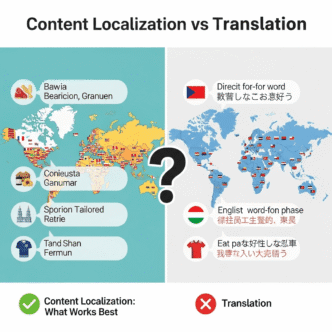
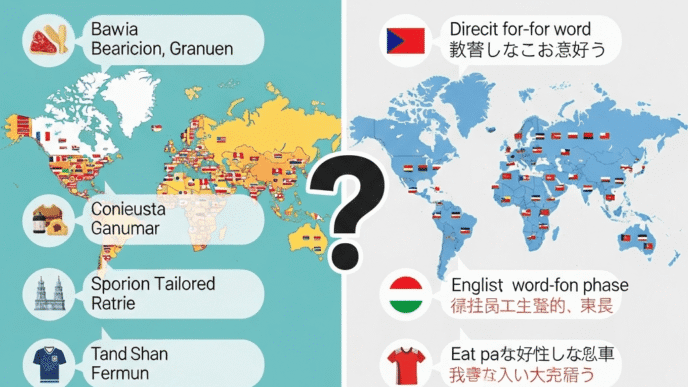
You’ve spent months translating your website into Spanish, hired a native copywriter, and launched with high hopes. Three months later? Your Spanish traffic is barely a trickle, and most visitors bounce within seconds.
Here’s the brutal truth: you optimized for the wrong keywords.
International keyword research isn’t just about translating “running shoes” to “zapatos para correr” and calling it a day. Different markets search differently, think differently, and even want different things when they type into Google.
I’ve watched businesses pour tens of thousands into multilingual content that ranks for absolutely nothing because they skipped proper keyword research. Meanwhile, their competitors—who invested in understanding local search behavior—are dominating the SERPs in every market.
In this guide, I’ll show you exactly how to uncover the keywords that actually drive traffic and conversions in international markets. No guesswork, no translations gone wrong, just data-driven strategies that work.
Let’s make your global SEO strategy actually, you know, work.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Makes International Keyword Research Different from Regular Keyword Research?
Here’s what most people get wrong: they think international keyword research is just regular keyword research in another language. It’s not even close.
When you’re researching keywords for a single market (let’s say the US), you’re dealing with:
- One language (mostly)
- One culture
- One set of search behaviors
- One competitive landscape
Go international, and suddenly you’re juggling:
- Multiple languages with regional variations
- Different cultural contexts and taboos
- Varied search engine preferences (Google vs. Yandex vs. Baidu)
- Unique seasonal patterns and shopping behaviors
- Different device preferences (mobile-first in some markets)
- Varying levels of search sophistication
Example: Americans searching for sneakers might type “best running shoes for marathon training.” Germans would search “Laufschuhe Marathon” (running shoes marathon), while French users prefer “chaussures de course longue distance” (long-distance running shoes). The intent is similar, but the search patterns? Completely different.
The Translation Trap That Kills International SEO
Let me tell you about the biggest mistake I see: direct translation.
You find “cheap flights” gets 200K monthly searches in the US, so you translate it to “vuelos baratos” for Spain. Sounds logical, right?
Wrong. In Spain, people actually search for “vuelos low cost” (using the English term) far more often than “vuelos baratos.” A direct translation just cost you 70% of potential traffic.
Pro Tip: Never, ever rely on direct translation for keywords. Always validate with actual search data from the target market. What people say and what people search are often two different things.
Why Should You Invest Time in International Keyword Research?
Still wondering if international keyword research is worth the effort? Let me break down what you’re missing without it:
Without proper research, you’re:
- Creating content nobody searches for
- Competing in oversaturated markets while missing easy wins
- Burning budget on translations that don’t drive ROI
- Confusing local audiences with awkward phrasing
- Losing to local competitors who understand the market
With proper research, you get:
- Lower CPCs in less competitive markets
- Higher conversion rates from intent-matched content
- Better resource allocation (translate what matters first)
- Cultural relevance that builds trust
- Competitive advantages in overlooked niches
According to Search Engine Journal, companies that conduct thorough global keyword strategy research see 3-4x higher international organic traffic growth compared to those using translated keywords alone.
The ROI is crystal clear: spend a week on research now, or spend months creating content that goes nowhere.
What Are the Key Challenges in International Keyword Research?
Let’s be honest—keyword localization isn’t easy. Here are the obstacles you’ll face (and how to overcome them):
Challenge 1: Language Variations Within the Same Country
Switzerland has four official languages. Belgium has three. India has hundreds. Even “Spanish” encompasses massive differences between Spain, Mexico, Argentina, and Colombia.
Solution: Research each language variant separately. Don’t assume Mexican Spanish keywords work in Spain—they often don’t.
Challenge 2: Different Search Engines, Different Data
Google dominates most of the world, but:
- Yandex rules Russia (around 60% market share)
- Baidu owns China (76% market share)
- Naver leads in South Korea (around 55% market share)
- Seznam is popular in Czech Republic
Each search engine has different keyword research tools and ranking factors.
Solution: Use market-specific keyword tools. For Russia, use Yandex.Wordstat. For China, use Baidu Keyword Planner. Don’t force Google data onto non-Google markets.
Challenge 3: Cultural Context and Search Intent
A keyword that’s perfectly innocent in one language might be offensive in another. Or it might exist but mean something entirely different.
Example: “Gift” means “poison” in German. Imagine optimizing a German e-commerce site for “gift” without understanding this nuance.
Solution: Always work with native speakers who understand local search behavior. Relying on tools alone will burn you eventually.
Challenge 4: Seasonal Patterns Vary Globally
Christmas shopping peaks in November-December in Western countries. But Chinese Singles Day (November 11) dwarfs Black Friday in China. Brazil’s biggest shopping season is Mother’s Day and Christmas, but timing differs.
Solution: Research seasonal trends separately for each market using Google Trends with location filters. For comprehensive seasonal strategy insights, check this international SEO guide.
Challenge 5: Competitive Landscapes Differ Dramatically
A keyword might be impossible to rank for in the US but wide open in Portugal. Or vice versa.
Solution: Analyze competition in each market independently. Don’t assume difficulty transfers across borders.
