You’ve got 127 blog posts gathering digital dust. Some were ranking beautifully six months ago. Now? Page 3. Page 4. Basically invisible.
Here’s the thing nobody tells you about content: publishing isn’t the finish line – it’s the starting gun. Your content starts decaying the moment you hit publish. Statistics get outdated. Competitors publish better versions. Google’s algorithm evolves. Your once-stellar post becomes yesterday’s news.
But here’s the silver lining: updating existing content is the most underutilized SEO strategy that actually works. While your competitors are obsessing over new posts, you’re sitting on a goldmine of partially-ranking content that needs just a little love to dominate.
A solid content refresh strategy can boost traffic 50-200% faster than creating new content. Why? Because you’re starting with authority, existing backlinks, and indexation history. You’re not building from zero – you’re amplifying what already works.
Today, I’m revealing exactly how to identify which content needs refreshing, how to update it strategically, and how to measure the ROI. This isn’t busywork – it’s the shortcut to rankings your competitors are missing.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Exactly Is A Content Refresh Strategy And Why Does It Matter?
Let’s start with clarity. A content refresh strategy is the systematic process of identifying, updating, and republishing existing content to maintain or improve its search rankings and value to readers.
Think of it like home maintenance. You wouldn’t build a new house every time something needs repair. You fix the roof, update the kitchen, refresh the paint. Your content library works the same way.
But most bloggers treat content like “set it and forget it.” They publish, celebrate briefly, then move on to the next piece. Meanwhile, that content slowly loses relevance, rankings decline, and traffic evaporates.
Content decay is real. According to HubSpot’s research, blog posts can lose up to 50% of their organic traffic within 2-3 years without updates. That’s not because they were bad – they’re just stale.
Here’s what makes content refreshing so powerful:
Faster results – Updated content re-enters Google’s crawl queue and can see ranking improvements in days or weeks, not months.
Leveraged authority – Your existing backlinks, domain authority, and indexation history all remain. You’re building on a foundation, not starting from scratch.
Better ROI – Updating a 2,000-word post takes 2-3 hours. Creating a new one takes 8-12 hours. The refresh delivers 70% of the value at 25% of the cost.
Compound growth – New content builds linearly. Refreshed content compounds – each update strengthens an already-ranking asset.
Pro Tip: The best time to start refreshing content is when posts are ranking positions 5-15. They’re close enough to page 1 that strategic updates can push them over. Waiting until they’re on page 5 means you’re fighting uphill.
How Does Update Old Content SEO Actually Work?
Let’s demystify the mechanics. Update old content SEO works because Google’s algorithm rewards freshness, comprehensiveness, and user satisfaction signals – all of which improve when you refresh strategically.
Google’s Freshness Algorithm considers multiple signals:
Query Deserves Freshness (QDF) – For time-sensitive queries (news, events, recent products), Google heavily weights recent content. A 2022 post about “best smartphones” can’t compete with an updated 2025 version.
Incremental freshness – Small updates signal your content remains relevant. Changing a date, updating statistics, or adding new sections tells Google you’re maintaining quality.
Content freshness – Substantial updates that improve comprehensiveness and value trigger re-evaluation of rankings.
Historical optimization (we’ll dive deeper later) – Google recognizes content that maintains quality over time, rewarding sites that consistently update rather than letting content rot.
What triggers Google to re-crawl and re-evaluate?
- Updating the publish/modified date
- Changing substantial text (20%+ of content)
- Adding new sections with current information
- Improving internal linking structure
- Updating meta descriptions and titles
- Republishing through social channels
Real-world evidence: When Backlinko updated their “Google Ranking Factors” post with current information and expanded from 1,000 to 3,000 words, organic traffic increased 89% within 60 days. The URL stayed the same, backlinks remained, but freshness and comprehensiveness signaled higher quality.
