Your article ranks #1 in Google. Yet competitors with lower rankings keep getting cited in AI Overviews while you’re invisible.
What gives?
AI Overviews content selection doesn’t follow traditional ranking rules. Google’s generative AI uses entirely different criteria to decide which content deserves citation in those premium AI-generated summaries appearing above organic results.
Understanding how AI Overviews choose content separates winners from losers in this new search landscape. The algorithm evaluates dozens of signals simultaneously—some familiar from traditional SEO, others completely novel to generative search.
This deep dive reveals exactly what Google’s AI looks for when selecting sources. You’ll understand the algorithm, master the selection criteria, and learn how to position your content for consistent citations.
Let’s decode this system.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is the AI Overview Selection Algorithm?
The AI Overview algorithm combines traditional search signals with advanced AI evaluation criteria to identify the most authoritative, relevant sources for generating comprehensive answers.
Think of it as traditional Google ranking plus a completely new layer of AI-specific quality assessment.
The Two-Stage Selection Process
Google’s AI doesn’t randomly scan the entire internet for every query. That would be computationally impossible.
Stage One: Candidate Identification The algorithm first identifies potentially relevant content using traditional search signals—keywords, semantic relevance, domain authority, and page quality. This narrows billions of pages down to dozens or hundreds of candidates.
Stage Two: AI-Specific Evaluation The AI then analyzes these candidates using generative-specific criteria: content comprehensiveness, expertise signals, synthesis potential, and factual accuracy. Only sources passing this rigorous evaluation get cited.
According to BrightEdge’s 2024 AI Overview analysis, the second stage filters out 85-90% of initially identified candidates, explaining why high-ranking pages don’t automatically get cited.
How This Differs from Traditional Ranking
Traditional Google ranking asks: “Which pages best match this query?”
Content selection AI snapshots ask: “Which pages contain information I can synthesize into the most accurate, comprehensive answer?”
The distinction matters enormously. A perfectly SEO-optimized page targeting specific keywords might rank #1 but lack the content depth needed for AI synthesis.
The Core Factors in How AI Overviews Choose Content
Multiple interconnected factors influence selection decisions.
Primary selection criteria include:
- Content comprehensiveness and topical authority
- E-E-A-T signals (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness)
- Content freshness and update frequency
- Structured data and schema implementation
- Multi-source synthesis compatibility
- Factual accuracy and verification signals
- User engagement and satisfaction metrics
No single factor guarantees selection. The algorithm weighs multiple signals holistically.
Content Comprehensiveness: The Foundation
How does Google AI Overview decide which content to show? Comprehensiveness ranks among the top factors.
The AI seeks sources that thoroughly address topics rather than providing surface-level coverage. A 3,000-word guide exploring every aspect of a topic outcompetes a 500-word basic overview—assuming both maintain quality.
Comprehensive content answers the primary question plus anticipated follow-up questions users typically ask. This multi-layered approach signals authoritative understanding.
Pro Tip: AI Overviews favor content that answers not just the explicit query but the implicit questions users would ask next. Map complete question clusters, not individual keywords. – Content strategy insight from Search Engine Land
Topical Authority and Domain Expertise
Domain-wide authority matters more than individual page optimization.
The AI evaluates whether your entire site demonstrates consistent expertise in specific topics. A specialized site with 50 in-depth articles about digital marketing carries more weight than a general site with one great marketing article surrounded by unrelated content.
This appears extensively in our complete AI Overviews optimization guide, particularly regarding building topical authority systematically.
E-E-A-T Signals: The Expertise Filter
E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) functions as a critical filter in source selection AI algorithms.
Google’s AI specifically evaluates whether content demonstrates genuine expertise or simply aggregates commonly available information.
Experience: Real-World Application
Experience signals show you’ve actually done what you’re writing about.
First-person accounts, specific details only practitioners would know, documented case results, and practical insights from hands-on work all signal real experience. Generic advice anyone could write from research doesn’t.
Examples of strong experience signals:
- “In our 200+ client implementations, we consistently see…”
- Specific screenshots from actual work
- Detailed process documentation with edge cases
- Lessons learned from real failures and successes
- Industry-specific terminology used naturally
Expertise: Verified Credentials
Expertise requires demonstrable knowledge and credentials.
