You’ve got an amazing online store. Your products are top-notch. Your prices are competitive. But somehow, your competitors are drowning in organic traffic while you’re scraping by with a trickle.
What’s their secret? They’ve mastered ecommerce keyword research—the art of discovering exactly what your customers are typing into Google when they’re ready to buy. This isn’t about guessing or hoping. It’s about systematically uncovering the high-converting search terms that bring in customers with credit cards in hand.
This guide will show you how to find profitable keywords that actually drive sales, not just vanity traffic. Let’s turn those search boxes into cash registers.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhy Ecommerce Keyword Research Is Different (And More Important)
Here’s the thing: keyword research for online stores isn’t like regular content marketing keyword research. You’re not trying to rank for “what is a blender”—you need to rank for “best vitamix blender deals” because that person is ready to buy TODAY.
According to Ahrefs, 96.55% of content gets zero search traffic from Google. That’s not because the content is bad—it’s because nobody is searching for what they wrote about. Or worse, they’re targeting keywords they’ll never rank for.
The difference between thriving ecommerce stores and struggling ones often comes down to one thing: targeting the RIGHT keywords. Not the highest volume keywords. Not the coolest-sounding keywords. The ones that actually convert.
Think of keyword research as your roadmap. Without it, you’re driving blind, hoping to stumble upon customers. With it, you know exactly where your buyers are and how to meet them there.
What Makes a Keyword “Profitable” for Ecommerce?
Not all keywords are created equal. Some bring tire-kickers. Others bring buyers. Understanding the difference is everything.
The three pillars of profitable ecommerce keywords:
1. Commercial Intent
People searching “how to clean leather boots” are researching. People searching “buy waterproof leather boots men size 10” are buying. Focus your energy on the latter.
2. Realistic Competition
Ranking #47 for “shoes” helps nobody. Ranking #3 for “vegan leather dress shoes women wide width” puts cash in the bank. Target keywords you can actually win.
3. Sufficient Search Volume
The perfect keyword that 5 people search per month won’t move the needle. Balance specificity with volume—aim for keywords with at least 100-500 monthly searches for niche products, 1,000+ for mainstream items.
Pro Tip: The sweet spot is keywords with strong buyer intent, manageable competition, and decent volume. Think “best organic cotton baby clothes” rather than “baby clothes” or “how to dress a baby.” One targets browsers, one targets researchers, and one targets buyers.
How Do You Start Ecommerce Keyword Research from Scratch?
Let’s break down how to do keyword research for ecommerce website step-by-step, even if you’re starting with zero data.
Step 1: Understand Your Products and Audience
Before touching any tools, answer these questions:
- What problems do your products solve?
- Who is your ideal customer?
- What words would THEY use (not industry jargon)?
- What questions do customers ask before buying?
Real example: A store selling ergonomic office chairs discovered customers searched for “chairs for back pain” and “best chair for sitting all day” way more than “ergonomic office chair.” Understanding customer language is half the battle.
Step 2: Make a Seed Keyword List
Start with 10-20 basic terms related to your products. These are your starting points, not your final targets.
For a coffee equipment store:
- espresso machine
- coffee grinder
- french press
- pour over coffee maker
- coffee beans
These seed keywords will explode into hundreds of variations once you plug them into research tools.
Step 3: Analyze Search Intent
Every keyword falls into one of four intent categories:
| Intent Type | What They Want | Example Keywords | Your Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Informational | Learning/Research | “how to make espresso,” “types of coffee makers” | Blog content, guides |
| Navigational | Specific brand/site | “Breville espresso machine,” “Amazon coffee grinder” | Brand pages, product pages |
| Commercial | Comparing options | “best espresso machines 2025,” “Breville vs Gaggia” | Comparison content, category pages |
| Transactional | Ready to buy NOW | “buy espresso machine,” “cheap coffee grinder free shipping” | Product pages, category pages |
Focus 80% of your product page optimization on commercial and transactional keywords. These convert. Save informational keywords for blog content that builds awareness and links to your products.
