Ever wondered why your blog posts get tons of traffic but your service pages barely register a blip? Or why some websites seem to effortlessly guide visitors from one piece of content to another while yours feels like a digital maze?
Here’s the secret sauce: internal linking for different content types isn’t a one-size-fits-all strategy. What works brilliantly for blog posts can completely backfire on static pages, and vice versa.
Most website owners treat all content the same when it comes to internal linking. Big mistake. It’s like using the same marketing approach for teenagers and retirees – technically possible, but wildly ineffective.
In this guide, we’ll decode the art and science of content type linking strategies, showing you exactly how to optimize internal links for blogs versus pages to maximize both user experience and SEO performance.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhy Does Internal Linking Strategy Differ Between Content Types?
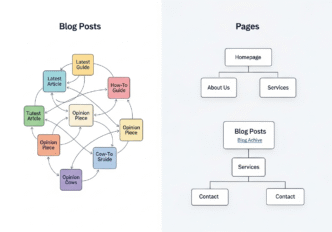
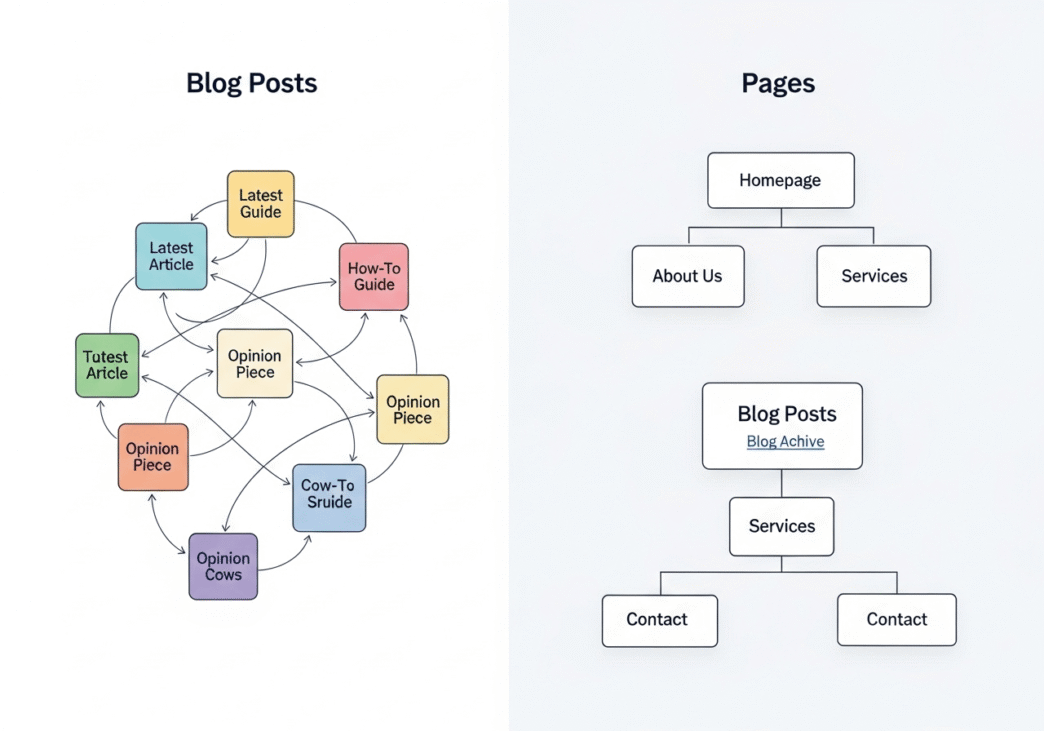
Think of your website as a library. Blog posts are like magazine articles – timely, engaging, meant to be consumed and shared. Static pages are like reference books – authoritative, comprehensive, designed for quick information retrieval.
Each serves a different purpose, attracts different user intent, and requires unique site structure considerations.