The ranking improvement mechanism:
- You update content substantially
- Google’s crawlers detect changes on next crawl
- Content re-enters ranking evaluation queue
- If improvements satisfy search intent better, rankings improve
- Higher rankings = more traffic = better user signals = even better rankings
It’s a virtuous cycle – but only if you update strategically, not randomly.
What Types Of Content Need Regular Refreshing?
Not all content needs the same refresh frequency. Understanding content decay prevention requires categorizing your content and applying appropriate maintenance schedules.
Time-Sensitive Content (Update every 3-6 months)
This content loses value fastest and needs aggressive refreshing:
- Statistics and data-driven posts
- “Best tools for [year]” articles
- Industry trend analyses
- Product comparisons and reviews
- Pricing information
- How-to guides for frequently-updated software
Example: Your “Best SEO Tools 2024” post is worthless in 2025 unless updated. New tools launched, pricing changed, features evolved.
Evergreen Content (Update every 12-18 months)
These posts age more gracefully but still need periodic love:
- Fundamental how-to guides
- Educational tutorials
- Concept explanations
- Strategy frameworks
- Beginner’s guides
Example: Your “How to Start a Blog” guide doesn’t change drastically year-to-year, but hosting platforms, WordPress versions, and best practices evolve enough to warrant annual updates.
Historical/Reference Content (Update as needed, typically 24+ months)
These posts maintain value longest:
- Historical analyses
- Case studies
- Original research findings
- Timeless principles
- Philosophical perspectives
Example: A post analyzing a historical event doesn’t need frequent updates, but you might add new insights or research every few years.
Here’s a decision matrix for refresh prioritization:
| Content Type | Decay Speed | Refresh Frequency | Priority Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Statistics/Data | Very Fast | 3-6 months | High |
| Tool Reviews | Fast | 6-12 months | High |
| How-To Guides | Medium | 12-18 months | Medium |
| Concept Explainers | Slow | 18-24 months | Medium |
| Case Studies | Very Slow | 24-36 months | Low |
| Timeless Principles | Minimal | As needed | Low |
Warning signs your content needs immediate refreshing:
- Traffic declined 30%+ over 6 months
- Dropped from page 1 to page 2-3
- Competitors now outrank you with better/newer content
- Statistics or examples are 2+ years old
- Screenshots show outdated interfaces
- Internal/external links are broken
- Comments ask about outdated information
Your blog SEO strategy should include quarterly content audits identifying posts in decay.
How Do You Identify Which Content To Refresh First?
Random updating wastes time. Strategic updating multiplies results. Here’s your content refresh strategy framework for identifying high-ROI refresh opportunities.
Method 1: The Declining Traffic Approach
Use Google Analytics to identify content losing traffic:
- Navigate to Behavior → Site Content → All Pages
- Compare last 6 months vs. previous 6 months
- Sort by “% Change” descending (most negative first)
- Filter for posts with meaningful baseline traffic (100+ monthly visits)
- Export posts with 30%+ traffic decline
Why this works: These posts had authority and traffic but are losing it. They’re easier to revive than starting new content.
Method 2: The Near-Miss Rankings
Use Google Search Console to find posts “almost” ranking well:
- Go to Performance → Search Results
- Filter for pages with Average Position 8-20
- Sort by Impressions (high to low)
- Identify posts with high impressions but low CTR
Why this works: Posts ranking positions 8-20 are tantalizingly close to page 1. Small improvements can trigger dramatic traffic increases.
Method 3: The Keyword Gap Analysis
Use Ahrefs or Semrush to find opportunity gaps:
- Identify posts ranking for 5-10 keywords
- Check competitors ranking for 20-30 variations
- Note semantic keywords you’re missing
- Flag for comprehensive refresh
Why this works: You’re already partially authoritative on the topic. Adding missing subtopics and keywords can multiply your ranking footprint.