For strategies on optimizing different page types, check our complete ecommerce SEO guide.
What Are the Best Keyword Research Tools for Online Stores?
You need tools to scale keyword research. Here’s the truth about the most popular options:
Essential Free Tools
Google Keyword Planner
- Best for: Finding search volume and basic ideas
- Limitations: Broad volume ranges unless you’re running ads
- Use case: Starting point for seed keyword expansion
Google Search Console
- Best for: Keywords you already rank for (but didn’t know)
- Limitations: Only shows your existing rankings
- Use case: Finding low-hanging fruit to optimize
Google Autocomplete & “People Also Ask”
- Best for: Real questions customers ask
- Limitations: No volume data, manual process
- Use case: Finding long-tail question keywords
Premium Tools Worth the Investment
| Tool | Best For | Pricing | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ahrefs | Comprehensive keyword & competitor analysis | $99-$999/mo | Massive keyword database, competitor keywords, ranking difficulty |
| SEMrush | All-in-one SEO platform | $119-$449/mo | Keyword magic tool, competitor analysis, position tracking |
| Ubersuggest | Budget-friendly option | Free-$29/mo | Basic keyword ideas, search volume, SEO difficulty |
| Long Tail Pro | Long-tail keyword focus | $37-$67/mo | Specific focus on low-competition keywords |
Pro Tip: Start with free tools if you’re bootstrapping. Once you’re making $5,000+/month, invest in Ahrefs or SEMrush—they pay for themselves by revealing opportunities free tools miss. I’ve personally found competitor keyword analysis alone worth the Ahrefs subscription.
For a store doing $50k+/month, premium tools are non-negotiable. They reveal what your competitors rank for, show keyword difficulty accurately, and uncover profitable long-tail terms that free tools miss entirely.
How to Find High-Converting Ecommerce Keywords Nobody Else Targets
This is where finding high-converting ecommerce keywords gets interesting. Most stores fight over the same obvious terms. Smart stores find overlooked goldmines.
Technique 1: The Modifier Method
Take your base product keyword and add buying modifiers:
Base keyword: “running shoes”
High-intent modifiers:
- best running shoes for [specific problem]
- [brand] running shoes sale
- buy running shoes online
- cheap running shoes free shipping
- running shoes near me
- running shoes deals
- top rated running shoes 2025
These modifiers signal buying intent. Someone searching “running shoes” might be browsing. Someone searching “best running shoes for plantar fasciitis women” is ready to buy.
Technique 2: Spy on Your Competitors
Use Ahrefs or SEMrush to enter your competitor’s URL and see every keyword they rank for. You’ll discover:
- Keywords you should target but aren’t
- Content gaps in your strategy
- Products they’re winning with
Real example: A jewelry store discovered their competitor ranked for 300+ “engagement ring” variations they’d never considered. Adding those specific terms to product titles and descriptions increased their organic traffic by 127% in 5 months.
Technique 3: Mine Your Own Search Data
If you already have traffic, Google Search Console is pure gold. Look for:
- Keywords ranking positions 11-30 (page 2-3)
- High impressions but low clicks (optimize title/description)
- Queries you rank for but don’t target (create dedicated content)
These are low-hanging fruit—you’re already on Google’s radar, you just need optimization to push into top positions.
Technique 4: Customer Language Mining
Read your customer reviews, support tickets, and social media comments. Customers use different words than you do.
You say: “moisture-wicking athletic apparel” They say: “workout clothes that don’t show sweat”
Guess which one gets more searches? Target the language real humans actually use.
Pro Tip: Create a spreadsheet with customer phrases from reviews, emails, and support tickets. Many of these become perfect long-tail keywords with zero competition because companies ignore actual customer language.
What’s the Best Keyword Strategy for Ecommerce Product Pages?