Pro Tip: Start with markets that speak your native language but in different regions (US vs. UK vs. Australia). This lets you master international keyword research mechanics before adding language barriers to the mix.
How Do You Start International Keyword Research the Right Way?
Ready to dive in? Here’s your step-by-step roadmap for how to do keyword research for international SEO campaigns that actually drives results.
Step 1: Identify Your Target Markets Strategically
Don’t just translate your site into “all the major languages.” That’s a recipe for mediocre results everywhere.
Instead, prioritize markets based on:
Business factors:
- Existing customer base in that region
- Product/service demand in the market
- Shipping or service delivery feasibility
- Competitive landscape saturation
- Market size and growth potential
SEO factors:
- Search volume for your industry
- Keyword competition levels
- Domain authority you can realistically achieve
- Language similarity to your existing content
- Search engine diversity (Google vs. local engines)
Create a prioritized list. Focus on 2-3 markets initially, then expand as you see success.
Step 2: Understand Local Search Behavior Through Data
Before touching keyword tools, understand how people in your target market actually search. This foundational research prevents expensive mistakes.
Research methods:
Google Trends with location filters:
- Compare search terms across regions
- Identify trending topics in specific markets
- Understand seasonal patterns
Reddit and local forums:
- See how native speakers discuss your topic
- Identify common questions and pain points
- Discover colloquial terms tools won’t find
Competitor analysis:
- Find local competitors ranking well
- Analyze their keyword strategy
- Identify gaps you can exploit
Native speaker interviews:
- Talk to locals about how they’d search for your product
- Ask about brand preferences and shopping behaviors
- Test your assumptions before committing resources
This qualitative research phase saves you from optimizing for keywords that technically exist but nobody actually uses.
Step 3: Build Your Seed Keyword List for Each Market
Now it’s time to create your foundation. But here’s the key: don’t just translate—think like a local.
Approach 1: Start with competitor keywords
Use tools like Ahrefs or SEMrush to analyze local competitors:
- Which keywords drive their traffic?
- What content formats rank in this market?
- Are there patterns in how they structure content?
Approach 2: Use marketplace insights
Check local Amazon, eBay, or regional marketplace search suggestions:
- What autocomplete suggestions appear?
- How do they categorize products?
- What terms appear in bestseller titles?
Approach 3: Leverage local Google autocomplete
Type your main topic into Google with location set to target market:
- What suggestions appear?
- How do locals phrase queries?
- What related searches show at the bottom?
Approach 4: Consult native content creators
Work with bloggers, influencers, or copywriters from the market:
- How would they search for your product?
- What terms sound natural vs. awkward?
- Are there regional slang terms to consider?
Pro Tip: Create separate keyword lists for each market in a shared spreadsheet. Include columns for: original keyword, literal translation, actual local term, search volume, difficulty, and notes. This becomes your international keyword bible.
What Are the Best Tools for International Keyword Research?
Let’s talk tools. Not all keyword research tools handle multilingual keywords equally well. Here’s your complete toolkit breakdown:
Google Keyword Planner: The Free Foundation
Pros:
- Free with Google Ads account
- Covers virtually every country and language
- Data directly from Google’s search engine
- Great for basic volume and competition data
Cons:
- Requires ad spend for precise volumes
- Limited competitive insights
- Doesn’t show keyword difficulty scores
- Basic compared to paid alternatives
Best for: Initial research when budget is tight, validating volumes across markets.
How to use it internationally:
- Set location to target country
- Set language to target language
- Never mix languages in one research session
- Export data separately for each market
Ahrefs Keywords Explorer: The Comprehensive Option
Pros:
- Supports 170+ countries
- Shows parent topics and keyword clusters
- Traffic potential estimates
- SERP feature tracking
- Historical trends data
Cons:
- Expensive ($129-999/month)
- Slight Google bias (less accurate for Yandex, Baidu)
- Learning curve for new users
Best for: Comprehensive global keyword strategy research when you need competitive insights and clustering.
International features:
- Country-specific difficulty scores
- Localized SERP analysis
- Multi-country keyword comparison
- Related terms in target language
SEMrush: The Competitive Intelligence Choice
Pros:
- Database covers 140+ countries
- Excellent competitor analysis
- Keyword Magic Tool for discovering variations
- Position tracking across markets
- Integration with Google Analytics
Cons:
- Pricing starts at $139.95/month
- Can be overwhelming with features
- Some markets have limited data
Best for: Understanding what competitors rank for in each market, finding market-specific keywords gaps.
Standout feature: Their “Keyword Gap” tool lets you compare your keywords vs. competitors across different countries simultaneously.
AnswerThePublic: The Question-Mining Goldmine
Pros:
- Visualizes questions people actually ask
- Supports multiple languages and countries
- Great for content ideation
- Shows prepositions and comparisons
Cons:
- Limited free searches per day
- No search volume data
- Better for content ideas than SEO metrics
Best for: Finding local search terms in question format, understanding how locals phrase their problems.
Yandex.Wordstat: Essential for Russian Markets
If you’re targeting Russia or Russian-speaking markets, this is mandatory.
Pros:
- Free to use
- Data from Yandex (Russia’s top search engine)
- Shows search queries and search history
- Regional breakdown within Russia
Cons:
- Interface primarily in Russian
- Requires Yandex account
- No integration with other tools
- Steeper learning curve for non-Russian speakers
Best for: Any Russian market research. Don’t skip this if you’re targeting Russia, Ukraine, Belarus, or Kazakhstan.
Baidu Keyword Planner: The China Gateway
For China, Baidu is the only game that matters.
Pros:
- Direct access to Baidu search data
- Essential for Chinese market entry
- Shows competition levels
- Free to use
Cons:
- Interface entirely in Chinese
- Requires Chinese phone number
- Complex setup process
- Limited documentation in English
Best for: Chinese market research when you’re serious about China expansion.
Reality check: You’ll likely need a Chinese partner or agency to navigate this effectively.
