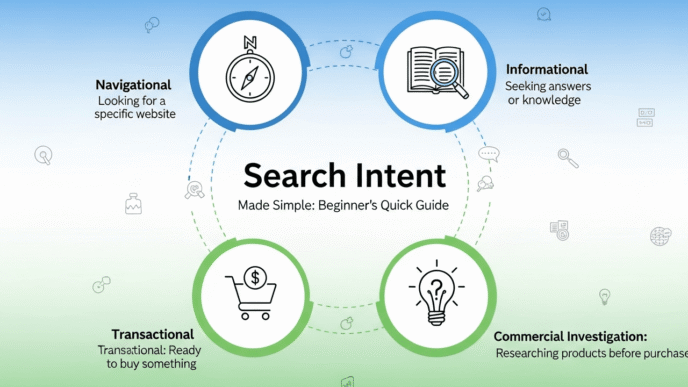
Ever created content you thought was perfect, only to watch it sink into Google’s digital graveyard? You’re not alone. The culprit? Misreading what people actually want when they search.
Learning how to identify search intent is like becoming a mind reader for your audience. It’s the difference between shooting arrows in the dark and hitting the bullseye every single time.
Here’s the brutal truth: 90% of content creators guess at user intent instead of analyzing it. They create what they think people want, not what search behavior actually reveals. That’s like opening a restaurant without asking what food people crave.
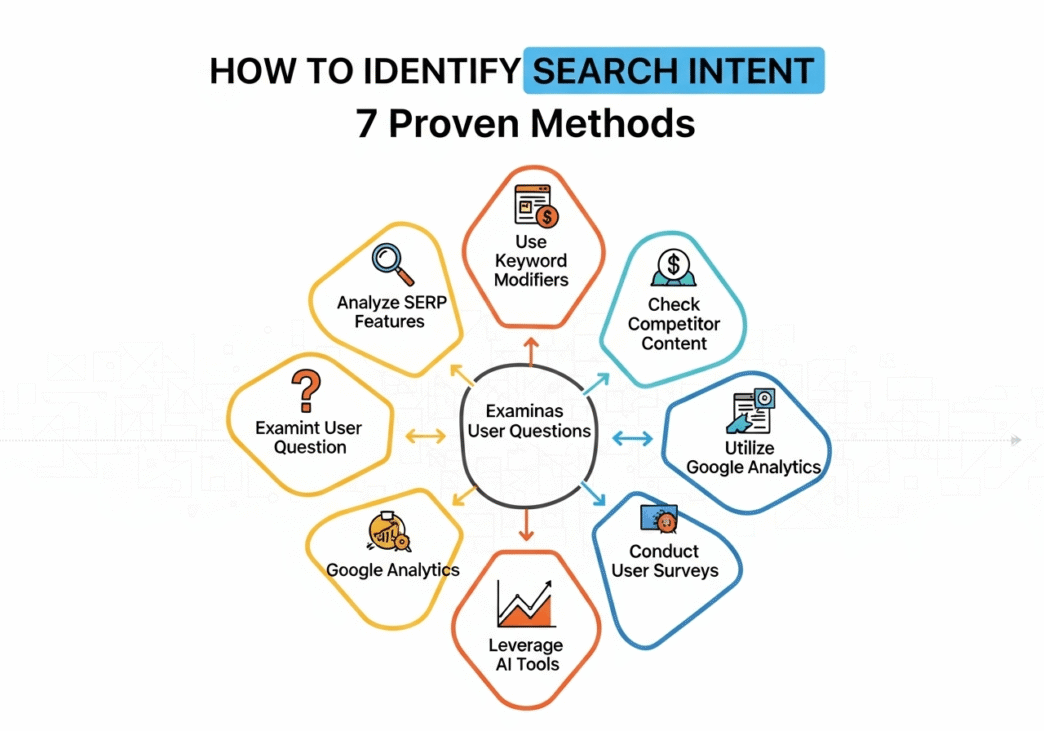
In this guide, we’ll reveal 7 proven search intent identification methods that’ll transform you from a content gambler into a strategic SEO mastermind. Ready to crack the code?
