Ever searched for “why does my phone battery drain so fast” and gotten perfect results about battery optimization—even though the top-ranking pages never used those exact words?
That’s not luck. That’s neural matching SEO doing what keyword matching could never do: understanding what you mean, not just what you typed.
Here’s what most SEO professionals still don’t understand: Google doesn’t just match words anymore. Their neural matching system connects concepts, understands synonyms in context, and bridges the gap between how people search and how content creators write.
And if you’re still optimizing for exact keyword matches in 2025, you’re fighting yesterday’s algorithm with tactics that stopped working years ago.
Let me show you exactly how Google neural matching works, why it’s revolutionizing search results, and—most importantly—how to optimize your content so Google’s AI recognizes it as the perfect match for queries, even when you don’t use the exact keywords.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is Neural Matching in Google Search?
Neural matching is Google’s AI-powered system that understands the concepts and intent behind search queries, then matches them to relevant content based on meaning rather than just keyword presence.
Think of it as Google’s “concept translator.” When someone searches, neural matching asks: “What is this person really trying to find?” Then it looks for content that answers that need—regardless of whether it uses the same words.
The Simple Explanation
Old Google (keyword matching):
- Query: “remedy for headache”
- Matches: Pages containing “remedy” AND “headache”
- Misses: Great pages about “headache relief” or “curing migraines”
New Google (neural matching):
- Query: “remedy for headache”
- Understands: Person wants solutions for head pain
- Matches: Pages about headache relief, migraine cures, tension headache solutions, pain management—even if they never say “remedy”
The system recognizes that “remedy,” “relief,” “cure,” “treatment,” and “solution” are conceptually related when discussing headaches.
When Google Introduced Neural Matching
Google launched neural matching in September 2018, though they’d been testing it for months before. According to Google’s announcement, it affects about 30% of queries—making it one of the most impactful AI systems they’ve deployed.
Why it matters: That 30% includes many long-tail, conversational queries where exact keyword matching fails. These are often the queries with highest commercial intent and lowest competition.
Pro Tip: Neural matching particularly helps with queries Google has never seen before (which represents about 15% of daily searches). If you’re targeting unique, specific long-tail keywords, neural matching is why you can rank without thousands of backlinks.
For understanding how neural matching fits into Google’s broader AI ecosystem, see the complete guide to AI and machine learning in search.
How Does Google Neural Matching Work? (The Non-Technical Version)
Let’s break down how Google neural matching works without drowning in computer science jargon.
The Neural Network Foundation
Neural matching uses neural networks—AI systems modeled loosely on how human brains process information. These networks have been trained on billions of searches to understand:
- Which queries are conceptually similar
- Which words and phrases mean the same thing in different contexts
- What concepts typically appear together
- How people express the same need in different ways
Simple analogy: Imagine you hired someone to organize your music library. They don’t just sort by song titles (keyword matching). They understand that:
- “Rock” and “Alternative Rock” are related but different
- “Chill” and “Relaxing” express similar moods
- A song about heartbreak fits multiple emotional categories
- Context matters (is this 80s rock or indie rock?)
Neural matching does this for search queries and web content—understanding relationships, context, and meaning beyond exact word matches.
Word Embeddings: How AI Understands Meaning
At the core of neural matching is something called word embeddings—a way of representing words as mathematical vectors that capture their meaning.
What this means practically:
Words with similar meanings cluster together in this mathematical space:
- “Dog,” “puppy,” “canine” are all close together
- “Fast,” “quick,” “rapid” form another cluster
- “Happy,” “joyful,” “delighted” group nearby
But here’s where it gets sophisticated: The system understands context:
- “Apple” near “fruit,” “orchard,” “pie” = the fruit
- “Apple” near “iPhone,” “Mac,” “tech” = the company
- Same word, different meaning, correctly understood by position relative to other concepts
Query-to-Document Matching
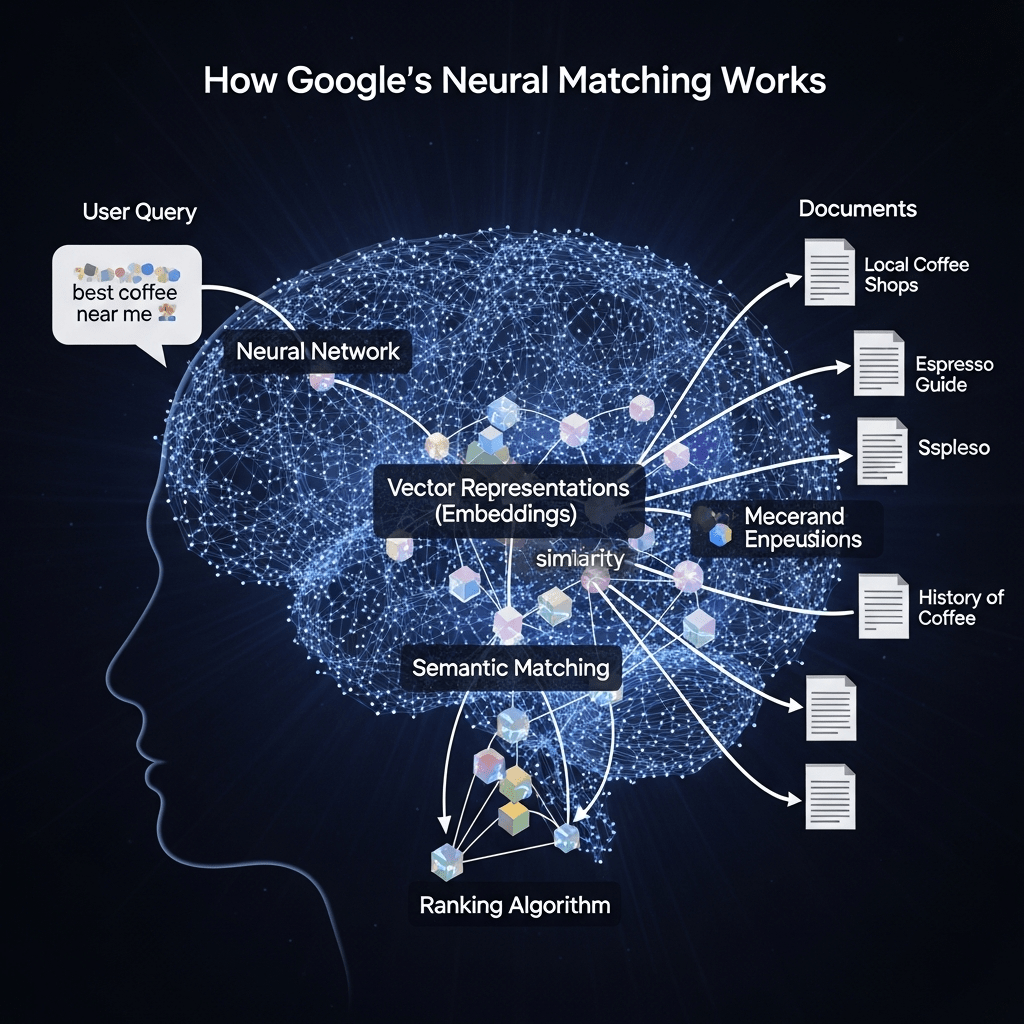
Here’s the process when you search:
Step 1: Query Understanding Neural matching converts your search query into a mathematical representation capturing its conceptual meaning.