Comparison: Which Tool Should You Use?
| Tool | Best For | Price Range | Markets Covered | Difficulty Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Google Keyword Planner | Beginners, validation | Free | 190+ countries | No |
| Ahrefs | Comprehensive research | $129-999/mo | 170+ countries | Yes |
| SEMrush | Competitive analysis | $140-500/mo | 140+ countries | Yes |
| AnswerThePublic | Content ideation | Free-$199/mo | Multiple languages | No |
| Yandex.Wordstat | Russian markets | Free | Russia & CIS | No |
| Baidu Keyword Tool | China market | Free | China only | Yes |
| Ubersuggest | Budget-conscious | $29-99/mo | Global | Yes |
Pro Tip: Don’t rely on a single tool for international keyword research. Use Google Keyword Planner for volume validation, Ahrefs or SEMrush for competition analysis, and market-specific tools (Yandex, Baidu) for local insights. The combination gives you the complete picture.
How Do You Analyze Search Intent Across Different Cultures?
This is where keyword localization gets fascinating—and tricky. The same query can have completely different intent depending on the culture.
Understanding the Four Types of Search Intent Globally
Informational intent:
- Users want to learn something
- Varies culturally based on education systems
- Question format differs by language
Example: Americans might search “how to make pasta,” while Italians would search specific pasta types by name, assuming you know basic cooking.
Navigational intent:
- Users want to reach a specific website
- Brand awareness varies dramatically by market
- Local equivalents replace global brands
Example: “Amazon alternatives” in India brings up Flipkart and Snapdeal, not Walmart or Target.
Commercial investigation:
- Users are researching before buying
- Review culture differs globally
- Trust signals vary by market
Example: Germans heavily value test results from Stiftung Warentest, while Americans trust Amazon reviews and YouTube comparisons.
Transactional intent:
- Users ready to buy
- Purchase modifiers differ culturally
- Payment preferences matter
Example: “buy” vs. “kopen” (Dutch) vs. “comprar” (Spanish)—but in Germany, “kaufen” is less common than product name + “bestellen” (order).
Decoding Intent Through SERP Analysis
The best way to understand intent in any market? Look at what’s already ranking.
Steps for SERP analysis:
Search from the target location (use VPN or Google’s location settings)
Analyze top 10 results:
- What content format dominates? (blog posts, product pages, videos, forums)
- How long is the content?
- What depth of information do they provide?
- Are results from global or local sites?
Check SERP features:
- Featured snippets indicate informational intent
- Shopping results indicate transactional intent
- Local packs indicate geographical intent
- People Also Ask boxes reveal related questions
Note cultural differences:
- Video content more prominent in some markets
- Forum discussions more trusted in others
- Government sites rank higher in certain countries
Real example: Searching “best coffee maker” in the US returns product reviews and buying guides. The same query in Italy (“migliore macchina caffè”) returns forums discussing espresso machine brands—Italians trust community opinions over professional reviews.
This isn’t just interesting trivia—it tells you what content format to create and what angle to take.
The “Search and Survey” Method for Intent Validation
Here’s a tactic that’s saved me countless times:
- Survey local customers in your target market (even 20-30 responses help)
- Ask them: “How would you search Google to find [your product/service]?”
- Compare their answers to your keyword research
- Identify gaps between what you thought they’d search and what they actually search
I’ve seen keyword strategies completely transform after this exercise. What the tool data suggested versus what real humans said? Often 40-50% different.
For more on aligning content with international search intent, explore this comprehensive international SEO resource.
What’s the Process for Validating Keywords Across Markets?
You’ve got a list of potential keywords. Now comes the crucial part: validation. Here’s how to separate winners from time-wasters.
Validation Step 1: Check Real Search Volume
Don’t trust search volume estimates blindly. Tools often extrapolate data, especially for smaller markets.
Validation tactics:
Google Trends comparison:
- Compare your keyword against known high-volume terms
- If your keyword barely registers, the volume estimate is probably inflated
- Check if search volume is rising, stable, or declining
Trend analysis:
- Is interest seasonal? (important for planning)
- Is it growing or dying?
- Are there sudden spikes? (might indicate one-time events)
Cross-tool verification:
- Check volume in multiple tools
- If tools disagree significantly, trust the lower number
- Conservative estimates prevent wasted effort
Validation Step 2: Assess Actual Competition
Keyword difficulty scores are helpful, but nothing beats manual SERP analysis.
Competition assessment framework:
Look at the top 10 ranking pages:
- Are they dedicated pages or just mentions?
- Domain authority of ranking sites
- Age of domains (new domains ranking = opportunity)
- Quality of content (thin content ranking = easy win)
- Are the top results even optimized for the keyword?
Green flags (easier to rank):
- Forum posts ranking in top 10
- Low-quality content
- Weak backlink profiles
- Old, outdated content
- No local sites ranking (for local keywords)
Red flags (harder to rank):
- Major brands dominating
- Comprehensive, recently updated content
- Strong backlink profiles
- SERP features taking up space
- Native language sites with deep content
Pro Tip: Create a simple scoring system (1-5) for competition in each market. This lets you compare opportunities across different regions and prioritize your efforts objectively.
Validation Step 3: Calculate Keyword Priority Score
Not all keywords deserve equal effort. Prioritize using a simple formula:
Keyword Priority Score = (Search Volume × Relevance × Conversion Potential) / Difficulty
Where:
- Search Volume = monthly searches (from your tool)
- Relevance = how closely it matches your offering (1-10 scale)
- Conversion Potential = how likely searchers are to convert (1-10 scale)
- Difficulty = keyword difficulty score (1-100 scale)
Example calculation:
Keyword: “comprar zapatos running online” (buy running shoes online – Spain)
- Search Volume: 1,200
- Relevance: 10 (perfect match for online running shoe store)
- Conversion Potential: 9 (high purchase intent)
- Difficulty: 35
Priority Score = (1,200 × 10 × 9) / 35 = 3,085
Compare this across all your keywords to identify the highest-ROI opportunities.
Validation Step 4: Test with Small-Scale Content
Before committing to full content production for a market, test your assumptions:
- Create 3-5 pieces targeting your top keywords
- Monitor performance for 2-3 months
- Track:
- How quickly you rank
- Actual traffic vs. predictions
- Engagement metrics (bounce rate, time on page)
- Conversion rates
This pilot approach prevents you from translating 500 pages only to discover the market doesn’t respond as expected.
How Do You Find Market-Specific Keywords That Competitors Miss?
Here’s where you can gain serious competitive advantages. Most companies research the obvious keywords and call it done. Let’s find the hidden gems.