The Fundamental Differences
Blog posts typically target:
- Informational queries (how-to, what-is, why-does)
- Top-of-funnel awareness stage visitors
- Social sharing and engagement
- Temporal relevance and trending topics
Static pages usually focus on:
- Transactional queries (buy, hire, contact)
- Bottom-of-funnel decision-making visitors
- Business conversion and lead generation
- Evergreen authority and trust building
Understanding these differences is crucial for developing effective internal linking strategy for blog posts versus pages.
How Should You Approach Blog Post Linking Differently?
Blog post linking operates like a conversation between friends. It’s natural, contextual, and adds value to the discussion without being pushy.
The Blog Post Linking Philosophy
Blog content thrives on editorial links – those natural, in-context connections that enhance the reader’s understanding. Your goal isn’t to sell; it’s to educate and engage.
Key principles for blog post internal linking:
- Contextual relevance over keyword targeting
- User journey enhancement rather than conversion pushing
- Related topic clustering to build topical authority
- Natural anchor text that flows with content
Strategic Blog Post Link Placement
| Link Position | Purpose | Best Practices |
|---|---|---|
| Introduction | Set context and expectations | 1-2 foundational links to essential background |
| Body Content | Support arguments and provide depth | 2-4 contextual links to related topics |
| Conclusion | Guide next steps and related reading | 1-2 strategic “what’s next” links |
| Author Bio | Build authority and encourage exploration | 1-2 links to best content or about page |
Pro Tip: Use the “Wikipedia model” for blog linking. Notice how Wikipedia articles naturally link to related concepts that enhance understanding without disrupting reading flow.
What Makes Static Page Linking Strategy Unique?
Static pages operate more like a sales presentation. Every internal link should either build trust, provide proof, or guide visitors toward conversion.
The Static Page Linking Mindset
Unlike blogs, static pages have clear business objectives. Your navigational links and editorial links should work together to move visitors through your conversion funnel.
Core static page linking strategies:
- Trust-building links to testimonials, case studies, credentials
- Proof links to portfolio, certifications, awards
- Conversion-focused links to contact forms, pricing, demos
- Support links to FAQs, resources, documentation
Strategic Static Page Architecture
Homepage linking priorities:
- Primary navigation to key service/product pages
- Trust signals to about, testimonials, case studies
- Value propositions to feature explanations
- Conversion paths to contact or signup forms
Service/Product page linking:
- Related services to expand consideration
- Case studies to provide social proof
- Contact information for easy conversion
- Support resources to address concerns
How Do Content Hierarchy and Site Structure Impact Linking?
Content hierarchy is like the organizational chart of your website. It determines how authority flows and how users navigate your digital ecosystem.
Understanding Information Architecture
Your site structure should reflect user intent and business priorities:
Tier 1 (Homepage): Maximum authority, broadest appeal Tier 2 (Main categories): Balanced authority, targeted intent
Tier 3 (Subcategories/services): Focused authority, specific intent Tier 4 (Blog posts/details): Contextual authority, educational intent
Content Type Hierarchy Differences
| Content Type | Typical Hierarchy Level | Authority Flow Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Homepage | Tier 1 | Distribute to all key pages |
| Service Pages | Tier 2-3 | Concentrate on conversion |
| Blog Categories | Tier 2-3 | Build topical clusters |
| Individual Blog Posts | Tier 4 | Support cluster authority |
| Product Pages | Tier 3-4 | Focus on related products |
Real Example: A digital marketing agency restructured their site hierarchy, moving case studies from Tier 4 (buried in blog) to Tier 2 (main navigation). Result? 156% increase in consultation requests within three months.
What Are the Best Practices for Blog vs Static Page Internal Links?
Let’s break down the tactical differences between how to internally link different page types.
Blog Post Internal Linking Best Practices
1. Context-First Approach Link when it genuinely adds value to the reader’s understanding. Don’t force connections.
2. Natural Anchor Text Use phrases that flow naturally: “as we discussed in our guide to keyword research” rather than “keyword research guide.
3. Related Content Clusters Build topical authority by linking related posts together. Create content silos that demonstrate expertise.
4. Strategic Timing Link earlier in posts when possible – readers are most engaged in the first few paragraphs.
Static Page Internal Linking Best Practices
1. Conversion-Focused Placement Every link should either build trust or move toward conversion. Be strategic about destination pages.