Product keyword research requires a different approach than blog content. Here’s the framework that works:
Primary Keyword Selection for Products
Your main product keyword should include:
- Product type (what it is)
- Key attribute (what makes it different)
- Target audience (who it’s for) – optional but powerful
Examples:
- “organic cotton baby onesies” (product + attribute)
- “waterproof hiking boots women” (product + attribute + audience)
- “wireless noise cancelling headphones” (attribute + product)
Secondary Keywords to Include
Each product page should target 3-7 related keywords naturally:
- Brand + product name variations
- Synonyms and related terms
- Question-based keywords
- Feature-specific terms
For wireless headphones:
- Primary: “wireless noise cancelling headphones”
- Secondary: “Bluetooth headphones,” “best headphones for travel,” “over-ear wireless headphones,” “active noise cancellation headphones”
Long-Tail Product Keywords
These ultra-specific terms have lower volume but convert like crazy:
- “best wireless headphones for small ears”
- “noise cancelling headphones for sleeping”
- “bluetooth headphones with best battery life”
- “headphones for autism sensory issues”
Most stores ignore these because volume looks low in tools. Big mistake. Collectively, long-tail keywords drive 40-60% of search traffic and convert better because they match specific needs.
Pro Tip: Create a keyword map—assign specific keywords to specific pages. Don’t let multiple pages compete for the same term (keyword cannibalization). One page, one primary keyword, plus related terms.
Learn more about optimizing product pages in our ecommerce SEO ultimate guide.
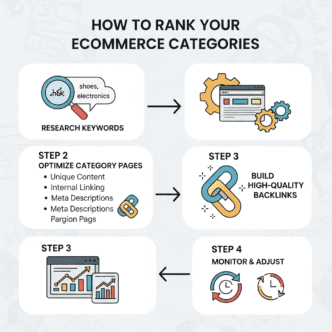
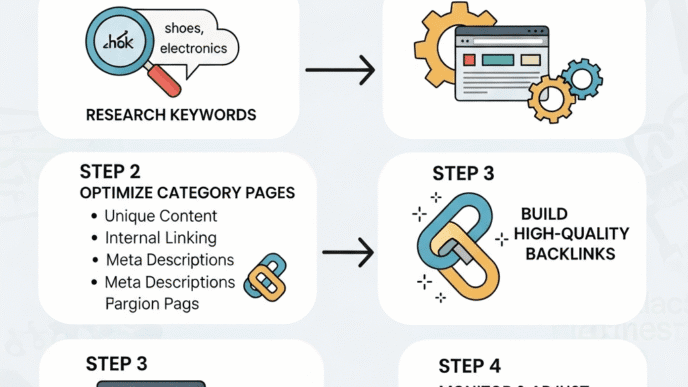
How Do You Research Keywords for Category Pages?
Category pages are your chance to capture broader, higher-volume terms. Keyword strategy for ecommerce category pages differs from product pages.
Category Page Keyword Patterns
Target keywords that indicate browsing/comparing:
- [Product category] plural (e.g., “running shoes”)
- “Best [product category]” (e.g., “best espresso machines”)
- “[Product category] for [use case]” (e.g., “laptops for video editing”)
- “[Brand] [product category]” (e.g., “Nike running shoes”)
Avoid These Category Page Mistakes
❌ Too specific: “red leather men’s size 10 running shoes” (that’s a product page keyword) ✅ Right level: “men’s running shoes” or “trail running shoes”
❌ Too broad: “shoes” (you’ll never rank against Amazon and Zappos) ✅ Right level: “minimalist running shoes” or “wide width running shoes”
Real-World Category Page Success
A supplement store struggled to rank for competitive terms like “protein powder.” By targeting more specific category keywords like “vegan protein powder” and “grass-fed whey protein,” they:
- Ranked in top 5 for 47 category keywords within 6 months
- Increased organic traffic by 312%
- Category pages became their #1 traffic source
The lesson? Specificity wins when you can’t compete with giants on broad terms.