Strategy 1: Mine Local Marketplaces and Classified Sites
Every market has its dominant marketplace where people buy and sell. These are goldmines for local search terms.
Platform examples by market:
- US: Amazon, Craigslist, Facebook Marketplace
- Germany: eBay.de, Mobile.de, Kleinanzeigen
- France: Leboncoin, Cdiscount
- Japan: Rakuten, Mercari
- Brazil: Mercado Livre, OLX
- Russia: Avito, Yandex.Market
What to extract:
- Product category names (often differ from English)
- How sellers describe products
- Filter options (reveal how people segment searches)
- Autocomplete suggestions
- Popular brands (might differ from global leaders)
Strategy 2: Analyze Local Social Media Trends
Different markets favor different platforms. Where attention goes, search trends follow.
Platform priorities by region:
| Region | Dominant Platforms | Research Value |
|---|---|---|
| US/UK | Twitter, Instagram, TikTok | Trending topics, hashtags |
| China | WeChat, Weibo, Douyin | Product discussions, trends |
| Russia | VKontakte, Odnoklassniki | Community interests |
| Japan | LINE, Twitter | Real-time trends |
| Brazil | Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp | Product recommendations |
| India | WhatsApp, Facebook, Instagram | Shopping behaviors |
How to use this:
- Monitor trending hashtags related to your industry
- See how locals describe products and problems
- Identify emerging topics before they hit search
- Find influencer content that drives searches
Strategy 3: Use the “Related Searches” Rabbit Hole
This old-school technique still uncovers gems:
- Search your main keyword in target market Google
- Scroll to bottom → “Related searches”
- Click each related search
- Repeat the process for those results
- Document new variations you find
After 3-4 iterations, you’ll discover market-specific keywords that never appeared in your tool research.
Strategy 4: Exploit Regional Spelling and Terminology Differences
Even within the same language, regional variations create opportunities.
British vs. American English examples:
- “Mobile” vs. “Cell phone”
- “Trousers” vs. “Pants”
- “Boot” (of car) vs. “Trunk”
- “Flat” vs. “Apartment”
Spanish variations:
- “Computadora” (Mexico) vs. “Ordenador” (Spain)
- “Celular” (Latin America) vs. “Móvil” (Spain)
- “Auto” (Mexico) vs. “Coche” (Spain)
Portuguese differences:
- Brazilian vs. European Portuguese have dramatic vocabulary differences
- “Trem” (Brazil) vs. “Comboio” (Portugal) for train
- Pronunciation affects search behavior
These aren’t just translation details—they’re separate keyword opportunities with different competition levels.
Pro Tip: Create a regional terminology glossary for each market. Document every variation you discover. This becomes invaluable for future content creation and helps maintain consistency across your international content.
Strategy 5: Look for Question Keywords in Native Forums
Every market has questions only locals ask. Find these through:
Market-specific Q&A platforms:
- Quora (English, Spanish, French, Italian, German, Japanese, Portuguese)
- Reddit local subreddits (r/de, r/france, r/mexico)
- Gutefrage (Germany)
- Yahoo Chiebukuro (Japan)
- Zhihu (China)
- Stack Exchange local communities
What to look for:
- Questions asked repeatedly
- Problems people struggle to solve
- Gaps in existing answers
- Terminology locals actually use
These question keywords often have lower competition but highly engaged audiences.
How Can You Scale International Keyword Research Efficiently?
Once you’ve mastered the process for one market, you need systems to scale across multiple markets without drowning in spreadsheets.
Building Your International Keyword Research Framework
Create a repeatable process that works for every new market:
Phase 1: Market Assessment (1-2 days)
- Identify search engines used
- Find top 5 local competitors
- Determine language variations
- Check seasonal patterns
Phase 2: Seed List Development (2-3 days)
- Translate core keywords (but don’t use them yet)
- Get native speaker input
- Mine competitor keywords
- Extract marketplace terms
Phase 3: Expansion and Validation (3-4 days)
- Use keyword tools for expansion
- Analyze search intent via SERPs
- Calculate priority scores
- Build content clusters
Phase 4: Documentation (1 day)
- Create market-specific keyword repository
- Document terminology preferences
- Note cultural considerations
- Build content calendar
Total time investment: 7-10 days per new market initially. As you refine your process, this drops to 3-5 days.
Using AI Tools for International Keyword Research
Let’s talk about the elephant in the room: AI-powered keyword research. Tools like ChatGPT, Claude, and specialized SEO AI tools can accelerate your research, but they have limitations.
Where AI helps:
Generating keyword variations:
- Ask: “Give me 50 ways people in Germany might search for running shoes”
- Faster than manual brainstorming
- Can suggest angles you missed
Understanding search intent:
- Explain what types of content rank for specific keywords
- Analyze SERP patterns across markets
- Identify content gaps
Cultural context:
- Get explanations for terminology differences
- Understand local shopping behaviors
- Learn about market-specific preferences
Where AI fails:
- Actual search volume data: AI can’t tell you how many people search for something
- Current trends: Training data cutoffs mean missed opportunities
- Native speaker nuance: AI might suggest grammatically correct but awkward phrases
- Regional slang: Local colloquialisms often missing from training data
Best practice: Use AI for ideation and context, but always validate with actual keyword tools and native speakers.
Pro Tip: Create AI prompts specific to each market that include context about your business, target audience, and specific questions to ask. Save these prompts and refine them each time you research a new market. This creates a cumulative knowledge base that makes each subsequent market easier.
Outsourcing International Keyword Research
At scale, you can’t do everything yourself. Here’s how to outsource effectively:
Option 1: Hire local SEO consultants
- Pros: Native understanding, market expertise, network connections
- Cons: Higher cost, coordination challenges, varying quality
- Best for: High-value markets where you need deep expertise
Option 2: Work with multilingual agencies
- Pros: Established processes, multiple markets covered, consistency
- Cons: Less specialized per market, expensive, may lack niche knowledge
- Best for: 5+ markets simultaneously
Option 3: Freelance native speakers with SEO knowledge
- Pros: Cost-effective, flexible, direct communication
- Cons: Quality varies, project management overhead, less strategic
- Best for: Validation and expansion of your initial research
Vetting questions for any hire:
- “How would you research keywords for [your industry] in [market]?”
- “What tools do you use for [specific market] keyword research?”