Query: “best way to remove red wine stains” Concepts identified: stain removal, wine specifically (not general stains), fabric care, household cleaning
Step 2: Document Analysis Web pages are also represented as conceptual vectors based on their content.
Page A: “Red wine stain removal guide” (obvious match) Page B: “Getting wine out of carpet: Complete guide” (neural matching connects this!) Page C: “Carpet cleaning tips” (too generic, weak connection)
Step 3: Semantic Matching Neural matching calculates conceptual similarity between query and documents:
- Pages A & B both score high (both specifically address the concept, different words)
- Page C scores lower (generic cleaning, doesn’t specifically address wine or stains)
Step 4: Ranking Integration Neural matching scores combine with other ranking factors (links, E-E-A-T, user signals) to determine final rankings.
What Makes It “Neural”?
The “neural” part refers to the network structure that learns these relationships through training on massive datasets:
Training process:
- Feed the system billions of query-click pairs
- “When people searched X, they clicked pages about Y”
- Network learns conceptual relationships from successful matches
- Patterns emerge: certain concepts consistently satisfy certain query intents
- System generalizes these patterns to new, unseen queries
The result: Google can match queries to relevant content even when there’s no keyword overlap, because the neural network learned conceptual relationships from billions of real user interactions.
Neural Matching vs Other Google AI Systems
People often confuse neural matching with RankBrain or BERT. Here’s how they’re different:
RankBrain (2015):
- Purpose: Interprets ambiguous queries, measures user satisfaction
- How it works: Machine learning from user behavior patterns
- Focus: “Which results satisfy users for this query?”
BERT (2019):
- Purpose: Understands natural language and context within queries
- How it works: Deep learning transformer networks analyzing word relationships
- Focus: “What does this query actually mean given word context?”
Neural Matching (2018):
- Purpose: Connects conceptually related queries and content
- How it works: Neural networks mapping semantic similarity
- Focus: “What concepts does this query represent, and which pages discuss those concepts?”
How they work together:
Query: “can you bring food through airport security”
- BERT understands: “through security” is critical context (not just general airport rules)
- Neural Matching recognizes: This relates to TSA regulations, carry-on rules, liquid restrictions concepts
- RankBrain measures: Which results actually satisfy users asking this specific question
Each system handles a different aspect of delivering the right result. They’re complementary, not competing.
Real Examples of Neural Matching in Action
Let’s look at actual neural matching vs keyword matching examples to see the difference.
Example 1: The Homeowner Query
Search: “insights into why a TV looks bad”
What traditional keyword matching would do:
- Look for pages with “TV,” “looks,” and “bad”
- Might return troubleshooting guides, TV reviews mentioning picture quality
- Miss highly relevant content using different terminology
What neural matching does: Google understands this query is about:
- Display quality issues
- Picture settings problems
- Resolution and color accuracy
- TV calibration
Pages that rank (even without exact keywords):
- “TV Picture Quality Settings Guide”
- “Calibrating Your Television for Better Image”
- “Why Your TV Colors Look Washed Out”
- “Display Settings That Ruin Picture Quality”
Notice: None use the exact phrase “looks bad,” but all address the underlying concept.
Example 2: The Health Query
Search: “why do I feel exhausted after eating”
Keyword matching approach:
- Match: “exhausted” + “eating”
- Miss: Articles about “post-meal fatigue” or “food coma”
Neural matching approach: Recognizes these concepts are related:
- “Exhausted” = “tired” = “fatigued” = “sleepy” = “drowsy”
- “After eating” = “post-meal” = “following dinner” = “food-induced”
- The query is about postprandial somnolence (medical term)
Results include:
- “Why You Feel Tired After Eating”
- “Post-Meal Fatigue Explained”
- “Food Coma: What Causes Sleepiness After Meals”
- “Managing Energy Levels Throughout the Day”
Neural matching connects the medical concept across all these different phrasings.