Method 4: The Quick Win Assessment
Create a scoring system for each post:
Priority Score = (Current Traffic × Ranking Position) + (Backlinks × 10) - (Months Since Update × 5)
Higher scores = Higher priority
Example calculation:
- Post gets 200 visits/month
- Ranks position 12
- Has 8 backlinks
- Last updated 18 months ago
Score = (200 × 12) + (8 × 10) – (18 × 5) = 2,400 + 80 – 90 = 2,390
Compare scores across all posts to prioritize refresh queue.
Method 5: The Competitor Displacement Strategy
Identify where competitors stole your rankings:
- Use Ahrefs’ “Competitors” report
- Find posts where you lost rankings in last 12 months
- Check which competitor now ranks there
- Analyze what they did better
- Plan refresh to reclaim position
Why this works: You had those rankings. Competitors didn’t invent new topics – they just executed better. You can take them back.
Pro Tip: Start with 5-10 posts from the “Near-Miss Rankings” method. These deliver the fastest ROI with the least effort. Once you’ve mastered the refresh process, expand to declining traffic posts and broader updates.
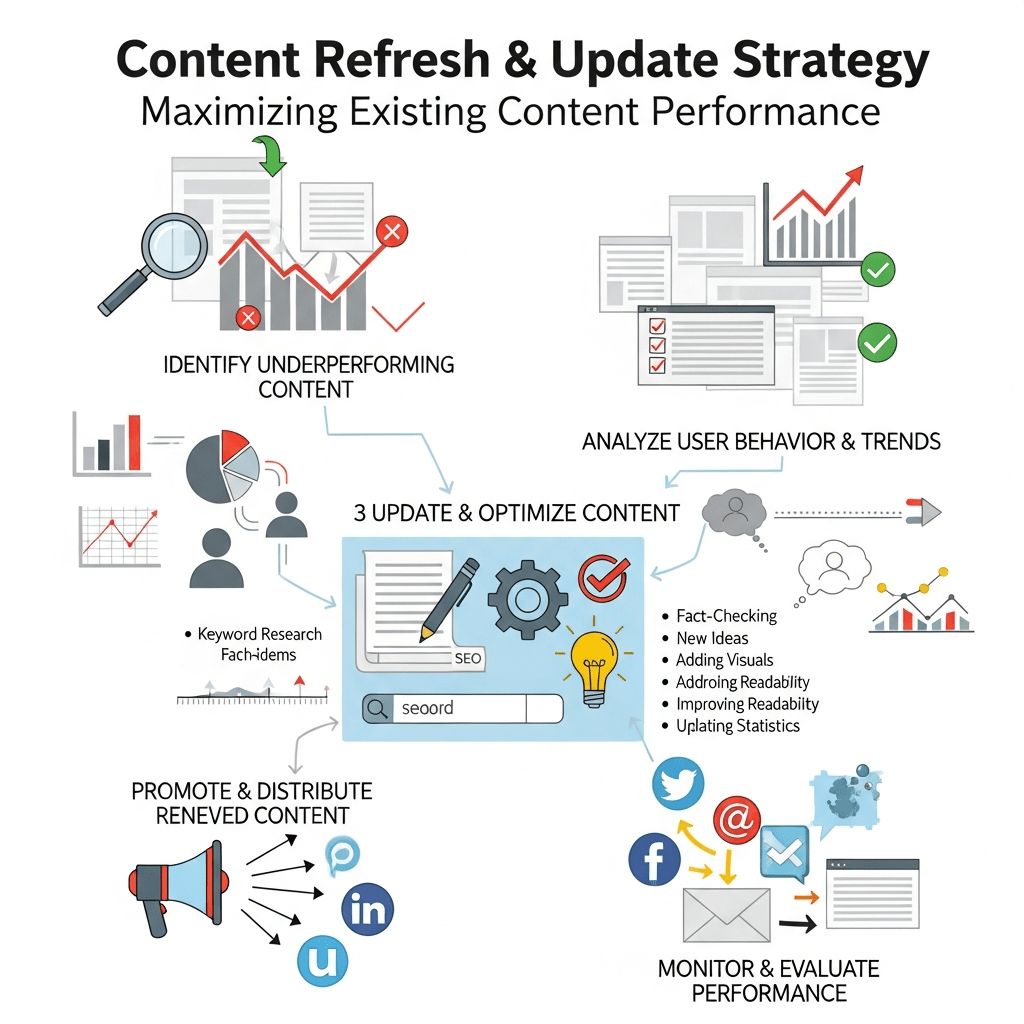
What’s The Step-By-Step Process For Content Refresh Strategy?