Table of Contents
Toggle
Why Is Learning How to Determine Search Intent for Keywords Crucial?
Search intent analysis isn’t just SEO theory – it’s your secret weapon for dominating search results. When you understand what users truly want, you create content that Google can’t ignore.
Think of Google as a matchmaker. It wants to connect searchers with content that perfectly satisfies their needs. When your content aligns with user intent research, you become Google’s favorite answer.
Studies show that content matching search intent gets 3x more organic traffic than misaligned content. More importantly, properly aligned content converts 5x better because it actually solves the user’s problem.
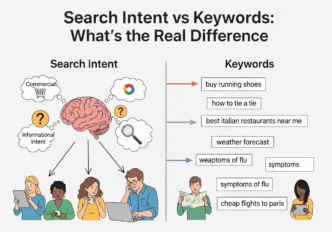
User query analysis reveals the hidden psychology behind every search. It’s like having a crystal ball that shows exactly what your audience needs at each stage of their journey.
What Are the Key Search Intent Signals You Should Look For?
Before diving into specific methods for analyzing search intent, you need to recognize the clues that reveal user motivation. These search intent signals are hiding in plain sight.
Language Pattern Indicators
Question words reveal information-seeking intent:
- “How to,” “What is,” “Why does,” “When should”
- “Best way to,” “Steps to,” “Guide for”
Comparison terms indicate commercial research:
- “vs,” “versus,” “compared to,” “alternatives”
- “Best,” “top,” “review,” “pros and cons”
Action words signal transactional intent:
- “Buy,” “purchase,” “order,” “download”
- “Hire,” “book,” “schedule,” “contact”
Brand mentions suggest navigational intent:
- Company names, product names, website names
- “[Brand] + login,” “[Brand] + support,” “[Brand] + pricing”
Search Volume and Competition Patterns
| Intent Type | Typical Search Volume | Competition Level | Commercial Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Informational | High volume, broad terms | Low-medium competition | Low immediate value |
| Commercial | Medium volume, specific | High competition | High research value |
| Transactional | Lower volume, targeted | Very high competition | Highest conversion value |
| Navigational | Varies by brand size | Low for own brand | Medium retention value |
Pro Tip: Don’t just look at search volume – analyze the competition. High competition for a keyword often indicates high commercial value and transactional intent.
How Can SERP Analysis Reveal True User Intent Behind Queries?
Search behavior analysis starts with studying what Google already knows. The search engine results page (SERP) is Google’s interpretation of user intent, based on billions of search interactions.
Method 1: SERP Feature Analysis
Google’s SERP features reveal intent like breadcrumbs:
Featured snippets indicate informational intent seeking quick answers Shopping results scream transactional intent Local pack shows location-based transactional needs People Also Ask boxes reveal related informational queries Knowledge panels suggest navigational or informational intent
SERP Content Type Analysis
| Content Type Ranking | Dominant Intent | What This Tells You |
|---|---|---|
| How-to articles, guides | Informational | Users want to learn or solve problems |
| Comparison pages, reviews | Commercial | Users are researching purchase decisions |
| Product pages, e-commerce | Transactional | Users are ready to buy |
| Brand homepages, about pages | Navigational | Users seeking specific websites |
Real Example: When analyzing “project management software,” the SERP shows comparison articles (60%), software company pages (30%), and review sites (10%). This reveals dominant commercial intent with some transactional overlap.
Method 2: Competitor Content Analysis
Study the top 10 results for your target keyword:
- What content formats are ranking? (Articles, videos, product pages)
- What angles do they take? (How-to, comparison, review)
- How comprehensive is their coverage?
- What user questions do they answer?
Pro Tip: Use the “Content Gap Analysis” technique – identify what top-ranking pages cover, then find opportunities they’re missing.
What Tools Can Help You Identify User Search Intent?
Keyword intent tools can supercharge your intent analysis techniques. Here are the best tools to identify user search intent without breaking the bank.