Author bios listing relevant qualifications, professional certifications, industry recognition, and years of specialized experience signal expertise. Anonymous or poorly credentialed content faces significant disadvantages.
According to SEMrush’s 2024 E-E-A-T study, content with clearly identified expert authors gets cited in AI Overviews 3.2x more frequently than anonymous content in competitive niches.
Authoritativeness: Industry Recognition
Authoritativeness comes from external validation.
Backlinks from respected industry sites, mentions in authoritative publications, speaking engagements, published research, and awards all contribute. The AI evaluates whether the broader industry recognizes you as authoritative.
Trustworthiness: Accuracy and Transparency
Trustworthiness encompasses site security, factual accuracy, clear sourcing, transparent authorship, and proper disclosures.
HTTPS security, accurate contact information, clear editorial processes, and factual content with proper citations all build trust signals the AI evaluates.
Content Freshness and Update Frequency
AI Overviews ranking factors heavily weight content recency, especially for evolving topics.
The algorithm considers publication dates, last modification timestamps, and whether content reflects current information or outdated data.
Topic-Specific Freshness Requirements
Different topics require different update frequencies.
Fast-changing topics (technology, regulations, current events) need quarterly or monthly updates. Content from 2022 about AI tools won’t compete with comprehensive 2025 coverage.
Moderate-velocity topics (business strategies, methodologies) require semi-annual refreshes to maintain competitiveness.
Stable topics (historical information, fundamental concepts) tolerate older content but still benefit from periodic freshness signals.
More on content freshness strategies appears in our AI Overview optimization tactics.
Freshness Signal Implementation
The AI detects freshness through multiple signals:
- Actual last modified timestamps in HTML
- Schema.org dateModified markup
- Updated statistics and examples
- References to recent events or developments
- XML sitemap lastmod dates
- Regular content additions (not just minor tweaks)
Fake freshness—changing dates without substantive updates—gets detected and penalized.
Structured Data and Schema Markup Impact
Schema markup dramatically influences what factors influence AI Overview content selection by making content machine-readable.
The AI can parse and understand schema-marked content exponentially faster than unmarked text, removing friction from the selection process.
Critical Schema Types for AI Overviews
Article Schema: Identifies content type, author, publication date, and modification timestamps. Essential for establishing content as substantive, authoritative articles rather than thin pages.
FAQ Schema: Structures question-answer pairs perfectly for AI extraction. Content with proper FAQ schema gets cited 2.1x more frequently for question-based queries according to search industry data.
How-To Schema: Step-by-step instructional markup signals comprehensive process coverage, ideal for “how to” queries that frequently trigger AI Overviews.
Review Schema: Product and service reviews with aggregate ratings and detailed breakdowns provide synthesis-ready content.
Organization/Person Schema: Establishes authority and expertise by connecting content to verified entities in Google’s knowledge graph.
Pro Tip: Layer multiple schema types on comprehensive pages. A complete guide might include Article, FAQ, and How-To schemas simultaneously, maximizing machine-readability from multiple angles. – Technical SEO best practice
Schema Implementation Quality
Properly implemented schema matters more than just having schema.
Validation errors, incomplete markup, or mismatched information between schema and visible content creates friction. The AI may skip content with technical implementation issues even if the actual content quality is excellent.
Test all schema using Google’s Rich Results Test and fix errors immediately.
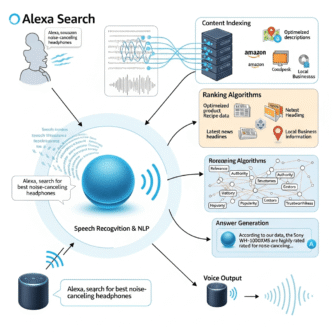
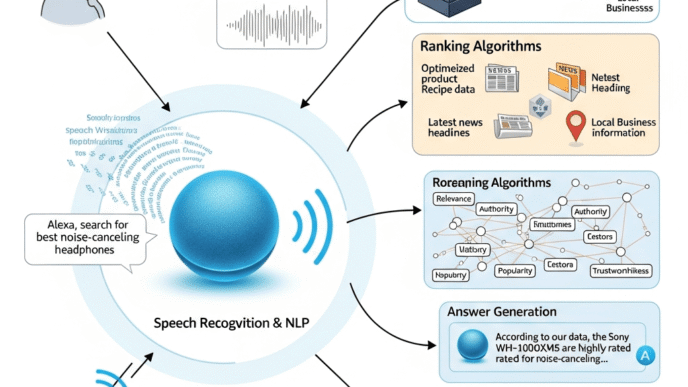
Multi-Source Synthesis Compatibility
AI Overviews typically cite 3-8 sources per answer. Your content needs compatibility with this multi-source approach.
