es-es/" />
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="x-default" href="https://example.com/" />
Common mistakes that’ll tank your rankings:
- Forgetting the x-default tag (your fallback URL)
- Mixing up language and country codes
- Not creating reciprocal links between versions
- Using incorrect ISO codes (en-UK instead of en-GB)
Pro Tip: Use Google Search Console’s International Targeting report to catch hreflang errors. According to a 2024 study by Ahrefs, 58% of international sites have hreflang implementation errors.
How Do You Conduct International Keyword Research?
Here’s where amateurs crash and burn: they assume keywords translate directly. They don’t.
The Smart Approach to Multi-Country SEO Keyword Research
Step 1: Don’t Just Translate—Transcreate
The keyword “sneakers” in the US becomes “trainers” in the UK and “zapatillas” in Spain. But wait—in Spain, people might search for “deportivas” more often depending on the region.
Tools for international keyword discovery:
- Google Keyword Planner (location-specific data)
- Ahrefs (database covers 171 countries)
- SEMrush (international keyword gap analysis)
- AnswerThePublic (local question variations)
Step 2: Understand Search Behavior Differences
Search volume isn’t everything. In Germany, searchers prefer longer, more detailed queries. In the US, shorter queries dominate.
Real-world example: When Zalando (Europe’s leading fashion platform) expanded, they discovered Germans search for “damenschuhe größe 38 schwarz leder” (women’s shoes size 38 black leather) while UK users search “black leather heels size 5.” Same product, totally different worldwide SEO approach needed.
Step 3: Map Search Intent Across Cultures
| Market | Product Search Pattern | What This Means |
|---|---|---|
| US | Brand-focused, quick decisions | Emphasize brand trust signals |
| Germany | Detailed specs, comparison shopping | Need comprehensive product data |
| Japan | Mobile-first, image-heavy | Visual content is critical |
| Brazil | Price-sensitive, payment options | Highlight flexible payment terms |
What Technical SEO Elements Matter Most for International Sites?
Server Location and CDN Configuration
Page speed isn’t just a ranking factor—it’s a conversion factor. According to Google’s research, a 1-second delay can reduce conversions by 7%.
Solution: Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN) like Cloudflare or AWS CloudFront to serve content from servers closest to your users.
Mobile Optimization for Global Markets
In 2025, mobile accounts for 72% of global internet traffic. But here’s the kicker—in countries like India and Indonesia, it’s over 85%.
Mobile-first checklist for global SEO:
- ✓ AMP pages for news/blog content in mobile-heavy markets
- ✓ Touch-friendly navigation (minimum 48x48px tap targets)
- ✓ Optimized images (WebP format, lazy loading)
- ✓ Fast mobile page speed (aim for under 3 seconds)
Structured Data and International Schema
Adding structured data markup helps Google understand your content context across languages.
Priority schema types for international sites:
- Organization schema (establish brand credibility)
- Product schema (essential for e-commerce)
- LocalBusiness schema (even if you’re not physically present)
- FAQ schema (captures long-tail international queries)
Expert Opinion from John Mueller (Google): “Hreflang and proper structured data are the two most underutilized tools in international SEO. Get these right, and you’re ahead of 70% of your competition.”
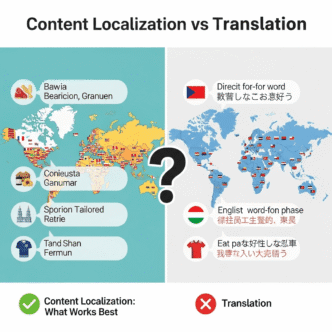
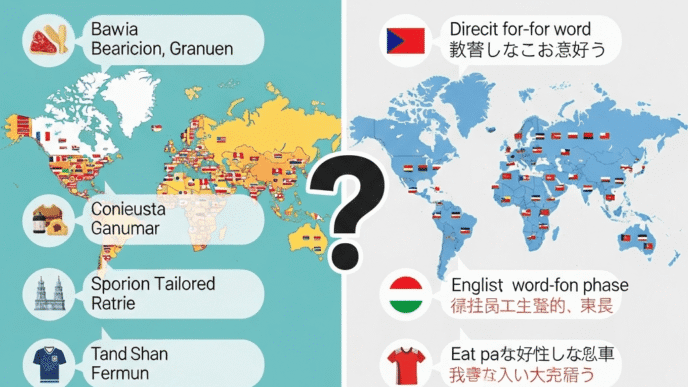
Should You Translate or Localize Your Content?