Example 3: The Technical Query
Search: “make computer run faster”
Traditional matching limitations:
- Focuses on pages with exact phrase
- Might miss technically superior content using proper terminology
Neural matching understanding: This query relates to:
- Computer performance optimization
- System speed improvements
- Resource management
- Hardware/software upgrades
- PC maintenance
Ranking content includes:
- PC Performance Optimization Guide”
- “Speed Up Your Computer: 10 Proven Methods”
- “System Resource Management Tips”
- “Hardware Upgrades That Boost Performance”
The best technical content doesn’t say “make run faster”—it uses proper terminology like “optimization” and “performance.” Neural matching bridges this vocabulary gap.
Example 4: The Shopping Query
Search: “affordable organic vegetables near me”
Neural matching connects:
- “Affordable” = “cheap” = “budget-friendly” = “inexpensive” = “low-cost”
- “Organic” = specific agricultural standard
- “Vegetables” = produce category
- “Near me” = local availability, geographic proximity
Results can include:
- “Budget Organic Produce: Where to Shop”
- “Cheap Organic Food Options in [City]”
- “Finding Inexpensive Organic Groceries”
- Farmers markets, co-ops, discount organic retailers
Even if business names don’t include “affordable” or “vegetables,” neural matching recognizes they satisfy the query intent.
The Pattern: Concept Over Keywords
What all these examples show:
✅ Neural matching prioritizes: Conceptual relevance, semantic similarity, intent satisfaction
❌ Neural matching deprioritizes: Exact keyword matching, forced keyword repetition, unnatural phrasing
The SEO implication: Writing naturally about topics while covering related concepts comprehensively beats keyword-stuffed content optimized for exact phrases.
How Neural Matching Affects Different Query Types
Neural matching technology impacts various search queries differently. Understanding these patterns helps you optimize appropriately.
Long-Tail Conversational Queries (Highest Impact)
Why neural matching matters most here:
- People use natural, varied language
- Exact keyword matching often fails
- Conceptual understanding is critical
Example: “what’s that disease where you can’t feel pain”
Neural matching understands:
- Medical condition query
- Symptom: inability to sense pain (analgesia)
- Relates to genetic conditions, nerve disorders
- Medical term: congenital insensitivity to pain (CIP)
Optimized content doesn’t need exact query phrasing:
- Can use medical terminology naturally
- Explains the concept comprehensively
- Covers related conditions and symptoms
- Neural matching connects the dots
Voice Search Queries (Major Impact)
Why it’s critical:
- Voice queries are more conversational
- People speak differently than they type
- Longer, more complex phrasing
Typed: “pizza near me” Spoken: “where can I get really good authentic Italian pizza that’s open right now”
Neural matching bridges the gap:
- Understands “really good” = high-rated, quality
- “Authentic Italian” = specific cuisine style
- “Open right now” = current availability
- Connects to: restaurant reviews, Italian restaurants, hours of operation
Optimization approach: Answer conversational questions naturally; neural matching will connect your content to various phrasings of similar intents.
Product Search Queries (Moderate Impact)
Neural matching helps when:
- People use colloquial product names
- Searching for product categories, not specific models
- Using descriptive phrases instead of technical terms
Example: “laptop that doesn’t get super hot”
Neural matching understands:
- Thermal management concern
- Looking for: cooling systems, efficient processors, good ventilation
- Technical equivalents: thermal throttling, heat dissipation, cooling solutions
Content can use technical terms:
- “Best Laptops with Superior Thermal Management”
- “Cool-Running Laptops for Heavy Use”
- “Laptops with Excellent Heat Dissipation”
All match the colloquial query through conceptual understanding.
Short Head Keywords (Lower Impact)
Why neural matching matters less:
- Clear, unambiguous queries
- Keywords well-established
- Less variation in phrasing
Example: “weather New York”
This is straightforward—doesn’t need conceptual interpretation. Traditional keyword matching handles it fine.
Neural matching still helps with:
- Related concepts people might actually want (forecast, radar, alerts)
- Informational needs beyond current conditions
- Context-specific variations
Ambiguous Queries (Critical Impact)
Where neural matching excels:
- Queries with multiple possible meanings
- Context determines the right interpretation
Example: “mercury”
Possible meanings:
- Chemical element (science)
- Planet (astronomy)
- Roman god (mythology)
- Car brand (automotive)
- Freddie Mercury (music)
Neural matching evaluates:
- User’s search history and context
- Related queries in session
- Geographic and demographic signals
- Which concept most likely intended
Then matches to conceptually appropriate content for that user’s likely intent.
The Optimization Principle
For all query types:
Instead of asking: “What exact keywords should I target?”
Ask: “What concepts and related topics should my content comprehensively cover?”
Neural matching rewards the latter approach.
Optimizing for Google Semantic Search: Practical Strategies
Now for the actionable part: optimizing for Google semantic search that neural matching powers.
Strategy #1: Topic Clusters Over Individual Keywords
Old approach:
- Target individual keywords one page at a time
- “Best coffee makers” = one page
- “Coffee maker reviews” = another page
- “How to choose coffee maker” = third page
Neural matching approach:
- Create comprehensive topic coverage
- One pillar page: “Complete Coffee Maker Guide”
- Covers buying advice, reviews, comparisons, usage tips
- Neural matching connects this to ALL related queries
Why it works: Neural matching recognizes comprehensive topical coverage. A single authoritative resource on “coffee makers” matches queries using any related phrasing because the conceptual match is strong.
Implementation:
- Identify your core topic
- List all related concepts and questions
- Create one comprehensive resource covering all angles
- Let neural matching connect it to various query formulations
Strategy #2: Use Semantic Keyword Variations Naturally
Don’t do this (keyword stuffing): “If you want to remove red wine stains, removing red wine stains is important. Red wine stain removal requires knowing how to remove red wine stains effectively.”