Free Search Intent Analysis Tools
| Tool | Best For | Key Features | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Search Console | Your existing content performance | Click-through rates, impressions by query | Only your site data |
| Google Keyword Planner | Basic intent signals | Search volume, competition levels | Limited intent classification |
| Answer The Public | Question-based intent discovery | Visual question mapping | No search volume data |
| Google Trends | Intent trend analysis | Seasonal patterns, related queries | No absolute volume numbers |
Premium Intent Analysis Tools
Semrush Keyword Magic Tool:
- Automated intent classification
- SERP feature tracking
- Related keyword clustering
- Competition analysis
Ahrefs Keywords Explorer:
- Intent probability scoring
- Parent topic identification
- SERP overview analysis
- Click potential metrics
Moz Keyword Explorer:
- Priority scoring system
- SERP feature tracking
- Organic click-through rate data
- Keyword difficulty assessment
Method 3: Advanced Google Search Operators
Use these search operators for deeper user intent research:
“Keyword” + inurl:review – Find review content (commercial intent) “Keyword” + inurl:buy – Identify purchase pages (transactional intent) “Keyword” + how OR what OR why – Discover informational content site:reddit.com “keyword” – Real user discussions and pain points
Pro Tip: Use Google’s “Search Tools” to filter by time periods and see how intent shifts seasonally or during industry events.
How to Research User Intent Behind Queries Using Question Analysis?
User query analysis goes beyond keywords to understand the questions behind searches. People don’t just search for topics – they search for solutions to specific problems.
Method 4: The “People Also Ask” Goldmine
Google’s “People Also Ask” (PAA) boxes are treasure troves of related intent signals:
- Search your target keyword
- Expand all PAA questions (they multiply as you click)
- Categorize questions by intent type
- Look for patterns in question progression
- Identify content gaps your competitors miss
Case Study: A SaaS company analyzed PAA for “email marketing automation.” They discovered 47 related questions spanning all intent types, from “What is email automation?” (informational) to “Best email automation pricing” (commercial). This insight guided their content strategy, resulting in 234% more qualified leads.
Method 5: Social Media and Forum Analysis
Real conversations reveal true intent better than any keyword tool:
Reddit analysis:
- Search “[keyword] reddit” in Google
- Study upvoted comments and questions
- Identify common pain points and solutions
Quora investigation:
- Find questions related to your keyword
- Analyze answer engagement levels
- Note what information users find most valuable
Facebook groups and LinkedIn discussions:
- Join industry-specific groups
- Monitor questions and discussions
- Document recurring themes and concerns
The Question Mapping Framework
| Question Type | Intent Category | Content Opportunity |
|---|---|---|
| “What is…” | Informational | Definition guides, explainer content |
| “How to…” | Informational | Tutorial content, step-by-step guides |
| “Best…” | Commercial | Comparison content, review roundups |
| “Where to buy…” | Transactional | Product pages, vendor directories |
Pro Tip: Create a “Question Bank” spreadsheet organizing all discovered questions by intent type. This becomes your never-ending content idea generator.
What Search Intent Identification Techniques Work Best for Beginners?
Search intent identification techniques for beginners should be simple, accurate, and immediately actionable. Here are foolproof methods that work every time.
Method 6: The 3-Second SERP Scan
This technique trains your eye to spot intent patterns instantly:
- Search your keyword in Google
- Scan the first 5 results for 3 seconds
- Ask yourself: “What do these pages help users DO?”
- Categorize based on the dominant action
If most results help users:
- Learn or understand → Informational intent
- Compare or research → Commercial intent
- Buy or act → Transactional intent
- Find a specific site → Navigational intent
The Beginner’s Intent Checklist
Step 1: Keyword Analysis
- ✅ Does it contain question words? (Informational)
- ✅ Does it mention brands? (Navigational)
- ✅ Does it include comparison terms? (Commercial)
- ✅ Does it contain action words? (Transactional)
Step 2: SERP Quick Check
- ✅ What’s the first result type?
- ✅ Are there shopping ads?
- ✅ Is there a featured snippet?
