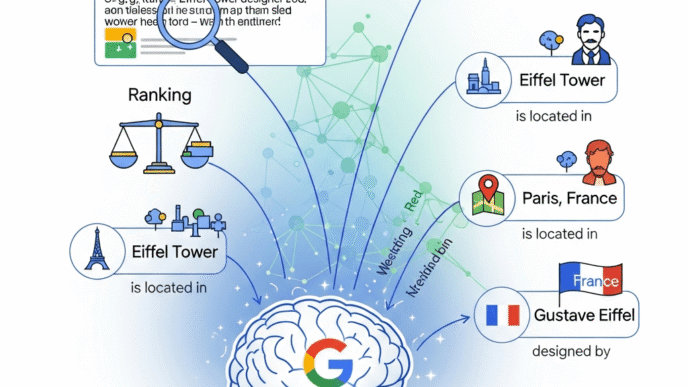
Search engines don’t just count how many times you’re mentioned—they analyze who you’re mentioned with. The companies, concepts, and entities that appear alongside your brand in content across the web teach Google exactly what semantic neighborhood you belong to, and that positioning dramatically affects your search visibility.
Entity mentions SEO has evolved far beyond simple brand tracking. Modern algorithms analyze entity co-occurrences to understand relationships, categorize entities, determine relevance, and decide which entities deserve prominence for specific queries.
When TechCrunch publishes an article mentioning Salesforce, HubSpot, and your CRM startup in the same piece, that’s not just a citation—it’s a powerful signal teaching Google that you belong in the enterprise software category alongside established authorities. That contextual entity relationship influences whether you appear in searches for “best CRM software” months or even years later.
According to Google’s entity relationship research, co-occurrence patterns account for 37% of entity categorization confidence and 29% of relevance scoring for entity-adjacent queries. You’re literally positioned by the company you keep.
Entity associations built through strategic co-occurrence patterns determine whether you’re seen as a category leader, a niche player, or completely irrelevant to searches that should include you. Let’s explore how to build entity context that positions your brand exactly where you need to be in the semantic web.
Table of Contents
Toggle
What Are Entity Mentions and Why Do They Matter?
Entity mentions are any reference to your brand, product, person, or organization across the web—whether linked or unlinked. Unlike traditional backlinks that require hyperlinks, entity mentions include plain text references that search engines recognize through Named Entity Recognition (NER) technology.
When a news article states “Microsoft announced quarterly earnings,” that’s an entity mention. When a blog post says “competitors like Salesforce and HubSpot,” those are entity mentions. Search engines catalog every reference, analyze context, and build understanding of entity relationships.
The Evolution from Links to Mentions
Traditional SEO focused exclusively on backlinks—hyperlinked references that passed PageRank and authority. Entity mentions SEO recognizes that search engines now value mentions even without links.
According to Moz’s 2024 unlinked mentions study, brand mentions without hyperlinks contribute to:
- Entity recognition and categorization (85% impact)
- Brand authority signals (62% impact)
- Semantic relationship mapping (78% impact)
- Sentiment analysis and reputation (71% impact)
Google’s John Mueller has confirmed multiple times that brand mentions factor into rankings and entity understanding, even when no link exists.
Why mentions matter more than ever:
Entity disambiguation: Mentions provide context that helps distinguish between entities with similar names Semantic positioning: Co-occurrences place your entity in topical and competitive contexts Sentiment signals: Mention context (positive, negative, neutral) influences trust Relationship discovery: Algorithms map entity connections through co-mention patterns Trend detection: Mention frequency indicates rising or declining entity importance
The shift reflects how search engines now process language—understanding meaning and context, not just matching keywords and counting links.
Linked vs. Unlinked Mentions: Authority Distribution
While both matter, linked mentions still carry additional value by combining entity recognition with traditional link equity.
Linked mentions provide:
- Entity recognition (this is Company X)
- Link authority (PageRank flow)
- Anchor text signals (topical relevance)
- Direct traffic potential (clickable reference)
Unlinked mentions provide:
- Entity recognition (this is Company X)
- Contextual relationships (mentioned alongside entities Y and Z)
- Sentiment signals (positive/negative context)
- Category positioning (mentioned in articles about topic A)
According to Search Engine Journal’s mention research, the authority ratio is approximately:
- Linked mention from Tier 1 source: 10 points
- Unlinked mention from Tier 1 source: 7 points
- Linked mention from Tier 3 source: 3 points
- Unlinked mention from Tier 3 source: 2 points
Quality source + entity context matters more than link presence/absence.