Do this (natural semantic coverage): “Wine spills on carpet are stressful, but removing the stain is manageable with quick action. The key to eliminating wine discoloration from fabric is treating it before it sets. Here’s how to clean up wine accidents effectively.”
Notice: Second example uses:
- “Wine spills” instead of “red wine stains”
- “Eliminating discoloration” instead of “removing stains”
- “Clean up accidents” instead of “remove stains”
Neural matching understands these are all conceptually related. Natural variation beats forced repetition.
Strategy #3: Cover Related Concepts Comprehensively
Neural matching looks for topical completeness.
Example: Article about “running for beginners”
Minimum (poor neural matching):
- Basic tips
- Mentions running shoes
- 500 words
Comprehensive (strong neural matching):
- Proper form and technique
- Choosing appropriate footwear
- Training schedules for beginners
- Injury prevention
- Nutrition for runners
- Progressive overload principles
- Common beginner mistakes
- Recovery and rest
- Motivation strategies
Why comprehensive wins: Neural matching recognizes this covers the full conceptual space around “beginning running.” It will match to queries about:
- “How to start running”
- “Running tips for beginners”
- “Getting started with jogging”
- “First time runner guide”
- “Learn to run from scratch”
All conceptually related, one comprehensive resource satisfies all.
Strategy #4: Answer Related Questions You Anticipate
Neural matching rewards anticipating user needs.
Main query: “how to make sourdough bread”
Related concepts people need:
- What is sourdough starter
- How long does fermentation take
- Why did my bread not rise
- Difference between sourdough and regular bread
- Equipment needed
- Troubleshooting common problems
Optimized content addresses these proactively: Not because you’re keyword stuffing, but because comprehensively explaining sourdough naturally requires covering these concepts.
Tools to find related concepts:
- Google’s “People Also Ask”
- Related Searches” at bottom of results
- AnswerThePublic for question variations
- AlsoAsked for question relationships
Strategy #5: Use Proper Terminology AND Common Language
Neural matching bridges vocabulary gaps.
Example: Technical topic for general audience
Don’t choose between:
- Technical terms only (alienates general users)
- Colloquial only (lacks depth)
Do both: “If your laptop overheats (gets excessively hot during use), the issue is likely thermal throttling—when the processor automatically slows down to prevent heat damage. This manifests as your computer feeling very warm and running slower than normal.”
Why this works:
- Uses technical term: “thermal throttling”
- Explains in common language: “overheats,” “gets hot,” “runs slower”
- Neural matching connects both vocabularies to appropriate queries
- Ranks for both technical and beginner searches
Strategy #6: Build Topical Authority Through Consistency
Neural matching evaluates your entire site’s topical focus.
Strong signal:
- 50+ articles about digital photography
- Covers cameras, techniques, editing, lighting, composition
- Consistent expertise in photography domain
Weak signal:
- 10 articles about random topics
- Photography, cooking, travel, finance, fitness
- No clear topical authority
Why topical focus matters: Neural matching evaluates whether your site is a conceptual authority on a subject. Sites recognized as authorities get stronger matches for related queries.
Strategic approach:
- Pick your core topic(s)
- Create comprehensive coverage
- Stay focused on related concepts
- Build depth before breadth
- Become the go-to resource for that conceptual space
Strategy #7: Optimize for User Intent, Not Just Keywords
Neural matching prioritizes intent satisfaction.
Query: “best laptop for video editing”
Wrong approach:
- List laptops with keyword “best laptop for video editing”
- Surface-level descriptions
- Generic recommendations
Right approach:
- Explain what video editing requires (processing power, RAM, graphics)
- Discuss different video editing levels (basic vs professional)
- Recommend specific models with justification
- Include real performance benchmarks
- Address specific use cases (4K editing, color grading, rendering)
Why intent optimization works: Neural matching recognizes when content truly satisfies the underlying need. Comprehensive intent-matched content outranks keyword-matched surface content.
Strategy #8: Update Content to Maintain Semantic Relevance
Neural matching evaluates freshness of concepts.
Outdated conceptual coverage: Article about “smartphone features” mentioning:
- Physical keyboards
- Removable batteries
- 3.5mm headphone jacks
Current conceptual coverage:
- 5G connectivity
- Multi-camera systems
- Foldable displays
- AI-powered features
Neural matching recognizes outdated conceptual frameworks and favors content reflecting current understanding of topics.
Maintenance strategy:
- Review top content quarterly
- Update with current concepts and terminology
- Add new related topics as they emerge
- Remove outdated references
- Keep semantic relevance fresh
For building systematic topical authority that neural matching rewards, see comprehensive strategies in AI-powered content optimization.
Neural Matching and Content Quality Signals
Semantic search algorithm evaluation goes beyond just concept matching—it integrates with quality assessment.
How Neural Matching Evaluates Content Depth
Shallow content (weak neural matching): “Dogs are good pets. They are loyal. People like dogs.”
Conceptual coverage: Dogs, pets, loyalty (minimal depth)
Deep content (strong neural matching): “Dogs offer companionship and emotional support that research shows reduces stress hormones and blood pressure. Different breeds suit different lifestyles—active families might prefer energetic labs, while apartment dwellers often choose smaller, quieter breeds like pugs. The commitment includes daily exercise, veterinary care, training, and socialization to ensure a well-adjusted pet.”
Conceptual coverage: Companionship, health benefits, breed selection, lifestyle matching, care requirements, training, socialization (comprehensive depth)
Neural matching rewards depth because comprehensive conceptual coverage indicates expertise and value.
The Semantic Completeness Factor
Query: “starting a podcast”
Incomplete semantic coverage:
- Mentions equipment
- Basic recording tips
- 800 words
Complete semantic coverage:
- Equipment selection and budget options
- Recording and editing software
- Audio quality optimization
- Content planning and structure
- Interview techniques
- Publishing platforms
- Promotion strategies
- Monetization options
- Legal considerations (music licensing, etc.)