- “Show me a sample keyword report you’ve created”
- “How do you handle regional language variations?”
Never hire someone for international keyword research without seeing examples of their previous work. The skill gap between good and mediocre is massive.
What Are Real-World Examples of International Keyword Research Done Right?
Theory is great, but let’s see how this actually works in practice.
Case Study 1: E-commerce Fashion Brand Expanding to Germany
Company: Mid-sized US fashion retailer Goal: Enter German market with translated site Challenge: Initial traffic was 80% lower than projected
Initial (failed) approach:
- Direct translation of US keywords
- “Shoes” → “Schuhe”
- “Women’s dresses” → “Damenkleider”
- “Plus size clothing” → “Übergrößen Kleidung”
Research findings:
- Germans search by specific product types, not generic categories
- “Sneaker” (English term) used more than German equivalent
- “Große Größen” (large sizes) preferred over “Übergrößen”
- Product material keywords much more important in Germany
Revised strategy:
- Focused on specific product types: “Lederstiefel” (leather boots), “Baumwollkleid” (cotton dress)
- Used hybrid English-German terms where appropriate: “Sneaker Damen” (women’s sneakers)
- Emphasized quality and material keywords
- Created content around German fashion concerns (quality, sustainability, fit)
Results (6 months post-revision):
- Organic traffic increased 340% from initial launch
- Conversion rate improved from 0.8% to 2.1%
- Bounce rate dropped from 67% to 41%
- Rankings achieved for 230 target keywords vs. 45 initially
Key takeaway: Local search behavior trumps literal translation every time. Understanding that Germans search with more specificity and care about different attributes changed everything.
Case Study 2: SaaS Company Targeting Spanish-Speaking Markets
Company: Project management software Markets: Spain, Mexico, Argentina, Colombia Challenge: Which Spanish-speaking market to prioritize, and how to customize for each
Research process:
- Analyzed search volume for core keywords across all four markets
- Evaluated competition in each market
- Assessed economic factors (willingness to pay for SaaS)
- Tested linguistic differences
Discoveries:
| Market | Primary Finding | Keyword Example | Competition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spain | Mature SaaS market, higher competition | “software gestión proyectos” | High |
| Mexico | Growing market, local tools dominate | “herramienta para proyectos” | Medium |
| Argentina | High interest, payment challenges | “app gestión trabajo” | Low |
| Colombia | Emerging market, mobile-first | “aplicación proyectos” (app vs. software) | Low |
Strategic decisions:
- Launched in Colombia first: Lower competition, mobile-friendly product fit market preference
- Different keyword targeting per market:
- Spain: Compete on advanced features
- Mexico: Emphasize ease of use and integration
- Colombia: Focus on mobile functionality
- Argentina: Highlight free tier and flexible pricing
Results:
- Colombia became fastest-growing market (180% YoY growth)
- Avoided head-to-head competition with entrenched Spanish competitors
- Learned market dynamics before tackling harder markets
- ROI on content creation: 4.2x within first year
Key takeaway: Not all markets in the same language are equal. Research helps you identify where you can win, not just where volume is highest. For more on market prioritization strategies, check this international SEO guide.
Case Study 3: Travel Blog Expanding to Asian Markets
Creator: English-language travel blogger Goal: Expand to Japanese and Korean markets Challenge: Completely different search behaviors and platforms
Research insights:
Japan:
- Google searches often longer, more specific: “2日間大阪観光おすすめコース” (2-day Osaka sightseeing recommended route)
- Yahoo! Japan still significant (though declining)
- Heavy emphasis on detailed itineraries
- Seasonal timing crucial (cherry blossom, autumn leaves)
Korea:
- Naver dominates search (55%+ market share)
- Visual content (Naver blog format) essential
- Keywords include specifics: “혼자 여행 제주도 맛집” (solo travel Jeju Island restaurants)
- Strong preference for personal experience content
Adapted approach:
- Created separate content strategies for each market
- Japan: Detailed day-by-day itineraries with transportation times
- Korea: Visual blog posts with personal photos and stories
- Used best tools for international keyword research: Naver Keyword Tool for Korea, Japanese Google Keyword Planner for Japan
- Partnered with local writers who understood search nuances
Results:
- Korean Naver blog traffic exceeded English blog within 8 months
- Japanese content ranked for 400+ long-tail keywords
- Monetization via affiliate links performing 2.3x better than English content
- Community engagement far higher in localized versions
Key takeaway: Sometimes the biggest insights come from understanding the platforms, not just the keywords. Search behavior follows platform design, and in markets where Google isn’t dominant, you need platform-specific strategies.
How Do You Track and Measure International Keyword Performance?
You’ve done the research, created the content, and launched in new markets. Now comes the critical part: measuring what’s actually working.
Setting Up Proper Tracking Infrastructure
International tracking requirements:
Separate Google Search Console properties for each language/region
- Set up country targeting appropriately
- Submit localized sitemaps
- Monitor hreflang errors (critical for international SEO)
Google Analytics 4 with proper segmentation
- Create segments for each market
- Set up custom reports by language
- Track conversions separately per region
- Monitor user behavior differences
Rank tracking tools configured by location
- Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Serpstat
- Set correct location for each keyword group
- Track local pack results if relevant
- Monitor SERP feature changes per market
- Market-specific conversion tracking
- Tag traffic sources by country/language
- Set up goals per market (they may differ)
- Track micro-conversions that indicate engagement
- Monitor currency-specific transaction values
Pro Tip: Create a centralized dashboard that shows performance across all markets in one view. This lets you quickly identify which markets are outperforming and which need attention. Tools like Google Data Studio (Looker Studio) or Tableau work well for this.
Key Metrics to Track by Market
Don’t just track rankings—measure actual business impact.
Essential metrics:
Metric What It Tells You Red Flags Organic impressions Keyword visibility growing Declining despite content additions Click-through rate Content relevance to searchers CTR below 2% for top 3 positions Average position Ranking progress Stuck outside top 20 after 6 months Organic traffic Actual visitors from search Traffic not matching impression growth Bounce rate Content meeting expectations Above 70% consistently Time on page Engagement with content Under 30 seconds average Pages per session Site exploration Under 1.5 pages Conversion rate Business value Below 1% for transactional content Revenue per visitor Market profitability Significantly lower than other markets Warning signs by metric:
High impressions but low clicks: Your titles/descriptions aren’t compelling in that language, or searchers don’t recognize your brand.