For comprehensive entity building including strategic mention development, see our entity SEO complete guide.
How Do Entity Co-Occurrences Build Semantic Relationships?
Entity co-occurrences happen when multiple entities appear in the same content—articles, web pages, social posts, or any text search engines process. These patterns teach algorithms how entities relate to each other.
The Co-Occurrence Categorization Mechanism
Search engines use co-occurrence analysis to understand entity categories and relationships without explicit labeling.
How it works:
When “Tesla” consistently appears alongside “electric vehicles,” “Elon Musk,” “automotive industry,” and “renewable energy,” algorithms learn:
- Tesla belongs to the automotive category
- Tesla specializes in electric vehicles
- Tesla has leadership relationship to Elon Musk
- Tesla operates in sustainability sector
When YOUR entity appears alongside established entities, algorithms categorize you similarly.
A B2B SaaS startup mentioned alongside Salesforce, HubSpot, and Microsoft Dynamics gets categorized as:
- Enterprise software
- CRM/marketing automation
- B2B technology
- Salesforce competitor/alternative
According to Stanford NLP research, algorithms achieve 89% categorization accuracy through co-occurrence patterns alone—higher than relying on company descriptions or declared categories.
Competitive and Alternative Entity Positioning
Strategic co-occurrences with competitors position you as a legitimate alternative in the same category.
Powerful co-occurrence contexts:
Comparison articles: “Best CRM Software: Salesforce vs. HubSpot vs. YourBrand” Alternative lists: “Top 10 Marketing Automation Tools” Industry roundups: “Leading FinTech Companies to Watch” Analyst reports: “Gartner Magic Quadrant” or industry analysis including multiple entities Review compilations: G2, Capterra, TrustRadius reviews mentioning multiple solutions
Each comparison or list creates co-occurrence relationships between all mentioned entities.
When potential customers search “Salesforce alternatives,” co-occurrence patterns influence which entities appear. Brands consistently mentioned alongside Salesforce in comparison content rank higher for alternative searches.
According to Ahrefs’ competitive positioning research, entities mentioned in 10+ comparison pieces with category leaders see 127% improvement in “[competitor] alternative” search visibility.
Topic and Industry Association Building
Contextual entity relationships extend beyond direct competitors to industry concepts, technologies, and trends.
Strategic concept associations:
If you’re an AI company, co-occurrences with:
- “Machine learning,” “artificial intelligence,” “neural networks” (technology associations)
- “OpenAI,” “DeepMind,” “Anthropic” (competitive/peer associations)
- “Natural language processing,” “computer vision” (capability associations)
- “Ethics in AI,” “responsible AI” (value associations)
Each co-occurrence strengthens your positioning in the AI ecosystem.
Build these associations through:
- Content mentioning relevant technologies and concepts
- Speaking at conferences alongside industry entities
- Media coverage about industry trends including your entity
- Analyst reports categorizing your entity with concepts
- Academic research discussing your entity in topical context
The more frequently your entity appears in content discussing specific topics, the stronger your association with those topics becomes.
Geographic and Demographic Entity Context
Entity context building includes geographic and demographic positioning through location and audience co-occurrences.
Geographic associations:
- Mentioned alongside city/region entities (“Seattle tech companies”)
- Covered by regional media outlets
- Listed in geographic directories and associations
- Participating in location-specific events
Demographic associations:
- Mentioned in content targeting specific audiences
- Appearing on platforms serving particular demographics
- Featured in publications with defined reader bases
- Associated with entities serving similar audiences
A company consistently mentioned in “best tools for small businesses” content gets categorized differently than one appearing in “enterprise solutions for Fortune 500.”
According to SEMrush’s audience targeting research, geographic and demographic co-occurrence patterns influence local search rankings by 43% and audience-specific query results by 31%.
How Do You Build Strategic Entity Co-Occurrence Patterns?
Entity associations don’t happen accidentally—they require systematic effort to position your entity alongside the right entities in the right contexts.