- Technical troubleshooting
- 3000+ words
Why completeness matters: Neural matching evaluates whether content covers the full conceptual space around a topic. Incomplete coverage results in weaker matching to comprehensive queries.
Natural Language Patterns Neural Matching Prefers
Forced/Unnatural (penalized): “Coffee makers are important. When you buy coffee makers, coffee maker quality matters. Best coffee makers brew coffee well.”
Natural (rewarded): “Choosing the right coffee maker depends on your brewing preferences and lifestyle. If you’re always rushing out the door, a programmable drip machine ensures fresh coffee when you wake up. Pour-over enthusiasts appreciate the control and ritual, while espresso lovers need machines with proper pressure systems.”
The difference:
- Natural language uses varied vocabulary
- Concepts flow logically
- Reads like human explanation
- Covers related ideas organically
Neural matching was trained on natural human language, so it recognizes and rewards natural patterns.
Entity Recognition and Neural Matching
Entities (specific people, places, things) strengthen neural matching:
Generic: “Use social media to promote your business. Post regularly and engage with followers.”
Entity-rich: “Use Instagram and TikTok to reach younger demographics, while LinkedIn and Facebook remain effective for B2B and older audiences. Tools like Hootsuite or Buffer streamline scheduling, and platforms like Canva simplify visual content creation.”
Why entities matter: Neural matching recognizes specific entities and their relationships to concepts. Entity-rich content demonstrates concrete, practical knowledge versus abstract generalities.
The E-E-A-T Connection
Neural matching correlates with E-E-A-T signals:
Experience signals:
- First-hand details show deep conceptual understanding
- “I tested 15 different…” demonstrates experiential knowledge
- Specific examples indicate genuine expertise
Expertise signals:
- Proper terminology used naturally
- Nuanced understanding of concepts
- Comprehensive coverage of related topics
Authority signals:
- Referenced by other content (conceptual authority)
- Consistent topical focus (subject matter authority)
- Entity mentions (recognized expert)
Trust signals:
- Accurate conceptual relationships
- No misleading semantic connections
- Transparent limitations acknowledged
The synergy: Strong E-E-A-T naturally produces the semantic richness that neural matching rewards. You can’t fake deep conceptual understanding—it emerges from genuine expertise.
Common Neural Matching Optimization Mistakes
Even understanding conceptual matching Google uses, marketers make these errors:
Mistake #1: Keyword Density Obsession
The flawed approach: “I need ‘best running shoes’ mentioned 15 times for neural matching.”
Why it fails: Neural matching specifically moves away from keyword density. Forced repetition creates unnatural language patterns that neural networks detect and devalue.
The fix: Use the main keyword 1-3 times naturally, then use semantic variations. Let concept coverage drive ranking, not keyword counting.
Mistake #2: Ignoring Conceptual Gaps
The problem: Article about “home workout routines” that never mentions:
- Space requirements
- Equipment alternatives
- Beginner modifications
- Progress tracking
- Injury prevention
Why it fails: Neural matching recognizes these are core concepts in the “home workout” semantic space. Missing them signals incomplete coverage.
The fix: Map the full conceptual territory of your topic before writing. Cover all major related concepts, not just the primary keyword.
Mistake #3: Forcing Unrelated Semantic Keywords
The mistake: Adding “healthy lifestyle” and “fitness goals” to every article about exercise, thinking more related keywords = better neural matching.
Why it fails: Forced inclusion of tangentially related concepts dilutes topical focus. Neural matching detects when concepts don’t naturally connect.
The fix: Include only concepts that naturally relate to your specific topic. Tighter focus beats broader but weaker conceptual coverage.
Mistake #4: Shallow Breadth Over Deep Depth
The approach: “I’ll mention 50 different topics briefly to cover more concepts.”
Why it fails: Neural matching values conceptual depth over superficial breadth. Mentioning something doesn’t demonstrate understanding of it.
The fix: Cover fewer concepts thoroughly rather than many concepts superficially. Deep semantic coverage of core topics beats shallow coverage of many topics.
Mistake #5: Neglecting Natural Language Flow
The problem: “Running benefits include cardiovascular health improvement, stamina increases, and caloric expenditure enhancement.”
Why it’s problematic: While technically using semantic variations, the language is stilted and unnatural. Neural networks trained on natural language detect this.
The fix: “Running strengthens your heart, builds endurance, and burns calories effectively.”
Natural phrasing using semantic variations beats forced academic-sounding language.
Mistake #6: Ignoring User Search Language
The disconnect:
- Users search: “why won’t my car start”
- Content uses only: “vehicle ignition system malfunction diagnosis”
Why it fails: Neural matching bridges vocabulary gaps, but starting with user language creates stronger matches. Pure technical jargon creates conceptual distance.
The fix: Lead with common language, then explain technical terms: “If your car won’t start, the issue could be your ignition system. This is the electrical system that cranks the engine…”
Mistake #7: Thin Content with Semantic Keywords
The attempt: 300-word article mentioning “dogs,” “puppies,” “canines,” “pet ownership,” “animal companions,” thinking semantic variation compensates for lack of depth.
Why it fails: Neural matching detects shallow content regardless of vocabulary variation. Semantic variety doesn’t replace substantive information.
The fix: Provide genuine value first, semantic optimization second. Depth of insight matters more than breadth of synonyms.
Measuring Neural Matching Success
You can’t directly measure neural matching performance, but you can track signals indicating it’s working for you.