Good traffic but high bounce rate: Intent mismatch—you’re ranking for the wrong keywords, or your content doesn’t match cultural expectations.
Low conversions despite engagement: Trust issues, pricing problems, or checkout friction specific to that market.
Comparing Performance Across Markets
Raw numbers don’t tell the story—context matters. A keyword ranking #5 in Germany might drive more traffic than a #1 ranking in Portugal simply due to market size.
Normalized comparison framework:
Calculate efficiency scores for each market:
- Traffic efficiency = Organic traffic / Total impressions
- Conversion efficiency = Conversions / Organic traffic
- Revenue efficiency = Revenue / Marketing investment
- Ranking velocity = Average position improvement / Time
This lets you identify which markets are truly succeeding relative to their potential, not just which have the biggest raw numbers.
Example analysis:
Market A: 10,000 monthly visitors, 50 conversions (0.5% conversion rate) Market B: 2,000 monthly visitors, 60 conversions (3% conversion rate)
Market B is actually performing better despite lower traffic. Your keyword strategy there is attracting more qualified visitors.
Iterating Based on Data
Monthly review process:
Week 1: Data collection
- Export ranking data from all tools
- Pull GA4 reports for each market
- Review Search Console performance
- Document notable changes
Week 2: Analysis
- Identify winning keywords (traffic + conversions)
- Find underperforming content
- Spot new keyword opportunities from search queries
- Compare markets against each other
Week 3: Strategic decisions
- Double down on what’s working (create similar content)
- Fix or deprioritize what’s not working
- Add new keywords to target list
- Adjust content calendar accordingly
Week 4: Implementation
- Brief content team on findings
- Update keyword targeting in existing content
- Plan new content based on insights
- Adjust paid campaigns if running
Pro Tip: Look at your “Queries” report in Google Search Console for each market. You’ll discover keywords you’re accidentally ranking for—often these are the best opportunities because you’re already halfway there. Optimize existing content for these surprise rankings and watch your traffic jump.
What Are the Common Mistakes That Kill International Keyword Success?
Let me save you from the painful lessons I’ve learned (and watched others learn) the hard way.
Mistake 1: The “Translate and Forget” Approach
What it looks like:
- Translating your English keyword list word-for-word
- Assuming search behavior is universal
- Not validating with actual search data
Why it fails: People in different markets search differently, even for the same products. Cultural context, language nuances, and local preferences all affect keyword choice.
Real example: A US company targeting France translated “car insurance” to “assurance voiture.” Turns out French people search for “assurance auto” 5x more often. Six months of content targeting the wrong term.
The fix:
- Always validate translations with native search data
- Use local keyword tools, not just translated Google Keyword Planner
- Consult native speakers before finalizing keyword lists
Mistake 2: Ignoring Search Engine Market Share
What it looks like:
- Only using Google-based tools for all markets
- Assuming Google dominates everywhere
- Missing 50%+ of search traffic in some regions
Why it fails: Russia uses Yandex. China uses Baidu. Korea prefers Naver. Czech Republic has Seznam. Your Google keyword research is worthless in these markets.
The fix:
- Research dominant search engine before starting keyword research
- Use market-appropriate tools (Yandex.Wordstat, Baidu Keyword Tool, Naver Keyword Tool)
- Understand ranking factors differ between search engines
Mistake 3: Not Accounting for Voice Search Differences
Voice search is growing globally, but the queries are dramatically different by language and culture.
English voice search: “What’s the best Italian restaurant near me?” Spanish voice search: “Restaurantes italianos cerca” (shorter, still typed style) Japanese voice search: “この近くで一番美味しいイタリアンは” (longer, more conversational)
Voice search behavior varies by:
- Language structure (how natural voice queries sound)
- Device penetration (smart speakers more common in some markets)
- Cultural comfort with voice technology
The fix:
- Research voice search adoption rates in target markets
- Adjust keyword strategy for markets with high voice usage
- Create content answering conversational queries
Mistake 4: Forgetting About Mobile Search Differences
Mobile search behavior isn’t universal. Some markets are mobile-first, others still heavily desktop.
Mobile-first markets:
- India (80%+ mobile searches)
- Indonesia (75%+ mobile)
- Philippines (72%+ mobile)
- Nigeria (70%+ mobile)
Desktop-still-significant markets:
- United States (40%+ desktop for many B2B queries)
- Germany (38%+ desktop)
- UK (35%+ desktop)
Why it matters:
- Mobile searches are often shorter
- Local intent higher on mobile
- Mobile searchers want quick answers
- Page speed and mobile UX more critical
The fix:
- Check mobile vs. desktop breakdown per market in Analytics
- Optimize for mobile-first if that’s where your audience is
- Test your content on mobile devices in target markets
Mistake 5: Overlooking Competitor Keyword Gaps
Too many people focus on high-volume keywords everyone’s chasing, missing the gaps where competitors are weak.
The opportunity:
- Find keywords competitors rank for but you don’t
- Identify keywords where weak content ranks (you can beat them)
- Discover entire topic clusters competitors haven’t covered
How to find gaps:
- Export competitor rankings (use Ahrefs or SEMrush)
- Filter for keywords:
- They rank in positions 1-10
- You don’t rank at all or rank below position 20
- Search volume over your minimum threshold
- Difficulty score you can realistically achieve
- Analyze those SERPs to understand why they rank
- Create superior content targeting those keywords
Real example: A client was fighting for “social media marketing” in Spanish (incredibly competitive). I found 40+ related keywords like “calendario contenido redes sociales” (social media content calendar) where competition was weak and intent was better. They now rank #1-3 for most of those and get more qualified traffic.
Mistake 6: Not Updating Keywords as Markets Evolve
International keyword research isn’t a one-time project. Language evolves, trends change, new competitors emerge, and search behavior shifts.
Evolution examples:
- COVID introduced new keywords globally (“contactless delivery,” “work from home”)
- AI tools created entirely new search categories in 2023-2024
- Sustainability keywords grew dramatically in European markets
- Cryptocurrency terms exploded then contracted based on market conditions
The fix:
- Quarterly keyword audits for each market
- Monitor trending searches in Google Trends
- Track new competitor content and keywords
- Stay connected to market news and changes
For ongoing international SEO strategy updates, bookmark this comprehensive international SEO guide.