Short answer: Localize. Always.
Translation = Converting words from one language to another
Localization = Adapting content for cultural context, local preferences, and market-specific needs
The Netflix Approach to Content Localization
Netflix doesn’t just subtitle their content—they adapt thumbnails, descriptions, and even which shows they promote based on regional preferences.
For your global website SEO, this means:
- Adapting examples (use local brands, local currency, local measurements)
- Cultural sensitivity (colors, imagery, idioms that work in one culture might offend in another)
- Local social proof (testimonials from local customers, local case studies)
- Regional compliance (GDPR in Europe, LGPD in Brazil, CCPA in California)
Case study: When Coca-Cola launched in China, they localized their brand name to “可口可乐” (Kě kǒu kě lè), which means “delicious happiness.” That’s not translation—that’s localization genius.
How Do You Build International Backlinks?
Link building for multi-country SEO requires a different playbook.
Regional Link Building Strategies That Work
Tactic 1: Local Media Outreach Partner with regional journalists and bloggers. A link from The Guardian (UK) carries more weight for UK rankings than a link from The New York Times.
Tactic 2: Country-Specific Directories
- Germany: meinestadt.de, gelbeseiten.de
- France: pagesjaunes.fr
- Spain: QDQ.com
Tactic 3: International PR Campaigns Create market-specific stories. What’s newsworthy in Tokyo might not interest readers in Toronto.
Tactic 4: Multilingual Content Partnerships Guest post on relevant sites in target languages. Just make sure the content is written by native speakers.
| Link Building Approach | Effectiveness | Difficulty | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Local directory listings | Medium | Low | Free-$50 |
| Regional PR campaigns | High | High | $500-$5,000 |
| Country-specific guest posts | High | Medium | $100-$1,000 |
| International influencer partnerships | Very High | High | $1,000-$10,000+ |
What Are the 12 Deadliest International SEO Mistakes to Avoid?
Mistake #1: Auto-Redirecting Based on IP Location
Why it’s catastrophic: It prevents Google from crawling all your regional versions and frustrates users who might be traveling or using VPNs.
According to Search Engine Journal, forced redirects cause a 23% increase in bounce rates for international sites.
The fix: Use geolocation to suggest a regional version with a dismissible banner, but let users choose.
Mistake #2: Duplicate Content Across Regional Sites
Having identical content in English for your US, UK, Canada, and Australia sites? Google sees that as duplication.
The fix: Create unique, localized content for each market. Even if it’s the same language, adjust examples, spelling (color vs colour), and cultural references.
Mistake #3: Ignoring Local Search Engines
Google dominates most markets, but not all:
- China: Baidu (70% market share)
- Russia: Yandex (45% market share)
- South Korea: Naver (56% market share)
Each requires specific optimization approaches beyond standard global SEO strategy.
Mistake #4: Using Automatic Translation Tools Without Review
Google Translate might seem convenient, but it creates embarrassing mistakes. Remember when KFC’s “Finger-lickin’ good” was translated to Chinese as “Eat your fingers off”?
The fix: Always use professional translators who understand SEO and your industry terminology.
Mistake #5: Incorrect Currency and Date Format Display
Showing USD to European customers or using MM/DD/YYYY dates in countries that use DD/MM/YYYY creates confusion and kills trust.
The fix: Implement automatic currency conversion and region-appropriate formatting.
Mistake #6: Poor Mobile Experience in Emerging Markets
In developing markets with slower internet speeds, your fancy animations and high-res images might never load.
Data from Think with Google shows that 53% of mobile users abandon sites that take longer than 3 seconds to load.
The fix: Create lightweight versions for bandwidth-constrained markets. Use adaptive loading based on connection speed.
Mistake #7: Neglecting Local Payment Methods
Not accepting Alipay in China or Boleto in Brazil? You’re basically turning away customers at the door.