Indicators Neural Matching Is Working
1. Ranking for Semantic Variations
Check Google Search Console for queries you rank for that:
- Don’t use your exact target keywords
- Use synonyms and related terms
- Phrase the concept differently
- Are longer, conversational versions
Example: Target: “email marketing tips”
Neural matching success signals:
- Ranking for: “how to improve email campaigns”
- Ranking for: “email newsletter best practices”
- Ranking for: “increasing email open rates”
- Ranking for: “getting more email subscribers”
These variations indicate neural matching is connecting your content to the broader semantic space.
2. Traffic from Long-Tail Queries
Analyze:
- Percentage of traffic from queries with 4+ words
- Diversity of query phrasings driving traffic
- “Tail” queries you rank for without specifically targeting
Strong neural matching shows:
- 50%+ traffic from long-tail variations
- Hundreds of unique query phrasings
- Rankings for related concepts you didn’t explicitly optimize for
3. Featured Snippets for Varied Queries
Monitor:
- Featured snippets your content wins
- Variety of questions triggering your snippets
- Conceptual diversity of snippet queries
Neural matching success:
- Same content snippet for multiple related questions
- Questions using different vocabulary
- Concept-based triggering vs. keyword-based
4. “People Also Ask” Inclusion
Track:
- Appearance in PAA boxes
- Variety of questions where you appear
- Conceptual relationship of PAA questions
Strong signal: Your content appears in PAA for conceptually related but verbally different questions.
Tools for Tracking Neural Matching Performance
Google Search Console (Free):
- Query report shows all variations ranking
- Filter by impressions >100 to find significant variations
- Compare actual queries to your target keywords
- Identify semantic variations driving traffic
Analysis approach: Export queries → Group semantically similar queries → Calculate percentage from variations vs. exact match
Ubersuggest or Bing Webmaster (Free):
- Keyword variations your site ranks for
- Related terms driving visibility
- “Question” queries indicating conceptual matching
Content Analysis:
- Identify your comprehensive content
- Check what conceptual variations it ranks for
- Compare against thinner content performance
The comparison reveals: Comprehensive semantic coverage correlates with broader query matching.
A/B Testing Semantic Optimization
Controlled test approach:
Control group:
- 10 pages optimized for exact keywords
- Standard keyword density
- Single-focus content
Test group:
- 10 pages optimized for semantic concepts
- Natural variation, comprehensive coverage
- Multi-concept depth
Measure after 3 months:
- Ranking keyword diversity
- Long-tail traffic percentage
- Overall visibility growth
- Engagement metrics (dwell time, bounce rate)
Expected results: Semantic optimization typically shows:
- 40-60% more ranking keyword variations
- 25-35% higher long-tail traffic percentage
- Better engagement (people find what they need)
Neural Matching and Voice Search Optimization
Query understanding AI through neural matching is critical for voice search success.
Why Neural Matching Matters More for Voice
Voice queries differ fundamentally:
Typed: “weather san francisco” Spoken: “what’s the weather going to be like in San Francisco this weekend”
The gap neural matching bridges:
- Conversational vs. telegraphic language
- Natural phrasing vs. keyword compression
- Question format vs. keyword format
- Context and specificity vs. brevity
Voice search would fail without neural matching. The system must understand that verbose natural questions seek the same information as compressed text queries.
Voice Search Query Patterns
Common voice patterns neural matching handles:
1. Natural Questions:
- “How do I get red wine out of my carpet”
- “What’s the best way to train a puppy”
- “Why does my phone battery die so quickly”
2. Conversational Modifiers:
- “Really good,” “super fast,” “actually works”
- “That doesn’t cost too much”
- “Near me that’s open right now”
3. Contextual References:
- “Like the one I saw on TV”
- “Similar to what my friend has”
- “For someone who’s never done it before”
4. Multi-Step Questions:
- “How long does it take to learn guitar and what’s the best way to start”
- “What causes headaches after eating and how can I prevent them”
Neural matching deconstructs these into conceptual components and matches to appropriate content.
Optimizing Content for Voice + Neural Matching
Strategy #1: Use Question-Based Headers
Instead of: “Carpet Wine Stain Removal” Use: “How Do You Remove Wine Stains from Carpet?”
Why it works: Matches the natural phrasing of voice queries while maintaining semantic relevance.
Strategy #2: Provide Direct, Conversational Answers
Voice-optimized format: “To remove wine from carpet, act quickly. Blot (don’t rub) the stain with a clean cloth to absorb as much wine as possible. Then mix one tablespoon of dish soap with two cups of warm water…”
Why this works:
- Answers the question directly (voice assistants pull this)
- Uses natural, speakable language
- Structured for voice assistant reading
- Neural matching connects to various query phrasings
Strategy #3: Cover “Near Me” Concepts Naturally
For local businesses: Don’t force “near me” into content. Instead:
- Mention specific neighborhoods and landmarks
- Include service areas and locations
- Use local terminology
- Reference local context
Neural matching understands: “Serving downtown Chicago, River North, and the Loop” matches queries for “pizza near me” when the searcher is in those areas.
Strategy #4: Answer Follow-Up Questions
Voice searchers often ask sequences:
- “How do I make sourdough bread”
- “How long does sourdough take”
- “Why didn’t my sourdough rise”
Optimized content anticipates these: Include all likely follow-ups in your comprehensive content. Neural matching will serve your content for the entire conversation sequence.
The Voice Search Future
As voice grows (projected 50%+ of searches by 2025):
- Neural matching becomes more critical
- Natural language patterns increasingly important
- Conversational content beats keyword-focused content
- Comprehensive resources that answer multiple questions win
The opportunity: Content optimized for neural matching is naturally voice-search-ready. You’re preparing for both current and future search behaviors simultaneously.
The Future of Neural Matching in AI Search
Semantic search signals and neural matching will only become more sophisticated. Here’s what’s coming.