- ✅ What’s in the “People Also Ask” section?
Step 3: User Journey Mapping
- ✅ Where would this search fit in the customer journey?
- ✅ What would the user want to do next?
- ✅ What information do they need to progress?
Method 7: The Intent Validation Framework
Before creating content, validate your intent analysis:
Test 1: Search Volume Sense Check
- Informational: Higher volume, broader terms
- Commercial: Medium volume, specific terms
- Transactional: Lower volume, action-oriented
Test 2: Competition Reality Check
- High competition = High commercial value
- Featured snippets = Strong informational intent
- Shopping results = Clear transactional intent
Test 3: Business Value Assessment
- Does this intent align with your business goals?
- Can you create content that satisfies this intent?
- Will this intent lead to your desired conversions?
Pro Tip: Start with informational intent keywords – they’re easier to rank for and build topical authority. Once you dominate informational searches, target commercial and transactional terms.
How Do Seasonal Patterns Affect Search Intent Analysis?
Search behavior analysis reveals that intent shifts dramatically with seasons, events, and industry cycles. Understanding these patterns gives you a massive competitive advantage.
Seasonal Intent Shifts
Holiday seasons:
- Increased transactional intent for gift-related keywords
- “Best gifts for…” searches spike in commercial intent
- “How to…” holiday content gains informational traction
Back-to-school periods:
- Educational keywords show higher informational intent
- Product searches become more transactional
- Comparison content performs better
Industry-specific cycles:
- Tax season increases “how to” informational searches
- Fitness keywords spike in January (informational + commercial)
- Travel searches peak before vacation seasons (commercial → transactional)
Intent Evolution Tracking
| Time Period | Keyword: “Wedding Photography” | Dominant Intent Shift |
|---|---|---|
| January-March | “Wedding photography tips” | Informational (planning) |
| April-June | “Best wedding photographers near me” | Commercial (research) |
| July-September | “Book wedding photographer” | Transactional (hiring) |
| October-December | “Wedding photography packages” | Commercial (comparison) |
Real Example: A fitness equipment company tracked “home gym” intent patterns. During COVID lockdowns, intent shifted from commercial (“best home gym equipment”) to informational (“how to workout at home”). They pivoted content strategy and saw 445% traffic increase.
For comprehensive seasonal intent tracking strategies, explore our detailed Search Intent Optimization Guide with advanced timing frameworks.
What Are the Most Common Intent Identification Mistakes?
Even experienced marketers make costly search intent analysis errors. Here are the biggest traps and how to avoid them.
Mistake #1: Single-Intent Assumption
Problem: Assuming each keyword has only one intent type Reality: Many keywords show mixed intent in SERPs Solution: Analyze the full SERP distribution and create content addressing the dominant intent while acknowledging secondary intents
Mistake #2: Personal Bias Projection
Problem: Assuming your intent matches user intent Reality: Your industry knowledge creates blind spots Solution: Always validate assumptions with data from SERPs, tools, and user research
Mistake #3: Static Intent Thinking
Problem: Assuming intent never changes Reality: Intent evolves with seasons, trends, and user sophistication Solution: Regular intent audits and content updates based on performance data
Mistake #4: Tool Over-Reliance
Problem: Trusting tool classifications without verification Reality: Tools can misclassify intent, especially for niche topics Solution: Use tools as starting points, then validate with manual SERP analysis
Pro Tip: Create an “Intent Validation Checklist” that combines multiple methods. Never rely on a single signal to determine search intent.
Advanced Techniques for Professional Intent Analysis
Ready to level up your intent analysis techniques? These advanced methods separate pros from amateurs.