The fix: Research and integrate region-preferred payment methods. This isn’t just about convenience—it’s about trust.
Mistake #8: Ignoring Local Holidays and Shopping Seasons
Running a Black Friday campaign in markets where Black Friday isn’t a thing? Wasted effort.
The fix: Create region-specific content calendars aligned with local events (Singles Day in China, Diwali in India, Boxing Day in UK/Australia).
Mistake #9: Using One Hosting Server for Global Sites
Hosting your global site on a US server means slow loading times for users in Asia and Europe.
The fix: Use a CDN or distributed hosting. According to Cloudflare data, CDNs can improve page load times by up to 50% for international visitors.
Mistake #10: Forgetting About Local Link Building
Building only US backlinks won’t help your rankings in Germany or Japan.
The fix: Develop region-specific link building strategies targeting local domains (.de, .jp, .co.uk) with relevant local content.
Mistake #11: Not Monitoring Local Competitors
Your biggest competitor in France might be completely different from your US competitor.
The fix: Conduct competitive analysis for each target market separately. Use tools like SEMrush to identify local competitors and their strategies.
Mistake #12: Skipping Multilingual Customer Support
Offering a French website but only English customer support? That’s a conversion killer.
The fix: Provide support in the same languages as your website content, or clearly indicate which languages your support team speaks.
Pro Tip: Create a pre-launch checklist for each new market. Test everything—language, currency, forms, checkout process, and customer support—before going live.
How Do AI and Machine Learning Impact International SEO in 2025?
AI-Powered Content Localization
Google’s Neural Machine Translation (NMT) has improved translation accuracy by 60% since 2023, but here’s the catch: it still can’t replace human cultural understanding.
The smart approach: Use AI for initial drafts, then have native speakers refine and optimize for local SEO.
AI-Driven Search Intent Analysis
Tools like ChatGPT and Claude can now analyze cross-cultural search patterns and suggest localized keyword variations you might miss.
Example: AI can identify that “cheap flights” in English markets corresponds to “vol pas cher” in French markets, but also reveal that French users more frequently search for “billet d’avion promotion” (flight ticket promotion).
Predictive Analytics for Market Selection
AI tools can now analyze market viability by processing:
- Search volume trends across regions
- Competitive density in different languages
- Economic indicators and buying power
- Cultural affinity for your product category
According to Gartner’s 2024 report, companies using AI for international market analysis see 34% faster market penetration compared to traditional methods.
Voice Search Optimization Across Languages
Voice search queries are fundamentally different from typed searches—they’re longer, more conversational, and heavily influenced by regional dialects.
The strategy: Optimize for natural language queries in each target language. “Okay Google, où puis-je trouver un restaurant italien près de moi?” is how French users search, not “restaurant italien Paris.”
AI-Generated Visual Content for International Markets
Tools like Midjourney and DALL-E are creating culturally-adapted visuals without expensive photo shoots.
Warning: Always review AI-generated images for cultural appropriateness. An AI might create imagery that’s offensive in certain markets.
How Do You Measure International SEO Success?
Key Metrics to Track by Region
Organic visibility metrics:
- Keyword rankings by country (track top 10 keywords per market)
- Organic traffic by geographic location
- Click-through rates by language version
- Featured snippet appearances by region
Engagement metrics:
- Bounce rate by country (high bounce rates might indicate localization issues)
- Time on page by region
- Pages per session by language
- Scroll depth by market (indicates content engagement)
Conversion metrics:
- Conversion rate by country
- Revenue by region
- Cost per acquisition by market
- Return on ad spend (ROAS) by geography
Technical health metrics:
- Page load speed by region
- Mobile usability scores per market
- Core Web Vitals by country
- Hreflang error rates
Tools for international SEO tracking:
- Google Analytics 4 (geographic segments and custom reports)
- Google Search Console (country-filtered performance data)
- Ahrefs/SEMrush (international rank tracking across 100+ countries)
- Hotjar (user behavior recordings by country)
- PageSpeed Insights (location-specific performance testing)
Setting Realistic KPIs by Market Maturity
| Market Stage | Expected Timeline | Primary KPIs |
|---|---|---|
| Launch (0-3 months) | Focus on indexing | Pages indexed, hreflang errors, crawl budget |
| Growth (3-9 months) | Build visibility | Keyword rankings, organic traffic, backlinks |
| Mature (9+ months) | Optimize conversions | Revenue, conversion rate, customer LTV |
Pro Tip: Don’t compare mature markets (like your home market) with new international markets. A 2% conversion rate in a new market might actually be excellent performance.