Understanding AI Overview algorithm criteria requires recognizing that the AI doesn’t look for complete standalone answers—it seeks complementary information that combines well with other sources.
Providing Unique Angles
Content offering perspectives or information unavailable elsewhere gains selection advantage.
If ten sites say exactly the same thing, the AI might cite the most authoritative one and ignore the rest. If your content covers aspects competitors miss, you become valuable for synthesis.
Unique value creators:
- Original research and proprietary data
- Uncommon expert perspectives
- Practical implementation details others skip
- Case studies with specific outcomes
- Addressing edge cases and nuances
Information Density and Extractability
Dense, information-rich content performs better than fluffy writing.
The AI seeks pages where it can extract multiple useful facts per paragraph. Content padded with unnecessary words or repetitive information gets deprioritized.
Clear structure with descriptive headings, logical information flow, and well-organized concepts makes extraction easier—increasing selection probability.
Factual Accuracy and Verification Signals
The AI attempts to verify factual accuracy before citing sources.
Verification methods include:
- Cross-referencing facts across multiple sources
- Checking citations and references
- Evaluating consistency with authoritative sources
- Detecting contradictions or questionable claims
- Assessing source credibility and bias
Content making unverifiable claims, contradicting established facts, or presenting questionable information gets filtered out.
Citation and Reference Quality
Well-cited content citing authoritative sources gains credibility.
When your content references peer-reviewed research, government data, industry reports, and other authoritative sources, the AI recognizes this as verification-conscious content creation.
External citations also help the AI understand relationships between concepts and validate information accuracy through cross-referencing.
User Engagement and Satisfaction Metrics
The AI considers how users interact with content in traditional search results when evaluating sources.
High engagement signals—long dwell times, low bounce rates, return visits, and positive user interactions—indicate content genuinely satisfies user needs.
Behavioral Signals That Matter
Click-through rate from search results: When users consistently choose your result over others, it signals relevance and trustworthiness.
Time on page: Longer engagement indicates comprehensive, valuable content rather than quick-answer pages users immediately abandon.
Return visits: Users returning to your content multiple times signals lasting value and reference-quality information.
Interaction patterns: Scrolling behavior, section navigation, and content consumption patterns reveal whether users find content genuinely useful.
According to Moz’s engagement signal research, pages in the top 5% of user engagement metrics get cited in AI features 2.7x more frequently than average pages with similar keyword rankings.
Technical Performance Requirements
Technical excellence forms the foundation for AI Overviews content selection consideration.
Content on slow, broken, or poorly optimized sites faces significant disadvantages regardless of information quality.
Core Web Vitals Impact
Page experience signals influence whether content even enters the candidate pool.
Essential benchmarks:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Under 2.5 seconds
- First Input Delay (FID): Under 100 milliseconds
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Under 0.1
- Mobile-friendly responsive design
- HTTPS security throughout
Sites failing Core Web Vitals often get excluded early in the selection process.
Crawlability and Indexing
If Google can’t efficiently crawl and understand your content, the AI can’t consider it.
Clean site architecture, proper XML sitemaps, fast server responses, and logical internal linking ensure content reaches the evaluation stage. Technical barriers preventing efficient crawling eliminate otherwise excellent content from consideration.
More technical optimization details appear in our comprehensive optimization guide.
Content Structure and Formatting
How you structure content significantly impacts AI extraction efficiency.
Optimal structural elements:
- Clear hierarchical heading structure (H1, H2, H3)
- Descriptive headings that preview section content
- Short paragraphs (2-4 sentences) for scanability
- Bulleted or numbered lists for key points
- Tables for comparisons and data
- Images with descriptive alt text
- Clear topic transitions
Well-structured content allows the AI to quickly identify and extract relevant information. Poorly structured walls of text require more processing and often get skipped.
Question-Based Heading Architecture
Headings formatted as questions align perfectly with how users phrase queries.