Multi-Layered Intent Mapping
Don’t just identify primary intent – map the complete user journey:
Layer 1: Primary intent classification Layer 2: Secondary intent opportunities
Layer 3: Intent progression pathways Layer 4: Conversion micro-moments
Cross-Device Intent Analysis
User intent varies by device and context:
Mobile searches often show higher local transactional intent Desktop searches typically involve more research (commercial intent) Voice searches lean heavily informational (“How do I…”) Tablet searches often mix research and entertainment
Intent Clustering Strategy
Group related keywords by intent patterns:
- Identify seed keywords in your niche
- Expand with intent-specific modifiers
- Group by user journey stage
- Create content clusters serving each intent type
- Link strategically between intent stages
Case Study: An e-commerce company used intent clustering for “coffee makers.” They created:
- Informational cluster: “How to choose coffee makers” (12 related articles)
- Commercial cluster: “Best coffee makers 2025” (comparison content)
- Transactional cluster: Product pages with optimized buying experience
Result? 67% increase in organic revenue and 43% improvement in conversion rates.
Your Search Intent Identification Action Plan
Ready to master how to research user intent behind queries? Here’s your step-by-step implementation roadmap:
Week 1: Foundation Building
- Audit existing content using the 3-second SERP scan method
- Create intent classification spreadsheet for your top 50 keywords
- Set up Google Search Console for ongoing intent performance tracking
- Begin competitor SERP analysis for your primary keywords
Week 2: Tool Integration
- Choose 2-3 intent analysis tools (start with free options)
- Create keyword research workflow incorporating intent identification
- Set up Google Alerts for your target keywords to monitor SERP changes
- Begin social media intent research in relevant communities
Week 3: Content Strategy Development
- Map content gaps by intent type using your research
- Create content calendar organized by intent categories
- Develop content templates for each intent type
- Plan internal linking strategy between intent stages
Week 4: Implementation and Testing
- Publish intent-optimized content starting with informational topics
- Monitor performance metrics specific to each intent type
- A/B test different intent approaches for similar keywords
- Document successful patterns for scaling
For advanced implementation strategies and professional frameworks, dive deeper into our comprehensive Search Intent Mastery Guide.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take to master search intent identification?
Most beginners see significant improvement within 2-3 weeks of consistent practice. The key is analyzing 5-10 keywords daily using multiple methods until pattern recognition becomes automatic.
Can search intent change for the same keyword over time?
Absolutely! Intent evolves with user sophistication, industry changes, and seasonal patterns. Monitor your target keywords quarterly and adjust content strategy accordingly.
What’s the biggest red flag that I’ve misidentified intent?
High bounce rates and low engagement are clear warning signs. If users quickly leave your page, you’ve likely mismatched their intent with your content approach.
Should I target multiple intents on one page?
Generally, focus on one primary intent per page for best results. However, comprehensive content can acknowledge secondary intents through additional sections or internal linking.
How do I handle keywords with mixed intent signals?
Analyze the SERP distribution to identify the dominant intent (usually 60%+ of results). Create content for the primary intent while acknowledging secondary intents through related sections.
What tools do professional SEOs use for intent analysis?
Most pros combine multiple approaches: Semrush or Ahrefs for data, manual SERP analysis for validation, and social listening for real user insights. No single tool provides complete intent pictures.
How does voice search affect intent identification?
Voice searches typically show stronger informational and local transactional intent. They’re more conversational and question-based, requiring natural language optimization strategies.
Final Thoughts: Intent Analysis Is Your SEO Superpower
Learning how to identify search intent transforms you from a content creator into a user experience architect. When you truly understand what people want, creating valuable content becomes effortless.
Your competitors are still playing the keyword volume game. You’ll be playing the user satisfaction game – and winning every time.
Remember: Google’s algorithm gets more sophisticated daily, but it still has one primary goal – satisfying user intent. When you align with this mission, you become Google’s preferred answer provider.
The 7 methods in this guide aren’t just techniques – they’re your roadmap to SEO mastery. Start with the basics, master the fundamentals, then advance to professional-level intent analysis.
Search intent identification isn’t about reading minds – it’s about reading data, understanding patterns, and creating content that perfectly matches user needs at every stage of their journey.
Your audience is searching right now. Make sure you’re ready with exactly what they need.
Ready to become a search intent master? Explore our advanced Search Intent Strategy Framework for professional-level techniques and industry case studies that’ll elevate your SEO game to the next level.