Multi-Modal Neural Matching
Current: Primarily text-to-text matching
Future: Cross-format conceptual matching
- Voice query → Video content match
- Image search → Text content match
- Text query → Podcast episode match
What this means: Create content in multiple formats covering the same concepts. Neural matching will connect appropriate formats to different query types.
Deeper Contextual Understanding
Current: Query-level semantic matching
Future: Session and user-level conceptual personalization
- Understanding user’s conceptual knowledge level
- Matching to appropriate depth/complexity
- Sequential topic exploration tracking
Preparation: Create content at multiple expertise levels for the same concepts. Let neural matching serve beginners vs. experts appropriately.
Cross-Language Neural Matching
Current: Within-language semantic matching
Future: Cross-language conceptual matching
- English query → Spanish content when semantically superior
- Concept translation beyond word translation
- Multilingual semantic web
Implication: Quality content in any language can match queries in other languages when conceptual match is strong.
Entity-Based Neural Matching
Current: Concept and topic matching
Future: Entity relationship mapping
- Deep understanding of entity connections
- Authority based on entity mentions and relationships
- Semantic web of entities and concepts
Strategy: Build entity-rich content mentioning specific people, places, things, brands. Establish clear entity relationships.
AI-Generated Content and Neural Matching
The challenge: As AI generates more content, how does Google’s neural matching handle it?
Likely evolution:
- Neural matching will detect AI-generation patterns
- Human-edited, expert-verified content will signal stronger
- Experience-based content (which AI can’t generate) becomes differentiator
- Conceptual depth from genuine expertise beats AI breadth
Your advantage: Real experience, genuine expertise, and first-hand knowledge create conceptual depth AI can’t replicate. This is your moat in an AI-content world.
Preparing for What’s Next
Future-proof neural matching optimization:
- Focus on comprehensive conceptual coverage (always valuable)
- Build genuine expertise and experience (AI can’t fake this)
- Create multi-format content (prepared for multi-modal matching)
- Establish entity authority (recognition beyond concepts)
- Maintain natural language patterns (works across all updates)
The constant: Regardless of how neural matching evolves, comprehensive, expert, authentic content about specific concepts will match relevant queries. Technology changes, but valuable content remains valuable.
Final Thoughts: Concepts Over Keywords in the Neural Age
Here’s what I need you to understand about neural matching SEO: It’s not another ranking factor to optimize for—it’s a fundamental shift in how search works.
The old question: “What keywords should I target?” The new question: “What concepts should I comprehensively cover?”
The old approach: Keyword research → keyword placement → exact match optimization The new approach: Topic research → comprehensive coverage → natural semantic variation
The old measure: Ranking for my target keyword The new measure: Ranking for hundreds of semantic variations
The paradigm shift: Google doesn’t match words anymore—it matches meaning. Your job isn’t to guess which words Google wants to see. Your job is to demonstrate deep understanding of concepts that matter to your audience.
The beautiful part: This aligns perfectly with creating genuinely valuable content. Neural matching rewards exactly what you should be doing anyway:
- Writing naturally for humans
- Covering topics comprehensively
- Demonstrating real expertise
- Providing authentic value
Your action plan:
This week:
- Audit your top 10 pages
- Identify conceptual gaps in coverage
- Note where you’re keyword-focused vs. concept-focused
This month:
- Expand your best content with comprehensive conceptual coverage
- Add semantic variations naturally
- Fill gaps in related concepts
This quarter:
- Build topical authority through consistent, deep coverage
- Create comprehensive resources, not keyword-targeted pages
- Let neural matching connect your expertise to diverse queries
This year:
- Become the definitive resource for your conceptual space
- Build semantic authority that compounds over time
- Watch as you rank for thousands of variations you never “targeted”
The opportunity: Most competitors are still stuck in keyword-matching thinking. By optimizing for neural matching through comprehensive conceptual coverage, you’re playing the game Google actually plays while they’re fighting yesterday’s algorithm.
Neural matching rewards the patient builder of genuine expertise over the tactical keyword optimizer. In 2025’s AI-powered search, that’s exactly where you want to be.
For understanding how neural matching integrates with other AI systems like RankBrain, BERT, and quality algorithms, explore the complete AI and machine learning SEO ecosystem.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is neural matching in Google search? Neural matching is Google’s AI system that understands the concepts and intent behind search queries, then matches them to relevant content based on semantic meaning rather than just keyword presence. It uses neural networks trained on billions of searches to understand that different words and phrases can express the same underlying concept, allowing Google to return relevant results even when there’s no exact keyword match between query and content.
Q: How is neural matching different from RankBrain and BERT? Neural matching focuses on connecting semantically related queries to conceptually relevant content. RankBrain interprets ambiguous queries and measures user satisfaction. BERT understands natural language context within queries. They work together: BERT understands what you’re asking, neural matching finds conceptually relevant content, and RankBrain determines which results best satisfy users. Each handles a different aspect of delivering the right result.
Q: Can I optimize directly for neural matching? Not directly—there’s no “neural matching optimization checklist.” Instead, optimize indirectly by: (1) Creating comprehensive topical coverage, (2) Using semantic keyword variations naturally, (3) Covering related concepts thoroughly, (4) Writing in natural language, (5) Building topical authority. Neural matching rewards content that demonstrates deep understanding of concepts, which emerges naturally from genuine expertise and comprehensive coverage.
Q: Does neural matching mean keywords don’t matter anymore? Keywords still matter, but their role changed. Use your target keyword naturally 1-3 times to establish topical relevance, then focus on comprehensive conceptual coverage using semantic variations. Neural matching understands that “running shoes,” “jogging sneakers,” and “athletic footwear” are semantically related. Natural variation beats forced repetition. Keywords help establish relevance; concepts determine ranking.