Finding Buyer Intent Keywords That Actually Convert
Finding buyer intent keywords is the secret sauce. Traffic without conversions is just expensive bandwidth.
High-Intent Keyword Signals
Look for keywords containing these modifiers:
Transactional modifiers:
- buy, purchase, order, shop
- cheap, affordable, discount, sale, deals
- free shipping, coupon, promo code
- in stock, available
Commercial investigation modifiers:
- best, top, review, comparison
- vs, versus, alternative
- [year] (e.g., “best laptops 2025”)
- for [specific use case]
Intent Analysis Exercise
Let’s compare three similar searches:
| Keyword | Monthly Volume | Buyer Intent | Priority |
|---|---|---|---|
| “coffee maker” | 74,000 | Low (browsing) | Low |
| “best drip coffee maker” | 8,100 | High (comparing) | High |
| “buy cuisinart coffee maker” | 320 | Very High (buying) | Medium |
The highest volume keyword has the lowest intent. The lowest volume has the highest intent. For ecommerce, prioritize intent over volume—always.
Pro Tip: Use Google’s “Searches related to” at the bottom of results pages. These often reveal high-intent variations you’d never think of. I’ve found some of my best converting keywords this way.
How to Organize Your Ecommerce SEO Keywords for Maximum Impact
You’ve found hundreds of keywords. Now what? Organization makes the difference between success and overwhelm.
Create a Keyword Mapping Spreadsheet
Essential columns:
- Keyword (the actual term)
- Search Volume (monthly searches)
- Keyword Difficulty (how hard to rank)
- Search Intent (informational/commercial/transactional)
- Target URL (which page targets this keyword)
- Current Ranking (if any)
- Priority (high/medium/low)
Keyword Assignment Strategy
Homepage: Brand name, store name variations Category Pages: Broader product category terms Product Pages: Specific product keywords + variations Blog Posts: Informational and commercial investigation keywords
Pro Tip: Use color coding in your spreadsheet—green for low competition + high volume, yellow for moderate competition, red for highly competitive. Prioritize green keywords first for quick wins.
Example from a pet supply store:
- Homepage: “PetCo Pet Supplies,” “pet store online”
- Category Page (Dog Food): “organic dog food,” “grain-free dog food,” “best dog food brands”
- Product Page: “Blue Buffalo grain-free dog food 30lb,” “large breed puppy food”
- Blog Post: “how to choose the right dog food,” “grain-free vs regular dog food”
No overlap, clear targeting, every page has a job.
What Role Does AI Play in Ecommerce Keyword Research?
AI is transforming keyword research for online stores in 2025. Here’s what’s actually useful (and what’s hype):
ChatGPT for Keyword Ideation
Use AI to brainstorm keyword variations quickly:
Prompt example: “I sell organic baby clothes. Generate 30 high-intent keyword variations that parents might search for when looking to buy organic baby clothing online.”
AI excels at generating variations you might not think of. But—and this is critical—verify volume and competition with actual tools. AI makes up data.
AI-Powered Keyword Tools
New tools like Surfer SEO and MarketMuse use AI to:
- Analyze top-ranking content
- Suggest related keywords to include
- Identify content gaps
- Predict keyword difficulty more accurately
These work well for content optimization but shouldn’t replace traditional keyword research tools for discovery.
Predictive Search Trends
Tools like Google Trends now use machine learning to predict rising keywords before they peak. For ecommerce, this means:
- Identifying seasonal trends early
- Catching new product categories as they emerge
- Adapting faster than competitors
Pro Tip: Use AI for brainstorming and content gap analysis, but validate everything with data from Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Google Keyword Planner. AI hallucinates keyword volumes—never trust it blindly.
For more on AI’s impact on ecommerce SEO, explore our comprehensive guide.