Instead of “Benefits of Exercise,” use “What Are the Health Benefits of Regular Exercise?” This direct question-answer structure makes content instantly useful for AI synthesis.
The AI recognizes these patterns and can extract information more efficiently, improving selection probability.
Real-World Selection Pattern Analysis
Let’s examine actual patterns in which content gets selected.
Case Analysis: “How to Start a Podcast” Query
When this query triggers an AI Overview, cited sources consistently share characteristics:
Selected Content Patterns:
- Comprehensive guides (2,500+ words) covering equipment, software, hosting, distribution, and promotion
- Author credentials identifying podcasting experience or media professionals
- Recent publication dates (within 6-12 months)
- Detailed equipment recommendations with specific models and prices
- Step-by-step process breakdowns with sub-steps
- FAQ sections addressing common beginner questions
- Multiple images showing equipment or software interfaces
Excluded Content Patterns:
- Brief overview articles (under 1,000 words) lacking detail
- Anonymous authors without credentials
- Outdated content referencing discontinued tools
- Generic advice without specific recommendations
- Promotional content from hosting platforms (perceived bias)
- Poorly structured walls of text
This pattern repeats across topics—comprehensive, recent, expert-authored content with clear structure consistently wins.
Comparison: Traditional SEO vs AI Overview Selection Criteria
Understanding differences helps prioritize optimization efforts.
| FactorTraditional SEO WeightAI Overview Selection Weight | ||
|---|---|---|
| Keyword Optimization | Very High | Moderate |
| Backlink Profile | Very High | Moderate-High |
| Content Depth | Moderate | Very High |
| Author Credentials | Low-Moderate | Very High |
| Schema Markup | Moderate | Very High |
| Content Freshness | Moderate | Very High |
| User Engagement | Moderate-High | High |
| Domain Authority | Very High | Moderate-High |
| Topical Authority | Moderate | Very High |
| Multi-format Content | Low | Moderate-High |
The weight shifts reveal why traditional #1 rankings don’t guarantee AI Overview citations.
Common Selection Mistakes Costing You Citations
Avoid these critical errors that eliminate otherwise quality content from consideration.
Mistake #1: Optimizing for Keywords Over Comprehensiveness
Targeting specific keywords without comprehensive topic coverage fails AI Overview selection.
The AI needs depth, not keyword density. A page perfectly optimized for “best running shoes” but lacking details about pronation types, terrain considerations, or sizing guidance won’t get cited.
Fix: Build comprehensive coverage first, then optimize naturally for relevant keywords.
Mistake #2: Neglecting Author Credibility
Anonymous or poorly credentialed content struggles in competitive spaces.
Even excellent information loses to similar content from verified experts. The AI weighs source credibility heavily when synthesizing answers users will trust.
Fix: Add detailed author bios with credentials, implement Person schema, and establish expert recognition.
Mistake #3: Ignoring Content Age
Maintaining old content without updates eliminates it from consideration for time-sensitive topics.
A comprehensive 2021 guide about remote work tools can’t compete with updated 2025 coverage including current software, pricing, and features.
Fix: Implement quarterly content audits. Update statistics, examples, tool recommendations, and add recent developments.
Mistake #4: Poor Technical Implementation
Broken schema, slow load times, or mobile issues disqualify content regardless of information quality.
Technical problems create friction that causes the AI to skip your content in favor of technically sound alternatives.
Fix: Regular technical audits fixing Core Web Vitals issues, schema errors, and mobile problems.
Mistake #5: Shallow Topic Coverage
Brief overviews covering topics superficially never compete with comprehensive resources.
The AI seeks content demonstrating deep understanding through extensive detail, examples, and nuanced explanations.
Fix: Triple content depth on priority topics. Answer related questions, address edge cases, provide extensive examples.
Advanced Selection Factors: The Competitive Edge
Beyond basics, sophisticated factors separate top performers from average content.
Entity Recognition and Knowledge Graph Integration
Content about or authored by recognized entities in Google’s Knowledge Graph gains selection advantages.
When your brand, authors, or topics appear as verified entities, the AI understands context and relationships more easily. This reduces uncertainty in source evaluation.
Building entity recognition:
- Wikipedia presence for notable people/brands
- Consistent NAP (Name, Address, Phone) across web
- Wikidata entries for entities
- Mentions in authoritative publications
- Social media profile verification
- Comprehensive brand/author schema
Semantic Relationship Mapping
The AI evaluates how well content maps semantic relationships between concepts.