What Does the Future Hold for International Search Optimization?
Emerging Trends in Global SEO (2025 and Beyond)
1. Hyper-Local SEO Within International Markets
It’s no longer enough to target “Germany”—you need to optimize for Berlin, Munich, and Hamburg separately. Each city has unique search patterns and cultural nuances.
2. Multimodal Search is Exploding
Users are combining voice, text, and visual searches. Google Lens queries grew 193% in 2024, with the strongest growth in Asian markets.
3. Zero-Click Searches Dominate Internationally
According to SparkToro data, 59% of Google searches in 2024 ended without a click. For international SEO, this means optimizing for featured snippets and “People Also Ask” boxes becomes critical.
4. Sustainability and Ethical SEO Matter More
European markets especially care about carbon footprint. A 2024 study found that 68% of European consumers prefer brands with eco-friendly websites.
The strategy: Optimize page weight, use green hosting, and communicate your sustainability efforts—it’s both good SEO and good business.
5. Local Language AI Assistants
ChatGPT, Claude, and Bard now support 100+ languages. Users are asking questions in their native languages more than ever, making conversational keyword optimization essential.
6. Privacy Regulations Shape International Tracking
GDPR, LGPD, and similar regulations mean you can’t track users the same way globally. First-party data and privacy-compliant analytics are the new standard.
Real-World International SEO Success Stories
Case Study 1: Booking.com’s Multilingual Mastery
Booking.com operates in 43 languages across 220+ countries. Their secret?
Key tactics:
- Machine translation + human review for 1.5 million property descriptions
- Localized trust signals (reviews from users in the same country)
- Regional payment methods (40+ payment options globally)
- Geo-targeted pricing showing local currency with no conversion needed
Results: 70% of their bookings come from outside their Netherlands headquarters.
Case Study 2: Canva’s Global Design Domination
Canva expanded from Australia to global dominance by focusing on visual content that transcends language barriers while maintaining localized interfaces.
Strategy highlights:
- Launched in 100+ languages (including right-to-left languages like Arabic)
- Created region-specific template libraries
- Partnered with local influencers for market-specific content
- Adapted their onboarding flow based on cultural design preferences
Results: From 10 million to 100+ million users in 4 years, with 90% coming from outside Australia.
Case Study 3: Shopify’s Merchant Expansion
Shopify’s international SEO strategy focused on empowering local entrepreneurs rather than just translating their platform.
Winning moves:
- Created country-specific merchant success guides
- Built local payment gateway integrations for 100+ countries
- Developed region-specific SEO content targeting “how to start a business in [country]”
- Established local support teams fluent in regional business practices
Results: International merchants now represent 60% of Shopify’s total merchant base.
Your International SEO Action Plan: A Step-by-Step Implementation Guide
Phase 1: Market Research & Strategy (Weeks 1-4)
- Identify 2-3 target markets based on demand, competition, and resources
- Conduct multilingual keyword research for each market
- Analyze local competitors and their strategies
- Choose URL structure (subdirectories recommended for most)
- Create localization budget and timeline
Phase 2: Technical Foundation (Weeks 5-8)
- Implement hreflang tags correctly
- Set up CDN for global content delivery
- Configure Google Search Console for each country
- Implement international structured data markup
- Set up analytics with geographic segmentation
Phase 3: Content Localization (Weeks 9-16)
- Translate and localize core pages with native speakers
- Adapt visual content for cultural relevance
- Create region-specific blog content
- Localize meta descriptions and title tags
- Set up multilingual sitemap
Phase 4: Link Building & Promotion (Weeks 17-24)
- Develop regional backlink acquisition campaigns
- Partner with local influencers and publishers
- Submit to country-specific directories
- Launch localized PR campaigns
- Build relationships with local media
Phase 5: Optimization & Scale (Month 7+)
- Analyze performance data by market
- A/B test localized landing pages
- Refine keyword targeting based on actual performance
- Expand to additional markets using proven framework
- Build dedicated regional teams if scaling significantly
Final Thoughts: Is International SEO Worth the Investment?