How to Track and Measure Keyword Performance
Keyword research for product pages doesn’t end at implementation. Tracking reveals what’s working and what needs adjustment.
Essential Metrics to Monitor
Rankings:
- Track positions for target keywords weekly
- Monitor movement (up/down/stable)
- Watch for sudden drops (competitor activity or algorithm changes)
Traffic:
- Organic sessions per keyword
- Landing page performance
- Traffic trends over time
Conversions:
- Conversion rate by keyword
- Revenue generated per keyword
- Cost per acquisition from organic
Click-Through Rate (CTR):
- Impressions vs. clicks in Search Console
- Optimize titles/descriptions for low-CTR high-ranking keywords
Tools for Tracking
| Tool | What It Tracks | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Google Search Console | Rankings, clicks, impressions, CTR | Free performance data |
| Google Analytics 4 | Traffic, conversions, revenue | Attribution and ROI |
| Ahrefs Rank Tracker | Keyword positions, competitor rankings | Daily rank monitoring |
| SEMrush Position Tracking | Rankings across locations, devices | Multi-location tracking |
Pro Tip: Set up automated weekly reports showing your top 20 keywords’ rankings and organic revenue. Review every Monday morning. This discipline catches problems early and celebrates wins.
Real example: An electronics store noticed their “best laptop for college students” keyword dropped from position 3 to 12 overnight. Quick investigation revealed a competitor published an updated 2025 guide. They refreshed their content within 48 hours and recovered their position within a week.
Common Ecommerce Keyword Research Mistakes to Avoid
Even experienced marketers make these errors. Learn from their pain:
Mistake 1: Targeting Only High-Volume Keywords
Everyone wants to rank for “coffee maker” (74,000 searches/month). Almost nobody succeeds. Meanwhile, “best pour over coffee maker for beginners” (800 searches) sits there ripe for the taking.
Fix: Target a mix—mostly medium and long-tail keywords (80%) with a few aspirational high-volume terms (20%).
Mistake 2: Ignoring Search Intent
Ranking for informational keywords when you need transactional traffic burns resources. Someone searching “how to use espresso machine” isn’t buying today.
Fix: Match content type to intent. Blog posts for informational, product pages for transactional.
Mistake 3: Keyword Cannibalization
Having multiple pages target the same keyword confuses Google and splits your ranking power.
Fix: Create a keyword map. One primary keyword per page. Related terms are fine, but avoid direct competition between your own pages.
Mistake 4: Never Updating Your Keyword Strategy
Keywords change. Trends shift. New competitors emerge. Yesterday’s perfect keyword might be tomorrow’s waste of effort.
Fix: Review your keyword strategy quarterly. Adjust based on performance data.
Mistake 5: Obsessing Over Exact Match
Modern Google understands context and synonyms. Stuffing exact-match keywords 47 times looks spammy and hurts rankings.
Fix: Use your primary keyword naturally 3-5 times. Include variations, synonyms, and related terms throughout.
Pro Tip: The biggest mistake is analysis paralysis—researching forever without implementing. Pick your top 10 keywords and optimize those pages this week. Perfection is the enemy of progress in SEO.
Real-World Keyword Research Case Study
Let’s walk through a complete ecommerce keyword research example with real results.
The Business: Mid-sized outdoor gear retailer, $2M annual revenue, struggling with organic visibility
The Challenge:
- Ranking for almost nothing
- Traffic dominated by branded searches (people who already knew them)
- Losing to big-box retailers on all major terms
The Research Process:
Month 1: Discovery
- Analyzed 500+ seed keywords using Ahrefs
- Identified 1,200 potential target keywords
- Prioritized based on difficulty, volume, and intent
- Competitor analysis revealed 300+ keywords they weren’t targeting
Month 2: Strategy
- Created keyword map for 50 top products
- Identified 20 “quick win” keywords (low competition, high intent)
- Developed content calendar for 12 informational blog posts
Month 3-6: Implementation
- Optimized product titles with primary keywords
- Rewrote 50 product descriptions with target keywords
- Published blog content targeting informational keywords
- Built internal links using keyword-rich anchor text
The Results (6 Months):
- Organic traffic increased 287%
- Ranked for 143 commercial keywords (up from 8)
- Revenue from organic search grew 312%
- Average keyword position improved from 47 to 12
Key Takeaway: They didn’t try to compete with REI and Cabela’s on “camping gear.” They targeted specific, lower-competition terms like “ultralight backpacking tent 2 person” and “best hiking boots for wide feet.” Specificity won.