How Can You Use International Keyword Data to Inform Content Strategy?
Keywords aren’t just for SEO—they’re market intelligence that should shape your entire content approach.
Building Content Clusters from Keyword Research
Don’t just create random pages. Build topic clusters that establish authority.
Cluster structure:
Pillar content: Comprehensive guide on main topic
- Example: “Complete Guide to Running Shoes” (targeting high-volume head term)
Cluster content: Specific subtopics
- “Best Running Shoes for Flat Feet”
- “How to Choose Running Shoe Size”
- “Running Shoe Care and Maintenance”
- “Trail Running vs. Road Running Shoes”
Supporting content: Long-tail questions
- “Do running shoes expire?”
- “Can you use running shoes for walking?”
- “How often should you replace running shoes?”
This structure works internationally because:
- Each market has slightly different supporting questions
- You can prioritize clusters by market demand
- Internal linking passes authority within clusters
- It matches how people actually search (broad → specific)
Adapting Content Formats by Market Preference
Your keyword research reveals what content formats work best in each market through SERP analysis.
Market-specific preferences:
Video-heavy markets:
- United States (YouTube dominates many SERPs)
- Brazil (high YouTube penetration)
- India (mobile video consumption high)
Text-focused markets:
- Germany (detailed written content preferred)
- Japan (comprehensive articles with images)
- France (authoritative long-form content)
Visual/infographic markets:
- South Korea (visual platforms like Naver)
- China (WeChat visual content)
- Instagram-heavy demographics globally
Forum/community content:
- Russia (forum discussions rank well)
- Italy (community trust important)
- Markets with low brand trust
Pro Tip: Don’t force your preferred content format onto every market. If video content doesn’t rank well in your target market’s SERPs, don’t waste resources creating videos. Follow what actually works in each region.
Creating Market-Specific Content Calendars
Use keyword data to build content calendars that match local rhythms.
Seasonal considerations:
Holiday shopping:
- US: Thanksgiving through Christmas (Nov-Dec)
- China: Singles Day (Nov 11), Chinese New Year
- Brazil: Mother’s Day (May), Christmas (Dec)
- Middle East: Ramadan (dates vary)
Weather patterns:
- Winter sports keywords peak opposite in Southern Hemisphere
- Gardening content timing completely flips
- Fashion seasons reversed
Local events:
- Oktoberfest in Germany drives specific searches
- Carnival in Brazil creates content opportunities
- Local festivals, sports seasons, cultural events
Content calendar framework:
Month Market A Topic Market B Topic Market C Topic January New Year fitness Summer sales (AU) Winter clothing February Valentine’s gifts Back to school (AU) Carnival prep (BR) March Spring cleaning Autumn fashion (AU) Easter content This ensures you’re not publishing summer content when your Southern Hemisphere audience is in winter.
Using Keyword Data for Product Development
Here’s where international keyword research becomes truly strategic—it can inform what products or services you offer in each market.
What keyword research reveals about market needs:
Example 1: E-commerce sizing
- UK searches for “size conversion chart” indicate sizing confusion
- High volume for “European shoe sizes” in US
- Solution: Add size conversion tools, clearer sizing information
Example 2: Feature priorities
- Japanese searches emphasize product durability keywords
- US searches focus on speed and convenience
- German searches highlight quality and certifications
- Solution: Emphasize different features in each market’s product pages
Example 3: Missing product categories
- High search volume for a product you don’t offer yet
- Low competition in that market
- Solution: Consider adding that product line specifically for that region
Real scenario: A furniture company discovered high search volume for “standing desks under €300” in Germany but minimal search in the US for the same price point. They created a Germany-specific product line at that price point and dominated those keywords, generating €2M additional revenue in year one.
What’s the Future of International Keyword Research?
Let’s peek around the corner at where global keyword strategy is heading.
AI-Powered Search and Its Impact on Keywords
Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE) and AI overviews are changing how people search and what results they see.
What’s changing:
- Zero-click searches increasing (AI answers the question directly)
- Conversational queries becoming more common
- Traditional keyword optimization less important for some query types
- Position zero becoming even more valuable
How to adapt internationally:
- Focus on conversational long-tail keywords in all markets
- Optimize for featured snippets and AI overviews
- Create comprehensive content that answers full questions
- Build authority that AI tools reference
Important note: AI search rollout varies by market. SGE launched in US first, with international expansion ongoing. Monitor when AI features arrive in your target markets and adjust accordingly.
Voice Search Evolution Across Languages
Voice search is growing, but adoption rates vary wildly by market and language.
High adoption markets:
- United States (55% of smartphone users)
- UK (43%)
- China (voice commerce exploding)
- India (multilingual voice search growing)
Lower adoption markets:
- Japan (cultural hesitancy)
- Germany (privacy concerns)
- France (moderate adoption)
Keyword implications:
- Questions become more important (“how do I…” vs. “how to…”)
- Natural language phrasing matters more
- Local accents and dialects affect results
- Featured snippet optimization crucial (voice assistants read them)
Visual Search and International SEO
Google Lens, Pinterest Lens, and similar tools are changing search behavior, especially for products.
Image search keywords differ:
- More descriptive, visual terms
- Color and style descriptors more important
- Brand recognition matters more
- Less reliance on traditional text keywords
International considerations:
- Image search more popular in some markets (fashion, home decor)
- Local visual preferences differ (color associations vary culturally)
- Alt text and image names need localization
- Product photography styles vary by market
Predictive Search and Auto-Suggestions
Search engines are getting better at predicting what you’ll search before you finish typing.
Why this matters internationally:
- Autocomplete suggestions vary dramatically by market
- Google learns from local search patterns
- Voice and predictive search intersect
- First-word choices matter more than ever
Research implication: Mine autocomplete suggestions for each market as part of your keyword research. These represent what people are actually searching, not what tools predict they search.
Pro Tip: Set up a simple automated script (or use tools like Answer The Public) to regularly capture autocomplete suggestions for your core keywords in each market. Track how these change over time—this gives you leading indicators of trend shifts before search volume data confirms it.
Expert Tips for Mastering International Keyword Research
Let me leave you with battle-tested tactics that separate good international keyword research from great.