2. Authority-Building Links Link to credentials, testimonials, case studies that support your value proposition.
3. Clear Value Proposition Make it obvious why someone should click. “See our results” is better than generic “click here.”
4. Reduced Cognitive Load Limit choices to prevent decision paralysis. 3-5 strategic links often work better than 15 options.
How Do Editorial Links vs Navigational Links Function Differently?
Understanding the distinction between editorial links and navigational links is crucial for effective content strategy.
Editorial Links: The Storytellers
Editorial links appear within content and serve the narrative. They’re contextual, valuable, and enhance understanding.
Best for:
- Blog posts explaining complex topics
- Case studies referencing methodologies
- How-to guides linking to prerequisite knowledge
- Research articles citing sources and related studies
Navigational Links: The Traffic Directors
Navigational links help users move between sections and find what they need. They’re structural, predictable, and efficiency-focused.
Best for:
- Header menus organizing main site sections
- Footer links providing access to important pages
- Breadcrumbs showing location within site hierarchy
- Related products showing similar options
Strategic Combination Approach
| Content Type | Editorial Link Ratio | Navigational Link Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Blog Posts | 70-80% | 20-30% |
| Service Pages | 40-50% | 50-60% |
| Product Pages | 30-40% | 60-70% |
| Homepage | 20-30% | 70-80% |
Pro Tip: Use heat mapping tools to understand how users interact with different link types. Editorial links often get higher engagement, while navigational links get more clicks.
What Content Formats Require Special Linking Considerations?
Different content formats demand unique internal links for various content formats strategies.
Long-Form Content (2000+ words)
- Table of contents with anchor links
- Section summaries linking to deep dives
- Regular contextual links (every 300-500 words)
- Related reading suggestions throughout
Video Content Pages
- Transcript links to related articles
- Equipment/tool links mentioned in videos
- Follow-up content for deeper learning
- Channel/playlist navigation
Resource Pages and Guides
- Step-by-step internal links to detailed processes
- Tool recommendations linking to reviews/comparisons
- Example links to case studies and implementations
- Update links to newer versions or related updates
E-commerce Product Pages
- Related products based on viewing/purchase behavior
- Category navigation for broader exploration
- Review links to detailed testimonials
- Support links for technical specifications
Case Study: An online course platform reorganized their lesson pages with strategic internal linking. They added “prerequisite links” to foundational concepts and “next steps” to advanced topics. Result? Course completion rates increased 67% and student satisfaction scores improved 34%.
How Can You Measure Internal Linking Success Across Content Types?
Measuring success requires different metrics for different content types.
Blog Post Performance Metrics
| Metric | What It Measures | Target Range |
|---|---|---|
| Time on Page | Content engagement | 2-4 minutes |
| Pages per Session | Internal link effectiveness | 2.5-4 pages |
| Social Shares | Content value perception | Varies by industry |
| Comment Engagement | Reader investment | Quality over quantity |
Static Page Performance Metrics
| Metric | What It Measures | Target Range |
|---|---|---|
| Conversion Rate | Business objective achievement | 2-5% (varies by industry) |
| Bounce Rate | Immediate value perception | Under 60% |
| Form Completions | Lead generation effectiveness | Track by source |
| Call-to-Action Clicks | Internal link relevance | 3-8% click rate |
Cross-Content Type Analysis
Use Google Analytics 4 to track:
- User flow between content types
- Conversion paths from blog to pages
- Exit points identifying optimization opportunities
- Content consumption patterns by traffic source
Pro Tip: Set up custom events in GA4 to track internal link clicks by content type. This reveals which linking strategies drive the most engagement and conversions.
What Are Common Mistakes in Content-Specific Internal Linking?
Let’s address the pitfalls that sabotage even well-intentioned internal linking strategy for blog posts and pages.