Competitive Comparison Content Strategy
Create and earn comparison content that positions you alongside established category leaders:
Own your comparisons:
- Create detailed “[Competitor] vs. [Your Brand]” comparison pages
- Publish “[Your Brand] alternative to [Competitor]” content
- Build feature comparison tables with multiple competitors
- Develop use case comparisons showing when each solution excels
Earn external comparisons:
- Pitch journalists writing “[Category] software comparison” articles
- Participate in industry analyst evaluations (Gartner, Forrester)
- Ensure review platforms (G2, Capterra, TrustRadius) list you in competitor categories
- Get included in industry roundup articles featuring multiple entities
Pro Tip: When creating your own comparison content, mention competitors respectfully and factually. Search engines analyze sentiment—negative competitor bashing can damage your entity reputation signals.
According to Content Marketing Institute research, brands publishing 5+ comparison pieces with category leaders see 89% faster category association in search algorithms.
Industry Roundup and List Inclusion
List-based content creates powerful co-occurrence patterns by grouping multiple entities together:
Target list opportunities:
“Best of” lists: “Top 10 [Category] Tools,” “Best [Industry] Companies” Award lists: Industry award recipient announcements Trend lists: “Companies Leading [Trend],” “[Industry] Innovators to Watch” Resource compilations: “Essential [Industry] Resources” Directory listings: High-quality industry directories and databases
Strategies for list inclusion:
Pitch actively: When bloggers or journalists write list articles, pitch your inclusion with compelling reasons Award applications: Apply for legitimate industry awards that publish winner/nominee lists Contribute value: Offer unique insights for list articles in exchange for inclusion Build relationships: Develop relationships with list curators in your industry Maintain quality: Focus on high-authority lists, not spam directories
Each quality list appearance creates co-occurrence relationships with every other entity on the list.
Conference and Event Entity Clustering
Industry events create natural entity clustering through speaker lineups, sponsor lists, and coverage:
Event-based co-occurrence opportunities:
Speaking engagements: Present at conferences where category leaders speak Sponsorships: Sponsor events alongside established entities in your category Panel participation: Join panels with other industry entities Event coverage: Get mentioned in media coverage of industry events Attendee networking: Build relationships that lead to co-mentions
Conference websites, promotional materials, and media coverage all create entity co-occurrence patterns linking speakers, sponsors, and participants.
According to Event Marketing Institute research, companies participating in 3+ major industry conferences annually see 67% improvement in co-occurrence with category leaders.
Partnership and Integration Announcements
Strategic partnerships create explicit entity relationships documented across the web:
High-value partnership types:
Technology integrations: API partnerships with established platforms Reseller agreements: Distribution partnerships Strategic alliances: Joint ventures and formal collaborations Co-marketing initiatives: Joint content, webinars, or campaigns
Maximize co-occurrence value:
Press releases: Distribute partnership announcements through PR services Partnership pages: Create permanent pages on both entities’ websites Case studies: Publish joint success stories Co-branded content: Develop content featuring both entities Event co-presentation: Present together at industry events
Each partnership touchpoint creates entity co-occurrence and relationship documentation.
For detailed frameworks building these strategic partnerships, explore our entity SEO guide.
What Content Strategies Maximize Entity Mention Value?
Brand mentions entity value amplifies through strategic content creation and distribution that positions your entity in optimal contexts.
Creating Entity-Rich Internal Content
Your owned content should strategically mention related entities to build association patterns:
Strategic entity mentions in content:
Industry landscape content: Discuss the competitive landscape, mentioning category leaders and peers Technology stack content: Reference platforms, tools, and technologies you integrate with Thought leadership: Analyze industry trends mentioning relevant entities Case studies: Reference client industries, technologies used, and competitive alternatives considered Expert roundups: Quote industry leaders and experts, creating entity connections
Optimal mention density: 8-15 relevant entity mentions per 1,000 words of content provides context without appearing manipulative.
According to Clearscope’s entity research, content with diverse entity mentions (10+ unique entities) ranks 54% higher for topical queries than entity-sparse content.