Tip 1: Create a Keyword Translation Database
Build a centralized resource that maps concepts across all your markets.
Structure:
- English concept/keyword
- Translation for each market
- Actual keyword used (may differ from translation)
- Search volume per market
- Competitive difficulty
- Notes on cultural context
This becomes institutional knowledge that saves time and prevents repeated mistakes as your team grows.
Tip 2: Establish Native Speaker Advisory Panels
For each major market, maintain relationships with 3-5 native speakers who understand your industry.
Not just translators—people who:
- Live in the market currently
- Are active online in that market
- Understand local search behavior
- Can provide quick validation on keyword choices
Pay them for quarterly reviews of your keyword strategy. The investment prevents massive mistakes and uncovers opportunities tools miss.
Tip 3: Test Keywords Before Full Content Investment
Before creating 50 pages targeting a keyword set, validate with small-scale tests:
- Create 3-5 pieces of high-quality content
- Target your top keyword opportunities
- Monitor for 60-90 days
- Measure actual performance vs. predictions
If results match predictions, scale up. If they don’t, investigate why before investing more.
Tip 4: Monitor Competitor Keyword Changes
Set up alerts to track when competitors enter new markets or adjust their keyword strategy.
What to monitor:
- New pages they create (indicates keyword opportunities they’ve identified)
- Changes to existing page optimization
- New markets they enter
- Keyword rankings they achieve
Tools for monitoring:
- SEMrush competitor alerts
- Ahrefs content alerts
- Google Alerts for competitor content
- Manual quarterly competitor audits
When a competitor suddenly ranks for new keywords in your shared markets, investigate why. They may have discovered something valuable.
Tip 5: Document Cultural Context Alongside Keywords
Don’t just track keywords—track the “why” behind them.
Document:
- Why this keyword is used vs. alternatives
- Cultural considerations for the topic
- Taboos or sensitive areas to avoid
- Local preferences affecting search behavior
- Seasonal patterns specific to that market
This context helps content creators, not just SEO teams, and prevents embarrassing cultural mistakes.
According to Aleyda Solis, international SEO consultant: “The biggest mistake companies make is treating international SEO as a translation project rather than a localization strategy. Keywords are cultural artifacts, not just words.”
For comprehensive guidance on turning keyword research into actual international rankings, explore this complete international SEO resource.
Frequently Asked Questions About International Keyword Research
How many keywords should I target per market?
Start with 20-30 primary keywords covering your core offerings, then expand to 100-200 supporting long-tail keywords as you create content. Quality over quantity—better to rank well for 50 relevant keywords than poorly for 500.
Should I do keyword research before or after building my international site structure?
Before. Your keyword research should inform your URL structure and content organization. If you build first and research later, you’ll likely need to restructure—expensive and time-consuming.
Can I use the same keyword research tools for all markets?
No. Google Keyword Planner works for most markets, but you need market-specific tools like Yandex.Wordstat (Russia), Baidu Keyword Tool (China), and Naver Keyword Tool (Korea) for comprehensive research in those regions.
How often should I update my international keyword research?
Quarterly audits for most markets. Monthly for rapidly changing markets or competitive industries. Annual deep-dive reviews minimum. Set calendar reminders so it doesn’t get forgotten.
What if there’s no search volume data for my target market?
Small markets often lack reliable volume data. In these cases: (1) Use similar-size market data as a proxy, (2) Rely more heavily on competition analysis, (3) Test with small content investments, (4) Monitor actual traffic rather than estimates.
How do I prioritize between markets with similar opportunity?
Consider: (1) Language similarity to existing markets (easier expansion), (2) Competition levels (go where you can win), (3) Business factors (shipping, payment, support capabilities), (4) Market maturity (early entry advantages vs. proven demand).
Should I create separate content for regional variations of the same language?
Yes, if: (1) Search volume justifies it, (2) Cultural or linguistic differences are significant, (3) You can maintain quality across versions. No, if: resources are limited—start with one variant (usually the largest market) then expand.
How do I handle keywords that don’t translate well or don’t exist in another language?
Document these! Some concepts don’t exist in all markets. You have three options: (1) Educate the market (create demand), (2) Find equivalent local concept, (3) Skip that keyword entirely. Education content works for innovative products; for commodity products, find the local equivalent.
What’s the minimum viable keyword list to start international content creation?
Start with:
- 5-10 high-intent commercial keywords
- 10-20 informational keywords
- 20-30 long-tail variations
- Total: 35-60 keywords
This gives you enough to create comprehensive initial content without overwhelming your resources.
How do I know if my international keyword strategy is working?
Track these indicators:
- Organic traffic growth in target market (20%+ quarterly = success)
- Ranking improvements for target keywords (50%+ keywords in top 20 within 6 months)
- Conversion rate from international traffic (should match or exceed domestic)
- Revenue per visitor by market (shows quality of traffic)
If traffic grows but conversions don’t, you have a keyword intent problem—revisit your research.
Final Thoughts: From Keywords to International Growth
Here’s the truth: international keyword research is one of those tasks that seems tedious until you see the results. Then it becomes the foundation of everything.
I’ve watched businesses 10x their international revenue by spending just two weeks on proper keyword research. And I’ve seen others waste $100K on translated content that never ranks because they skipped this step.
The companies winning internationally aren’t necessarily bigger, better funded, or more established. They’re the ones who took time to understand how people actually search in each market.
Your action plan starting today:
Week 1: Choose your first international market based on business factors and opportunity Week 2: Conduct thorough keyword research using the frameworks in this guide Week 3: Create your first 5-10 pieces of content targeting top keywords Week 4: Set up tracking and monitoring systems
Then repeat for your next market. Build the systems once, and scale them across every new region.
The internet connects the world, but search behavior is stubbornly local. Your job is to bridge that gap—one keyword at a time.
Remember: you’re not just researching keywords. You’re learning how millions of people think, search, and solve problems in languages and cultures different from your own. That’s not just SEO—that’s market intelligence that can transform your entire business strategy.
Now stop reading and start researching. Your next international market is waiting, and your competitors are already looking for those keywords.
Need more help with your international expansion? Check out the comprehensive international SEO guide for strategies on hreflang implementation, international link building, technical SEO, and market-specific tactics that complement your keyword research.
The world is your market. Make sure they can find you.