Expert Insights on Ecommerce Keyword Research
Rand Fishkin, founder of SparkToro:
“The biggest mistake I see is ecommerce sites targeting only product-specific keywords. You need to own the entire customer journey—from ‘how do I choose X’ to ‘buy X online.’ Build topical authority.”
Aleyda Solis, international SEO consultant:
“Stop obsessing over search volume. I’ve seen keywords with 50 searches/month generate more revenue than keywords with 5,000 searches because the intent was perfect. Quality over quantity.”
Brian Dean, founder of Backlinko:
“The best keywords for ecommerce are the ones nobody thinks to target. Dig deeper than the first level of keyword tools. That’s where the goldmines are.”
These experts agree: success in ecommerce keyword research comes from strategic thinking, not just tool usage. Tools show you data; strategy determines what to do with it.
Advanced Keyword Research Techniques
Once you’ve mastered the basics, these advanced tactics separate leaders from followers:
Seasonal Keyword Planning
Some products spike seasonally. Research and prepare content 3-6 months ahead:
- “Christmas gifts for mom” (start optimizing in September)
- “back to school backpacks” (target by June)
- “swimwear” (optimize in February for summer)
Use Google Trends to identify seasonal patterns and time your optimization accordingly.
Competitor Keyword Gap Analysis
Find keywords your competitors rank for but you don’t:
- Enter 3-5 competitor URLs into Ahrefs
- Use the “Content Gap” tool
- Filter for keywords ALL competitors rank for but you don’t
- Prioritize based on relevance and opportunity
This reveals blind spots in your strategy—keywords the market has validated but you’re missing.
Voice Search Optimization
More shoppers use voice assistants. Voice queries are longer and more conversational:
- Text: “coffee maker”
- Voice: “what’s the best coffee maker for small kitchens under $100”
Target question-based long-tail keywords that mirror natural speech patterns.
Local SEO Keywords for Ecommerce
Even online-only stores can benefit from local intent:
- “buy [product] near me”
- “[product] same-day delivery [city]”
- “online [product] store shipping to [state]”
These often have less competition and capture location-specific intent.
Pro Tip: Create separate landing pages for major cities if you offer localized shipping/service. “Fast Coffee Equipment Delivery in Chicago” targets local intent without needing a physical presence.
Tools and Resources for Ongoing Keyword Research
Bookmark these for continuous improvement:
Free Resources:
- Google Keyword Planner – Search volume and ideas
- Google Trends – Trending topics and seasonal patterns
- Answer the Public – Question-based keyword ideas
- Google Search Console – Your current rankings
Premium Tools:
- Ahrefs – Comprehensive keyword and competitor analysis
- SEMrush – All-in-one SEO platform
- Moz Keyword Explorer – Keyword difficulty and SERP analysis
Community Resources:
- Reddit (search your niche subreddits for customer language)
- Amazon reviews (see what customers say about competitor products)
- Quora (discover questions customers ask)
Learn how to implement these keywords effectively in our ecommerce SEO guide.