Let’s get tactical. Here’s the proven content refresh strategy to improve search rankings that consistently delivers results.
Step 1: Content Audit (30 minutes per post)
Before touching anything, understand what you’re working with:
- Current keyword rankings (Search Console or rank tracker)
- Current traffic levels (Google Analytics)
- Existing backlinks (Ahrefs/Semrush)
- Current word count
- Last update date
- Competitor analysis for target keyword
Document this baseline. You’ll measure success against it.
Step 2: Identify Refresh Opportunities (20 minutes)
Analyze what’s missing or outdated:
✓ Statistics over 18 months old ✓ Broken internal or external links ✓ Screenshots of old interfaces ✓ Missing semantic keywords competitors cover ✓ Thin sections that need expansion ✓ Outdated examples or case studies ✓ Missing internal links to newer content ✓ Opportunities for better media (images, videos, infographics)
Create a checklist of specific improvements needed.
Step 3: Research Current Best Practices (45 minutes)
Don’t just update – improve:
- Check what’s currently ranking in positions 1-3
- Note their word count, structure, and topics covered
- Identify content gaps you can fill
- Find fresh statistics from authoritative sources
- Look for recent industry developments to include
- Identify new tools or methods to mention
Your refresh should leapfrog current competition, not just match it.
Step 4: Execute Strategic Updates (2-4 hours)
This is where the magic happens. Make these updates methodically:
Update Statistics – Replace old data with current figures, linking to authoritative sources. Even changing “In 2022…” to “In 2024…” with updated stats signals freshness.
Expand Thin Sections – If competitors cover a subtopic in 300 words and you have 100, expand to 400 words with better examples and depth.
Add New Sections – Include recent developments, new tools, emerging trends, or additional perspectives missing from original content.
Improve Examples – Replace outdated examples with current, relevant ones. Real-world case studies from the last 12 months carry more weight.
Fix All Links – Update or remove broken links. Add internal links to newer related content. This strengthens your site’s authority web.
Refresh Media – Update screenshots showing old interfaces. Add new images, infographics, or videos that improve understanding.
Enhance Readability – Break long paragraphs into shorter ones. Add subheadings for better scannability. Improve transitions.
Optimize Technical Elements – Update title tag and meta description if needed. Improve header hierarchy. Add schema markup if missing.
Step 5: Update Publish Date Strategically (5 minutes)
This is controversial but important. You have two options:
Option A: Update “Last Modified” date – Shows freshness without changing original publish date. Maintains content age authority.
Option B: Republish with new date – Treats refresh as new content. Better for heavily rewritten pieces (50%+ new content).
My recommendation: Use Option A for updates under 40% new content. Use Option B when you’ve essentially rewritten the post.
Step 6: Republish and Promote (30 minutes)
Don’t just save and forget:
- Share on social media as “updated guide”
- Email your list highlighting improvements
- Ping internal links pointing to the post
- Submit updated URL to Search Console for re-indexing
- Update any related content that references this post
Fresh content that sits silently won’t get crawled quickly. Signal to Google it’s been updated.
Step 7: Monitor Results (Ongoing)
Track these metrics weekly for 60 days post-refresh:
- Keyword ranking changes (Search Console)
- Organic traffic changes (Google Analytics)
- Click-through rate improvements
- Time on page and engagement metrics
- Any new backlinks earned
Document what worked and what didn’t. This data informs future refresh strategies.
Pro Tip: Create a refresh template documenting each step with checkboxes. This systematizes the process so anyone on your team can execute consistently. Standardization is how you scale refresh operations.