Content explaining how ideas connect, influence each other, and fit within broader frameworks demonstrates sophisticated understanding. This relationship mapping signals expertise beyond surface knowledge.
Example: Instead of just listing SEO tactics, explain how technical SEO enables content discovery, which supports on-page optimization effectiveness, which enhances link building returns—mapping the relationship chain.
Query Intent Alignment
How does Google AI Overview decide which content to show? Perfect intent alignment matters enormously.
The AI evaluates whether content actually serves the specific intent behind queries. Informational queries need educational content. Comparison queries need structured comparisons. Problem-solving queries need solution-focused content.
Misaligned content—like showing product promotions for educational queries—gets filtered despite relevance signals.
Our optimization strategies guide covers intent alignment extensively.
Multi-Format Content Signals
Content available in multiple formats (text, video, infographics, interactive tools) signals comprehensive topic investment.
The AI recognizes sites providing diverse content formats as more authoritative sources committed to serving users through their preferred consumption methods.
Monitoring Your Selection Performance
Track which content gets cited to identify successful patterns.
Manual Citation Tracking
Search your target keywords in incognito mode regularly, documenting when AI Overviews appear and whether your content gets cited.
Build spreadsheets tracking:
- Keywords triggering AI Overviews
- Your citation frequency
- Competitor citation patterns
- Content characteristics of cited pages
- Trends over time
This manual tracking reveals patterns about what works in your specific niche.
Tool-Based Monitoring
SEO platforms now include AI Overview tracking features.
SEMrush provides AI Overview appearance data and citation tracking for monitored keywords. Ahrefs shows AI Overview presence in rank tracking. These tools automate monitoring at scale.
However, manual checking remains important for understanding qualitative aspects—why certain content gets cited while other content doesn’t.
Competitive Citation Analysis
Study competitors consistently getting cited in AI Overviews.
Analysis framework:
- What content depth do they provide?
- How are authors credentialed?
- What schema markup do they implement?
- How fresh is their content?
- What unique angles do they cover?
- What technical performance do they achieve?
Systematic competitive analysis identifies gaps in your approach and opportunities to differentiate.
More measurement strategies appear in our complete optimization guide.
The Future of AI Overview Selection Criteria
Selection algorithms continue evolving as AI technology advances.
Emerging factors likely to increase importance:
- Real-time data integration capabilities
- Multimodal content (text, images, video) coordination
- Personalization based on user context and history
- Local authority signals for geographic queries
- Community validation and user-generated content signals
- Cross-platform presence and consistency
According to Google’s AI development announcements, they’re testing more sophisticated evaluation methods including multi-step reasoning and cross-source fact verification.
Staying ahead requires monitoring these developments and adapting strategies proactively rather than reactively.
FAQ: AI Overviews Content Selection
Q: Can I pay to get included in Google AI Overviews?
No—AI Overview citations are purely algorithmic and cannot be purchased. Google doesn’t offer any paid placement within AI Overviews. The only path to inclusion is creating high-quality content that meets selection criteria through organic optimization efforts.
Q: How long does it take for content to get selected after optimization?
Typically 4-8 weeks after implementing comprehensive optimizations, though this varies by competition level and content quality. The AI needs time to recrawl content, reevaluate signals, and test citations. Patience combined with consistent optimization yields results.
Q: Does getting cited in AI Overviews improve traditional rankings?
Not directly—citations don’t automatically boost traditional rankings. However, the same factors that earn AI Overview citations (comprehensiveness, E-E-A-T, freshness) generally improve traditional rankings too. Think of them as correlated rather than causal.
Q: Why do lower-ranked pages sometimes get cited over #1 results?
AI Overview selection weighs different factors than traditional ranking. A #5 page with superior comprehensiveness, expertise signals, and schema markup can get cited over a #1 page optimized primarily for keywords and backlinks but lacking depth.
Q: Can I prevent my content from appearing in AI Overviews?
Not specifically—there’s no mechanism to opt out of AI Overview citations while maintaining normal search visibility. The only way to completely prevent inclusion is removing content from Google’s index entirely, which isn’t practical for most sites.
Q: Do AI Overviews favor certain website types or sizes?