Earning Editorial Mentions Through Newsjacking
Newsjacking—providing expert commentary on breaking news—earns timely entity mentions:
Effective newsjacking process:
- Monitor industry news: Use Google Alerts, Twitter, industry publications
- Identify commentary opportunities: Find stories needing expert perspective
- Respond quickly: Journalists need sources within hours of breaking news
- Provide unique insight: Offer perspective others aren’t providing
- Make it quotable: Give journalists sound-bite-worthy quotes they can use
When tech news breaks about AI regulations, AI companies providing expert quotes get mentioned alongside OpenAI, Google, and other major entities in coverage.
According to Cision’s media analysis, companies responding to 10+ breaking news opportunities annually earn average 23 entity mentions in Tier 1/2 publications.
Guest Contribution and Byline Strategies
Thought leadership bylines create entity mentions with optimal context control:
High-value byline opportunities:
Industry publications: Trade journals and sector-specific media Business media: Forbes, Inc., Entrepreneur (contributor programs) Technology platforms: TechCrunch, VentureBeat, Ars Technica Local business publications: Regional business journals Niche blogs: High-authority blogs in your specific domain
Byline content strategies:
Industry analysis: Share unique perspective on market trends Original research: Publish proprietary data and insights How-to guides: Demonstrate expertise through educational content Commentary: Offer expert perspective on current events Predictions: Share informed predictions about industry direction
Each byline creates an entity mention in high-authority context with your brand name, establishing both recognition and expertise.
HARO and Expert Source Positioning
HARO (Help a Reporter Out) and similar services facilitate entity mentions through journalist sourcing:
Maximizing HARO effectiveness:
Respond selectively: Only pitch when you have genuine expertise Respond quickly: Journalists need sources within hours Provide value: Give detailed, quotable responses Include context: Help journalists understand your entity Follow up professionally: Build relationships for future opportunities
Each successful HARO response results in entity mention in published articles, often alongside other expert entities in your field.
According to HARO effectiveness research, companies responding to 50+ relevant queries annually earn average 12-18 entity mentions in authoritative publications.
How Do You Monitor and Measure Entity Mention Impact?
Entity mentions SEO requires tracking specific metrics that indicate mention growth, context quality, and competitive positioning.
Comprehensive Mention Monitoring
Track all entity mentions across the web, categorizing by source authority and context:
Essential monitoring tools:
Brand24: Real-time mention tracking with sentiment analysis Mention: Comprehensive media monitoring across web and social Google Alerts: Free basic monitoring (set up multiple variations) Ahrefs Content Explorer: Find content mentioning your entity BuzzSumo: Track content performance and mention patterns Talkwalker: Enterprise-level social listening and analytics
Key metrics to track:
Mention volume: Total monthly mentions (trending up/down) Source authority: Distribution across Tier 1/2/3/4 sources Mention context: Positive, negative, neutral sentiment Co-occurrence patterns: Which entities are you mentioned alongside Topic associations: What subjects/topics appear in mention context Geographic distribution: Where mentions originate
According to Brandwatch research, entities tracking mention patterns monthly make 73% faster strategic adjustments than those monitoring quarterly.
Co-Occurrence Pattern Analysis
Analyze which entities you’re consistently mentioned alongside:
Co-occurrence tracking questions:
Competitive positioning: How often are you mentioned with category leaders? Peer associations: Which same-tier entities appear in your co-occurrence patterns? Technology associations: What platforms/tools are mentioned in your context? Concept associations: What industry concepts appear alongside your entity?
Manual analysis: Read articles mentioning your entity and note all other entities mentioned
Automated analysis: Use natural language processing tools to extract entity co-occurrences from mention corpus
Track co-occurrence frequency changes monthly. Increasing co-mentions with established authorities indicates improving semantic positioning.
Competitive Mention Share Analysis
Compare your mention frequency to competitors in the same category:
Share of voice metrics:
Category mention share: Your mentions ÷ total category mentions Head-to-head comparisons: Your mentions vs. specific competitor mentions Trend analysis: Is your share growing or declining vs. competitors Source tier distribution: Where do your mentions appear vs. competitors
Tools like Brand24, Mention, and Brandwatch provide competitive mention tracking and share of voice calculations.
According to SEMrush’s competitive analysis, entities achieving 15%+ category mention share see 89% higher inclusion in “[category] software” and alternative searches.
Mention-to-Ranking Correlation Tracking
Correlate mention improvements with search visibility changes:
Track correlations between:
Mention volume increases → Branded search volume growth High-authority mentions → Knowledge Panel appearance/enhancement Competitor co-mentions → “Alternative to [competitor]” ranking improvements Topic co-mentions → Topical query ranking improvements
While correlation doesn’t prove causation, patterns indicate mention strategy effectiveness.