Let’s be blunt: international SEO is hard, expensive, and time-consuming. But for businesses ready to expand globally, it’s also one of the highest-ROI marketing investments you can make.
The math checks out: According to Common Sense Advisory, 76% of online shoppers prefer to buy products with information in their native language, and 40% will never buy from websites in other languages.
If you’re selling a \$50 product and can capture just 1,000 additional international customers per month through proper SEO, that’s \$600,000 in annual revenue. Even with a 50% profit margin, that’s $300,000—plenty to fund your international SEO efforts.
But here’s my honest advice: Don’t try to conquer the world overnight. Pick one new market, execute flawlessly, learn from mistakes, and then scale. The companies that fail at international SEO are the ones who spread themselves too thin.
The verdict? If you have product-market fit in your home country, international SEO isn’t just worth it—it’s essential for long-term growth. The global market is massive, and your competitors are already claiming their share.
The question isn’t whether you should do international SEO. It’s whether you can afford not to.
Frequently Asked Questions About International SEO
Q: How long does it take to see results from international SEO efforts?
A: Typically 4-6 months for established markets with existing search volume, and 9-12 months for highly competitive new markets. International SEO takes longer than domestic because you’re building domain authority and trust from scratch in new regions. The timeline accelerates if your brand already has some recognition in the target market.
Q: Do I need separate hosting for each country I target?
A: Not necessarily. A quality CDN (Content Delivery Network) can serve content quickly to global audiences without separate hosting. However, China is the major exception—due to the Great Firewall and hosting regulations, you’ll need a local hosting provider and an ICP license to operate effectively in mainland China.
Q: Should I target countries or languages with my international SEO strategy?
A: Both! Use hreflang to specify language-country combinations (en-US, en-GB, en-AU) rather than just language codes. Regional differences matter significantly even within the same language. British users search differently than American users, and Spanish speakers in Spain have different search behaviors than those in Mexico or Argentina.
Q: Can I use machine translation for my international content?
A: For initial drafts, maybe. For published content? Absolutely not. Machine translation misses cultural context, industry terminology, and SEO optimization. Always have native speakers who understand your industry review and refine the content. According to CSA Research, 40% of consumers won’t buy from websites with poor translations.
Q: How many international markets should I target simultaneously?
A: Start with 1-3 high-opportunity markets maximum. Master those before expanding. Companies that try to launch in 10+ markets simultaneously typically fail in all of them due to diluted resources and poor localization. Focus beats breadth every time.
Q: Is international SEO worth it for small businesses with limited budgets?
A: Absolutely—if you choose your markets strategically. Start with one country where: (1) you already have some organic demand, (2) competition is manageable, (3) language/cultural barriers are low, or (4) your product solves an underserved need. Even a small business can dominate in carefully selected international markets.
Q: What’s the biggest mistake companies make with international SEO?
A: Treating it as a pure translation project. Successful international SEO requires localization (adapting to cultural context), technical implementation (hreflang, hosting, speed), local link building, and understanding regional search behavior. Companies that just translate their site and call it “international SEO” usually see terrible results.
Q: How do I handle international SEO if my product names don’t translate well?
A: Keep branded product names consistent globally but localize the descriptions, benefits, and category placement. For example, “iPhone” stays “iPhone” worldwide, but the marketing copy describing it changes dramatically by market. Focus your localization efforts on the searchable content, not necessarily the product names.
Q: Should I use subdirectories, subdomains, or separate domains for international SEO?
A: For most businesses, subdirectories (example.com/de/) are the sweet spot. They consolidate domain authority, are easier to manage, and provide strong enough geo-targeting signals. Only use separate ccTLD domains if you have substantial resources to build authority independently in each market.
Q: How important are local backlinks for international SEO rankings?