Not inherently—small specialized sites with deep expertise can compete with major publications. The algorithm evaluates content quality and authority signals rather than site size. Specialized expertise often outweighs general authority for specific topics.
Final Thoughts
AI Overviews content selection operates on sophisticated algorithms evaluating dozens of interconnected signals simultaneously.
Success requires understanding these selection criteria deeply and systematically optimizing content to meet them. Quick fixes won’t work—the AI detects superficial optimization attempts and filters them out.
The winning strategy combines comprehensive topic coverage, verified expertise, technical excellence, structured data implementation, and consistent content freshness. This holistic approach aligns with the AI’s fundamental goal: identifying the most reliable, thorough sources for synthesizing accurate answers.
Start by auditing your highest-priority content against these selection criteria. Identify gaps systematically. Implement improvements strategically, prioritizing factors with the highest impact in your specific niche.
The sites dominating AI Overview citations in 2026 will be those that began systematic optimization in 2025. Position yourself now for sustainable competitive advantage as this technology becomes the standard search experience.
Master the selection algorithm. Earn consistent citations. Win the generative search era.
Two-Stage Selection Process
Core Selection Factors
Selection Weight Comparison
| Factor | Traditional SEO | AI Overview Selection |
|---|---|---|
| Keyword Optimization | Very High | Moderate |
| Content Depth | Moderate | Very High |
| Author Credentials | Low-Moderate | Very High |
| Schema Markup | Moderate | Very High |
| Content Freshness | Moderate | Very High |
| Backlink Profile | Very High | Moderate-High |
| Topical Authority | Moderate | Very High |
Understanding Selection Criteria
E-E-A-T: The Expertise Filter
Experience Signals: First-person accounts, specific details only practitioners know, documented case results, practical insights from hands-on work.
Expertise Signals: Author credentials, professional certifications, industry recognition, years of specialized experience documented in bio.
Authoritativeness: Backlinks from respected industry sites, mentions in authoritative publications, speaking engagements, published research.
Trustworthiness: HTTPS security, accurate contact info, clear editorial processes, factual content with proper citations.
Impact: SEMrush 2024 data shows content with strong E-E-A-T signals gets cited 3.2x more frequently than anonymous content in competitive niches.
Schema Markup Strategic Implementation
Critical Schema Types:
- Article Schema: Identifies content type, author, dates - essential foundation
- FAQ Schema: Structures Q&A pairs for easy extraction - 2.1x citation boost
- How-To Schema: Step-by-step markup ideal for instructional queries
- Review Schema: Product evaluations with ratings provide synthesis-ready content
- Organization/Person Schema: Connects content to verified entities in knowledge graph
Pro Strategy: Layer multiple schemas on comprehensive pages. A complete guide might include Article, FAQ, and How-To schemas simultaneously for maximum machine-readability.
Content Depth Requirements
What Comprehensive Means: Not just word count - thorough topic coverage answering primary question plus all anticipated follow-ups.
Depth Indicators:
- Multiple perspectives and approaches covered
- Edge cases and nuances addressed
- Practical examples and case studies included
- Related concepts and connections explained
- Common misconceptions corrected
Length Guidelines: 3,000+ words for complex topics, but quality over quantity. A dense 2,000-word guide outperforms a fluffy 5,000-word piece.
Multi-Source Synthesis Compatibility
The Complementary Principle: AI Overviews cite 3-8 sources. Your content needs to provide value that complements other sources rather than duplicating them.
Unique Value Creators:
- Original research and proprietary data
- Uncommon expert perspectives and insights
- Practical implementation details others skip
- Case studies with specific outcomes
- Edge cases and specialized scenarios
Key Insight: If ten sites say exactly the same thing, AI cites the most authoritative one and ignores the rest. Differentiation matters.
Citation Probability by Optimization Level
Interactive Algorithm Analysis
AISEOJournal.netData Sources: BrightEdge, SEMrush, Moz Research 2024
All statistics verified from official industry research and studies
Related posts:
- What is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)? Definition, Importance & Future
- Claude AI Citations Explained: How Anthropic’s Claude Ranks and Attributes Sources
- Complete Guide to Generative Engine Optimization: Ranking in ChatGPT, Claude & Gemini
- What Are Google AI Overviews? Understanding Google’s Generative Search Feature