Q: How do I know if neural matching is working for my content? Check Google Search Console for: (1) Ranking for semantic variations of your target keywords, (2) Traffic from long-tail queries using different phrasing, (3) Featured snippets for multiple related questions, (4) High percentage of traffic from conversational queries. If you rank for hundreds of query variations beyond your exact target keywords, neural matching is successfully connecting your content to related concepts.
Q: What’s the difference between keyword matching and neural matching? Keyword matching looks for exact or close word matches between query and content. Neural matching understands concepts, recognizing that “car won’t start” and “vehicle ignition problems” are semantically related even with different words. Keyword matching: “Does page contain these words?” Neural matching: “Does this page discuss concepts relevant to the query’s intent?” Neural matching is why you can rank without using exact query phrasing.
Q: Does neural matching work for all types of queries? Neural matching affects about 30% of queries according to Google—particularly long-tail, conversational, and ambiguous queries where exact keyword matching fails. Short, clear queries like “Facebook” or “weather” need less neural interpretation. Complex, conversational queries like “why does my laptop get super hot when I’m working” benefit most from neural matching’s conceptual understanding. Voice search queries especially depend on it.
Q: How does neural matching affect voice search optimization? Voice queries are conversational, longer, and use natural language—exactly where neural matching excels. People speak differently than they type (“What’s the best way to remove wine stains from carpet” vs. “remove wine stain carpet”). Neural matching bridges this gap, connecting verbose spoken queries to content written for text search. Content optimized for neural matching through natural language and comprehensive concepts is automatically voice-search-ready.
Q: Should I use synonyms and related terms throughout my content for neural matching? Use them naturally, not artificially. Forcing synonyms (“best shoes, top footwear, finest sneakers, premier running shoes”) creates unnatural patterns neural networks detect. Instead, cover your topic comprehensively—semantic variations emerge naturally when explaining concepts thoroughly. Write to inform humans; neural matching will recognize the conceptual depth without forced synonym insertion.
🧠 Neural Matching: Google's Semantic Search Revolution
🎯 What is Neural Matching?
Google's AI-powered system that understands concepts and intent behind searches, matching them to relevant content based on meaning—not just keyword presence. Launched September 2018, it affects ~30% of queries and revolutionized how search connects users to information.
Keyword Matching vs Neural Matching
✗ Miss semantic variations
✗ Fail on synonyms
✗ Can't understand concepts
✗ Struggles with new queries
✓ Connect related ideas
✓ Handle synonyms naturally
✓ Grasp semantic meaning
✓ Excel with new queries
How Neural Matching Works
Convert to concepts
Identify intent
Find related content
Rank by meaning
Real Examples: Neural Matching in Action
Only shows pages with exact phrase "battery drain fast" - misses excellent content about "battery optimization," "power management," "battery life improvement
Understands concepts: battery optimization, power consumption, background apps, battery health—ranks relevant content regardless of exact wording
Requires pages to say "remedy" and "headache" - misses "headache relief," "migraine cure," "pain management"
Recognizes remedy = relief = cure = treatment = solution when discussing headaches. Matches conceptually related content.
Neural Matching vs Other Google AI
🎯 Neural Matching
Purpose: Connect conceptually related queries and content
Focus: "What concepts does this represent?"
Strength: Semantic similarity matching
🧠 RankBrain
Purpose: Interpret ambiguous queries, measure satisfaction
Focus: "Which results satisfy users?"
Strength: User behavior learning
💬 BERT
Purpose: Understand natural language context
Focus: "What does this query mean?"
Strength: Word relationship analysis
| Feature | Keyword Matching | Neural Matching |
|---|---|---|
| Understanding | Match exact words | Understand concepts |
| Synonyms | Limited recognition | Full semantic understanding |
| New Queries | Poor performance | Excellent handling |
| Voice Search | Struggles with natural language | Perfect for conversational queries |
| Context | Ignores meaning | Context-aware matching |
| Long-Tail | Weak performance | Strong performance |
| Related Topics | Can't connect | Automatically connects |
Query Type Impact Analysis
% represents how significantly neural matching improves results for each query type
Optimization Strategy Comparison
Optimization Strategies for Neural Matching
📚 Topic Clusters
Create comprehensive coverage of concepts rather than targeting individual keywords. Neural matching rewards topical authority and semantic completeness.
🔄 Natural Variations
Use semantic keyword variations naturally throughout content. Write for humans—neural matching will connect the concepts automatically.
🎯 Intent Focus
Optimize for user intent, not keywords. Cover all related concepts people need when searching your topic area comprehensively.
❓ Answer Questions
Address related questions proactively. Neural matching connects your content to various query formulations of similar concepts.
🗣️ Voice-Ready
Write conversationally for voice search. Neural matching bridges the gap between spoken queries and written content naturally.
🏗️ Build Authority
Develop topical authority through consistent, deep coverage. Neural matching recognizes sites as conceptual authorities in specific domains.
💡 Key Takeaway
Optimize for concepts, not keywords. Neural matching rewards comprehensive topical coverage using natural language and semantic variations. Write to inform humans deeply about concepts—neural matching will automatically connect your content to hundreds of query variations. The future is semantic, not keyword-based.
Source: seoprojournal.com - AI Search Intelligence
Based on Google's official announcements, neural network research, and semantic search analysis (2018-2025)
Interactive guide to understanding Google's neural matching technology
Related posts:
- What is Artificial Intelligence in SEO? A Simple Explanation for Non-Technical Marketers
- AI SEO Glossary: 50+ Terms Every Beginner Must Know in 2025
- How Google’s RankBrain Algorithm Works: Beginner’s Guide to AI Search(Visual guide)
- Semantic SEO Strategy: 7 Actionable Ways to Optimize for Intent-Based Search(Visual guide)