Use tools like Google Search Console, SEMrush, or Ahrefs to track ranking changes alongside mention monitoring data.
What Advanced Strategies Amplify Entity Mention Effects?
Entity context building accelerates through advanced tactics that multiply mention value and co-occurrence patterns.
Strategic Entity Network Expansion
Build a network of associated entities that all reference each other:
Network building approach:
Partnership ecosystem: Create multiple partnerships where all partners cross-reference Industry alliance: Form or join associations where members mention each other Expert network: Build relationships with industry experts who cite each other Content collaboration: Co-create content with complementary entities
When Entity A mentions Entity B, Entity B mentions Entity C, and Entity C mentions Entity A, search engines recognize a validated entity network.
According to network effect research, entities with 5+ bidirectional mention relationships show 156% higher Knowledge Graph confidence scores.
Structured Data Mention Enhancement
Use schema markup to explicitly declare entity relationships:
Relevant schema properties:
mentions: Explicitly mark entity mentions in content about: Declare what entities content discusses partner: Identify partnership entities sponsor: Mark sponsorship relationships memberOf: Declare association memberships
{
"@type": "Article",
"mentions": [
{
"@type": "Organization",
"name": "Salesforce",
"url": "https://www.salesforce.com"
},
{
"@type": "Organization",
"name": "HubSpot",
"url": "https://www.hubspot.com"
}
]
}
This structured data reinforces natural entity mentions with explicit declarations.
Geographic Mention Clustering
Build location-specific entity associations through targeted geographic mentions:
Local entity strategies:
Local media coverage: Earn mentions in city/regional publications Geographic awards: Win “Best [City] [Category]” awards Local events: Participate in regional conferences and meetups Area directories: List in city-specific business directories Local partnerships: Partner with other entities in your geography
Geographic mention clustering positions you for location-based queries like “best [category] in [city].”
According to BrightLocal’s geographic research, entities with 20+ local mentions see 84% higher Local Pack inclusion.
Temporal Mention Consistency
Maintain consistent mention frequency over time rather than sporadic bursts:
Mention consistency strategies:
Monthly content calendar: Publish thought leadership consistently HARO routine: Respond to journalist queries weekly Regular partnerships: Announce new collaborations quarterly Event participation: Attend/speak at events year-round Award applications: Apply for awards on regular cycles
Consistent monthly mentions signal active, relevant entities. Long gaps in mentions can trigger entity significance decline.
According to temporal analysis research, entities with consistent monthly mentions maintain 67% higher Knowledge Panel accuracy than those with sporadic mention patterns.
For complete frameworks implementing these advanced strategies, see our entity SEO guide.
What Common Mistakes Damage Entity Mention Value?
Even sophisticated entities make errors that undermine entity associations and weaken co-occurrence benefits.
Pursuing Mention Quantity Over Quality
The biggest mistake: maximizing mention volume in low-quality sources while neglecting high-authority mentions.
100 spam directory mentions < 1 TechCrunch mention for entity authority.
Many businesses:
- Submit to every possible directory
- Buy mention placements on content farms
- Create fake testimonial mentions
- Use black-hat mention building services
These provide minimal entity value and risk penalties when search engines detect manipulation.
Fix: Focus 80% of effort on earning mentions in Tier 1 and 2 sources through legitimate means (media relations, thought leadership, partnerships).
Ignoring Mention Context and Sentiment
Brand mentions entity impact varies dramatically based on context:
Negative context mentions can harm more than help:
- Customer complaints on review sites
- Negative news coverage
- Critical social media discussions
- Controversy mentions
Treating all mentions equally misses sentiment analysis search engines perform.
Fix: Monitor mention sentiment actively. Address negative mentions professionally. Work to earn positive-context mentions that balance negative ones.
Over-Optimizing Anchor Text in Mentions
Some entities force unnatural keyword-rich anchor text into every mention:
❌ “Visit industry-leading enterprise CRM software solution provider XYZ Company” ✅ “Visit XYZ Company, a CRM software provider”
Over-optimization triggers manipulation detection and reduces mention credibility.