Blog Post Linking Mistakes
Over-optimization: Stuffing posts with keyword-rich anchor text Solution: Use natural language that enhances readability
Irrelevant linking: Adding links just to hit a quota Solution: Only link when it genuinely adds value
Timing issues: All links clustered at the end Solution: Distribute links throughout content naturally
Static Page Linking Mistakes
Conversion tunnel vision: Every link pushes toward sale Solution: Build trust with educational and proof links
Navigation overload: Too many choices causing paralysis Solution: Prioritize 3-5 most important paths
Trust signal neglect: Missing links to credentials and testimonials Solution: Include authority-building links strategically
Universal Linking Mistakes
Mobile ignorance: Links too small or close together Solution: Test internal links on mobile devices
Broken link neglect: Dead links harming user experience Solution: Regular audits using tools like our comprehensive internal linking guide
Advanced Strategies for Content Type Optimization
Ready to level up your content type linking strategies? Here are advanced techniques:
Dynamic Content Linking
Use algorithms to suggest related content based on:
- User browsing behavior
- Content similarity scores
- Conversion probability
- Seasonal relevance
Persona-Based Linking
Customize internal links based on:
- Traffic source (social vs search vs direct)
- Device type (mobile vs desktop)
- Geographic location
- Previous site behavior
Content Lifecycle Linking
Adapt linking strategies as content ages:
- New content: Link to related evergreen resources
- Trending content: Cross-link to capitalize on momentum
- Evergreen content: Update links to newer related content
- Outdated content: Redirect or update with fresh links
Pro Tip: Use A/B testing to optimize internal link placement and anchor text for different content types. What works for blog posts often fails on product pages.
Your Content-Specific Internal Linking Action Plan
Ready to implement? Here’s your roadmap:
Week 1: Content Audit and Classification
- Categorize all content by type and purpose
- Analyze current linking patterns across content types
- Identify high-performing and underperforming content
- Map user journeys between different content types
Week 2: Strategy Development
- Define linking objectives for each content type
- Create linking guidelines for content creators
- Establish measurement protocols for success tracking
- Design content hierarchy optimization plan
Week 3: Implementation and Testing
- Start with highest-impact pages (homepage, top blog posts)
- A/B test different linking approaches by content type
- Update existing content with improved internal links
- Train content team on new linking strategies
Week 4: Monitor and Optimize
- Track performance metrics by content type
- Identify successful patterns for scaling
- Adjust strategies based on early results
- Plan next month’s optimization priorities
Frequently Asked Questions
Should blog posts link to product pages?
Yes, but strategically. Link when the product genuinely solves a problem discussed in the blog post. Avoid forced, salesy connections that disrupt reading flow.
How many internal links should different content types have?
It varies by content type. Blog posts typically perform well with 3-5 contextual links, while service pages might need 8-12 strategic links for trust-building and navigation.
Do internal links from blog posts carry less weight than page links?
Not necessarily. Google values relevance and context over content type. A highly relevant blog post link can be more valuable than a random page link.
Should I use different anchor text strategies for blogs vs pages?
Absolutely. Blog posts benefit from natural, conversational anchor text, while static pages can use more direct, keyword-focused anchor text when appropriate.
How do I avoid cannibalization between similar content types?
Focus on user intent differentiation. Ensure blog posts target informational queries while pages target transactional queries, even for similar topics.
Final Thoughts: Content-Specific Linking Is Your Competitive Advantage
Internal linking for different content types isn’t just an SEO tactic – it’s a user experience strategy that can transform your website’s performance.
The websites dominating search results understand that blog post linking requires finesse and context, while page linking demands strategic focus and conversion optimization.
Your competitors are probably using the same linking approach across all content types. You’ll be crafting customized experiences that guide users naturally toward their goals.
Remember: great internal linking feels invisible to users but creates obvious value. When done right, visitors follow your links because they want to, not because you forced them to.
Start by understanding your content’s purpose, then build linking strategies that serve that purpose. Whether it’s educating through blog posts or converting through service pages, every internal link should earn its place.
Your content deserves a linking strategy as unique as its purpose. Time to give it one.
Ready to master advanced internal linking techniques? Explore our complete Internal Linking SEO Framework for detailed strategies that work across all content types and industries.