Creating Your 30-Day Keyword Research Action Plan
Let’s turn everything into a concrete action plan:
Week 1: Foundation
- [ ] List 20-30 seed keywords related to your products
- [ ] Set up Google Search Console and Analytics (if not done)
- [ ] Choose one keyword research tool (start with free, upgrade later)
- [ ] Analyze search intent for seed keywords
Week 2: Research
- [ ] Use tools to expand seed keywords into 200+ variations
- [ ] Analyze top 3 competitors’ keyword strategies
- [ ] Export keywords to spreadsheet with volume, difficulty, intent
- [ ] Identify 20 “quick win” keywords (low difficulty, high intent)
Week 3: Strategy
- [ ] Create keyword map assigning keywords to specific pages
- [ ] Prioritize keywords by potential ROI
- [ ] Identify content gaps needing new pages
- [ ] Plan 10 blog posts targeting informational keywords
Week 4: Implementation
- [ ] Optimize top 10 product pages with target keywords
- [ ] Update category page titles and descriptions
- [ ] Write first 2 blog posts
- [ ] Set up rank tracking for priority keywords
Pro Tip: Don’t try to optimize everything at once. Focus on your top 20% of products first. Perfect those, measure results, then expand. Momentum beats perfection.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many keywords should I target per product page?
One primary keyword, plus 3-7 secondary related keywords. Don’t keyword stuff—focus on one main term and naturally include variations. Quality over quantity always wins.
How long does it take to rank for ecommerce keywords?
Expect 3-6 months for competitive terms, 1-3 months for long-tail keywords. Quick wins (optimizing pages already ranking 11-30) can show results in 2-4 weeks. SEO is a marathon, not a sprint.
Should I target branded keywords?
Yes, but don’t obsess over them. If you’re “Acme Widgets,” you’ll naturally rank for “Acme Widgets” searches. Focus energy on non-branded commercial terms where real growth happens.
How do I find keywords with low competition?
Look for long-tail variations (4+ words), use keyword difficulty metrics in Ahrefs/SEMrush, and target specific niches. “Running shoes” is impossible. “Trail running shoes for overpronation women” is achievable.
Can I target the same keywords as my competitors?
Yes, but focus on gaps first—keywords they’re missing. Competing head-on requires better content, more links, and often higher domain authority. Play to your strengths by finding underserved keywords.
How often should I update my keyword research?
Quarterly reviews minimum, monthly if you’re in a fast-moving industry. Always monitor performance and adjust based on what’s working vs. what’s not.
Do I need expensive tools for keyword research?
Start with free tools (Google Keyword Planner, Search Console, Trends). Once you’re making $5k+/month, invest in Ahrefs or SEMrush—they’ll pay for themselves through discovered opportunities.
What’s the difference between short-tail and long-tail keywords?
Short-tail (1-2 words) have high volume, high competition, vague intent. Long-tail (3+ words) have lower volume, lower competition, specific intent. For ecommerce, long-tail often converts better despite lower volume.
Should I target misspellings?
Google handles most misspellings automatically now. Don’t optimize for misspellings—focus on correct spellings and Google will match misspelled queries.
Final Thoughts: Your Keyword Research Journey
Ecommerce keyword research isn’t a one-time project—it’s an ongoing strategic advantage. The stores dominating organic search didn’t get there by accident. They systematically identified what customers search for, optimized for those terms, and continuously refined their strategy based on data.
The difference between struggling stores and thriving ones often comes down to this: struggling stores guess what keywords to target. Thriving stores know.
You now have the framework, tools, and strategies to find profitable keywords that actually drive sales. Start small—pick 10 products and find the perfect keywords for them this week. Optimize those pages. Track the results. Then expand.
Remember: every keyword you rank for is a new door customers can walk through to find you. The more doors you build, the more traffic flows in. And unlike paid ads, this traffic compounds over time.
Stop guessing. Start researching. Your organic traffic growth begins today.
Ready to master ecommerce SEO beyond just keywords? Our comprehensive ecommerce SEO guide covers technical optimization, link building, content strategy, and everything else you need to dominate organic search.
Want proven SEO strategies delivered weekly? Visit seoprojournal.com for actionable guides, case studies, and expert insights that drive real results for online stores.