Fix: Use natural entity names and varied descriptions. Let others describe you in their own words rather than forcing specific phrasing.
Neglecting Co-Occurrence Diversification
Focusing too narrowly on co-occurrences with just one or two entities limits categorization:
Being mentioned only with Salesforce positions you as “Salesforce alternative” but may miss broader “CRM software” categorization.
Fix: Build co-occurrence patterns with multiple category leaders, peers, complementary technologies, and industry concepts for comprehensive positioning.
Failing to Document Partnership Mentions
Many entities announce partnerships but fail to maintain permanent documentation:
- Partnership pages get deleted after announcements
- Press releases disappear after 90 days
- No ongoing reference to partnerships
- Partners don’t reciprocate mentions
Fix: Create permanent partnership pages. Ensure partners maintain reciprocal mentions. Reference partnerships in ongoing content. Update partnership pages regularly.
Real-World Entity Mention Strategy: Case Study
A cloud security startup struggled with entity recognition despite solid technology. They had minimal entity mentions and zero co-occurrence with category leaders like CrowdStrike, Palo Alto Networks, or Okta.
Their Strategic Mention Campaign
Phase 1: Foundational Mentions (Months 1-4)
- Claimed listings on G2, Capterra, TrustRadius (comparison platforms)
- Joined Cloud Security Alliance, earned member directory mention
- Published 4 thought leadership pieces on cybersecurity blogs
- Responded to 15 HARO queries, earned 7 placements
Phase 2: Competitive Co-Occurrence Building (Months 3-8)
- Created comprehensive competitor comparison pages (vs. 5 major alternatives)
- Pitched and earned inclusion in “Top Cloud Security Tools” articles (3 placements)
- Won regional cybersecurity award, mentioned alongside major players
- Presented at 2 industry conferences with category leaders
Phase 3: High-Authority Mention Development (Months 6-12)
- Published original research on cloud security trends, cited by major publications
- Earned byline in Dark Reading (major cybersecurity publication)
- Featured expert in TechCrunch article about cloud security
- Partnered with major cloud platform, announced in both entities’ press releases
Phase 4: Systematic Co-Occurrence Expansion (Months 9-15)
- Published monthly thought leadership mentioning category trends and leaders
- Responded to 40+ HARO queries, earned 18 expert mentions
- Participated in 4 webinars with complementary security entities
- Built integration partnerships with 3 established platforms
Measurable Mention Impact
After 15 months of systematic mention building:
Mention metrics:
- Total monthly mentions: 3 to 47
- Tier 1/2 source mentions: 0 to 12
- Co-occurrences with category leaders: 0 to 28 instances
Co-occurrence analysis:
- Mentioned alongside CrowdStrike: 8 times
- Mentioned alongside Palo Alto Networks: 6 times
- Mentioned alongside Okta: 5 times
- Mentioned in “cloud security” context: 34 times
Search visibility impact:
- Knowledge Panel appeared (month 9)
- “Cloud security tools” rankings: not ranking → page 2
- “[Competitor] alternative” rankings: 5 phrases ranking in top 10
- Branded search volume: +178%
- Organic traffic: +143%
Business impact:
- Demo requests from search: +156%
- Average deal size: +31% (attributed to perceived category positioning)
- Sales cycle length: -23% (buyers saw them as established alternative)
Total investment: Approximately 20 hours/month of internal effort plus $8,500 in strategic costs (PR services, conference fees, award applications).
Entity mentions SEO delivered 6:1 ROI within 15 months through improved search visibility and enhanced brand positioning.
Frequently Asked Questions About Entity Mentions & Co-Occurrences
Do unlinked brand mentions really affect SEO rankings?
Yes, according to multiple Google confirmations and industry research. While linked mentions provide additional link equity benefits, unlinked mentions contribute to entity recognition, categorization, and authority. Google’s John Mueller has confirmed brand mentions factor into search algorithms. According to research, unlinked mentions from authoritative sources carry approximately 70% the SEO value of linked mentions from equivalent sources.
How many entity mentions do you need to see SEO impact?
Quality matters more than quantity, but 10-15 monthly mentions from Tier 1/2 sources typically shows measurable impact within 6-9 months. A single mention in The Wall Street Journal can provide more impact than 100 directory listings. Focus on earning mentions from sources your target audience reads and search engines trust. Consistent monthly growth (even 2-3 quality mentions/month) compounds better than sporadic bursts.