A: Extremely important. A link from a .de domain carries more weight for German rankings than a link from a .com domain. Aim for 60-70% of your backlinks to come from the target country’s domains. Local links signal relevance and authority to region-specific search engines.
Q: Do I need to worry about international SEO if I only ship domestically?
A: If you truly only serve one country, then no. However, if you have digital products, services, or might expand shipping in the future, implementing basic international SEO now (even if you’re not actively targeting other markets) prevents issues down the road and captures international interest organically.
Additional Resources for International SEO Success:
- Google Search Central: International & Multilingual Sites
- W3C Internationalization Standards
- Hreflang Tags Generator Tool
Remember: International SEO is a marathon, not a sprint. Start small, execute well, and scale strategically.
Complete International SEO Process Guide
A comprehensive framework for expanding your website globally with proven strategies and data-driven insights.
Why International SEO Matters
Market Research & Planning
Identify target markets and assess opportunities before investing resources.
Essential Activities:
- Analyze international traffic potential using Google Analytics
- Research keyword demand in target markets
- Evaluate competition per market
- Assess cultural and linguistic requirements
- Calculate ROI projections per market
- Define budget and resource allocation
Market Opportunity Assessment Framework
Technical Infrastructure Setup
Build the technical foundation for international SEO success.
URL Structure Decision:
| Structure | Example | Best For | Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| ccTLD | example.de | Large enterprises, 3-5 markets | High |
| Subdomain | de.example.com | Regional autonomy needed | Medium |
| Subdirectory | example.com/de/ | Most businesses, 5+ markets | Low |
Technical Checklist:
- Choose and implement URL structure
- Set up CDN for global performance
- Configure server locations or edge caching
- Implement SSL certificates
- Set up geotargeting in Google Search Console
- Create language-specific XML sitemaps
International Keyword Research
Discover what your target audience actually searches for in each market.
Keyword Research Impact on Rankings
Research Process:
- Use local keyword tools (Yandex, Baidu, Naver)
- Analyze local competitor keywords
- Research search intent per market
- Identify long-tail opportunities
- Map keywords to content structure
- Document regional variations in terminology
Content Localization
Create culturally relevant content that resonates with local audiences.
Translation vs Localization Impact
Localization Checklist:
- Hire native speakers or localization agencies
- Adapt cultural references and examples
- Localize images, videos, and visual content
- Convert currencies, dates, and measurements
- Ensure legal and regulatory compliance
- Implement quality review process
Hreflang Implementation
Tell search engines which language version to show to which users.
Implementation Methods:
- HTML head tags (best for small-medium sites)
- HTTP headers (for PDFs and non-HTML files)
- XML sitemap (best for large sites)
- Include self-referential tags on every page
- Implement bidirectional linking
- Add x-default tag for unmatched users
- Validate with Google Search Console
Technical SEO Optimization
Optimize technical elements for international search engines.
Page Speed Impact by Market Tier
Technical Optimization:
- Optimize page speed globally (target LCP < 2.5s)
- Implement proper canonical tags per language
- Set HTML lang attributes correctly
- Configure mobile-first optimization
- Add structured data in local languages
- Ensure proper crawlability per market
International Link Building
Build authority in each target market through local backlinks.
Link Building Strategies:
- Partner with local bloggers and influencers
- Create market-specific content for outreach
- Build citations in local directories
- Participate in local industry forums
- Sponsor local events and organizations
- Leverage PR in target markets
Implementation Timeline
Month 1-2: Research & Planning
Market research, competitor analysis, keyword research, strategy development
Month 2-3: Technical Setup
URL structure implementation, hreflang setup, CDN configuration
Month 3-5: Content Creation
Localization, content adaptation, quality review, publication
Month 5-6: Link Building Launch
Outreach campaigns, partnerships, local PR, citation building
Month 6-12: Optimization
Monitor performance, refine strategy, expand content, scale successful tactics
Monitoring & Optimization
Track performance and continuously improve results.
Key Metrics to Track:
- Organic traffic per market
- Keyword rankings in local search engines
- Conversion rates by country/language
- Hreflang error rates in Search Console
- Page speed from target locations
- Local backlink growth
- Engagement metrics per market
- Revenue per visitor by region