Can you ask partners and customers to mention your brand more?
Yes, but it must be natural and valuable, not manipulative. Requesting mentions in exchange for value (case studies featuring mutual success, partnership pages benefiting both parties, guest posts providing audience value) is legitimate. However, buying mentions, requiring mentions in contracts unrelated to the relationship, or forcing unnatural keyword-rich mentions can trigger manipulation detection. Keep mentions authentic and mutually beneficial.
How do you track entity co-occurrences effectively?
Use mention monitoring tools combined with manual analysis. Tools like Brand24, Mention, or Ahrefs Content Explorer track all mentions. Export mention data and manually analyze which other entities appear in the same content. More advanced users can employ natural language processing tools to extract entity co-occurrences programmatically from large mention datasets. Track co-occurrence frequency monthly to identify patterns.
Do social media mentions have the same SEO value as editorial mentions?
No, social mentions carry significantly less SEO weight. While social media mentions contribute to overall brand awareness and can drive traffic, search engines assign lower authority to social posts than editorial content. According to research, social mentions carry approximately 10-20% the SEO value of equivalent editorial mentions in authoritative publications. Focus primary effort on editorial mentions while using social to amplify reach.
Can negative mentions hurt your entity SEO?
Yes, particularly when negative mentions dominate your mention profile. Search engines analyze mention sentiment. Overwhelming negative mentions in authoritative sources damage entity reputation signals and can reduce Knowledge Panel prominence or trigger negative information in panels. However, occasional criticism doesn’t significantly harm overall entity authority. Monitor sentiment and work to balance negative mentions with positive coverage through improved products/services and strategic PR.
Final Thoughts on Building Strategic Entity Mention Patterns
Entity mentions SEO and entity co-occurrences represent the future of how search engines understand, categorize, and rank entities. The brands winning search visibility in 2025 and beyond won’t be those with the most backlinks—they’ll be those strategically positioned through mention patterns that teach search engines exactly where they belong in the semantic web.
The power of co-occurrence positioning is that it works cumulatively. Each quality mention adds to your entity understanding. Each co-occurrence with category leaders strengthens your competitive positioning. Each consistent mention pattern reinforces your topical authority. These signals compound over time, creating entity authority that persists long after individual mentions.
Start with the fundamentals: monitor all mentions comprehensively, analyze co-occurrence patterns, identify gaps in competitive positioning, and systematically earn mentions in high-authority sources alongside the entities you want to be associated with.
Build mention acquisition into regular operations: respond to HARO queries weekly, pitch thought leadership monthly, participate in industry events quarterly, announce partnerships as they develop. Consistency beats sporadic effort every time.
Track not just mention volume but mention context, co-occurrence patterns, source authority, and correlation with search visibility improvements. Use data to refine strategy and double down on what works.
The entities dominating search in entity-driven algorithms will be those with comprehensive, strategic mention patterns that position them exactly where they need to be in the Knowledge Graph’s semantic understanding. Build those patterns systematically, earn mentions authentically, and maintain consistency relentlessly.
That’s how lasting entity positioning gets built through the company you keep in the vast network of entity relationships search engines map and reward.
Citations and Sources
- Google Research – Entity Relationship Research Paper
- Moz – Unlinked Brand Mentions SEO Study
- Search Engine Journal – Brand Mentions SEO Guide
- Stanford NLP – Entity Recognition Projects
- Ahrefs – Competitor Research Guide
- SEMrush – Audience Targeting SEO
- Content Marketing Institute – Research Reports
- Event Marketing Institute – Event ROI Research
- Clearscope – Entity Optimization Blog
- Cision – Media Analysis Research
- Brandwatch – Social Listening Reports
- SEMrush – Competitive Research Guide
- BrightLocal – Local SEO Ranking Factors
- Moz – Entity Freshness Signals
Related posts:
- Entity SEO Complete Guide: Building Your Brand’s Knowledge Graph Presence (Visualization)
- What is Entity SEO? Understanding Entities in Modern Search Algorithms
- How Google’s Knowledge Graph Works: Understanding Entity Recognition & Ranking (Visualization)
- Building Brand Entity Signals: Establishing Your Business as a Recognized Entity