How Do You Update And Republish Old Blog Posts For SEO?
The mechanics of how to update and republish old blog posts for SEO matter more than most realize. Small tactical errors can negate all your hard work.
The Technical Republishing Checklist:
1. Never Change the URL
This is critical. Changing URLs loses:
- All existing backlinks (they’d need 301 redirects)
- Historical ranking authority
- Social share counts
- Bookmark traffic
Keep the URL identical. Only change if absolutely necessary (wrong keyword in slug), and always 301 redirect properly.
2. Update the Modified Date
Most CMS platforms have separate “published” and “modified” dates. Update the modified date to signal freshness while maintaining publish date for authority.
WordPress users: Most themes show “Last Updated” automatically when you save changes. Verify yours does.
3. Optimize the Title and Meta Description
If your post targets different keywords now, or you want to improve CTR, update these:
Title optimization:
- Include current year if relevant (“Best SEO Tools 2025”)
- Add power words (“Complete,” “Ultimate,” “Proven”)
- Front-load target keyword
- Stay under 60 characters
Meta description optimization:
- Include target keyword naturally
- Add compelling value proposition
- Include call-to-action if appropriate
- Stay under 155 characters
4. Improve Internal Linking
Your site has more content now than when you originally published. Add links to:
- Newer related posts
- Your pillar/hub pages
- Relevant cluster content
- Updated resources
Also update older posts to link to this refreshed content. Two-way linking strengthens authority.
5. Add Visual Content
Google increasingly values multimedia:
- Update screenshots if showing interfaces
- Add custom images or graphics
- Embed relevant videos (yours or authoritative sources)
- Include data visualizations for statistics
Visual-heavy posts tend to earn more backlinks and social shares.
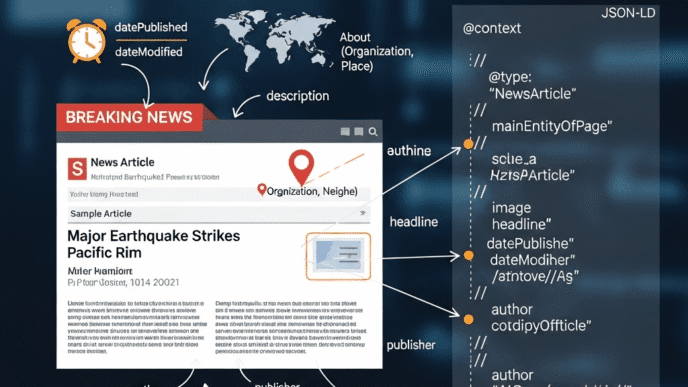
6. Implement or Update Schema Markup
Add structured data to help Google understand your content:
- Article schema with updated dateModified
- FAQ schema for question sections
- How-To schema for step-by-step guides
- Review schema for product reviews
Use Google’s Schema Markup Validator to test implementation.
7. Request Immediate Re-Indexing
Don’t wait for Google to discover your changes organically:
Method 1: Submit URL through Google Search Console’s URL Inspection tool → Request Indexing
Method 2: Share on social platforms (especially Twitter/X) → Social signals trigger crawling
Method 3: Update your sitemap’s lastmod date → Resubmit sitemap to Search Console
Method 4: Post on high-traffic platforms (Reddit, LinkedIn) → External signals accelerate discovery
8. Create an “Updated Content” Distribution Campaign
Treat refreshed content as new:
Email your list: “We just updated our guide on [topic] with 2025 data and insights”
Social media: Share with context about what’s new (“Just refreshed with 10 new case studies”)
Internal promotion: Add to site sidebar as “Recently Updated”
Outreach: If you added new research or data, email sites that linked before asking if they want to update their links with new info
The “Substantial Update” Threshold:
Google’s Gary Ilyes has stated that “meaningful” updates get treated differently than minor tweaks. Aim for:
- 20%+ new or modified content (minimum)
- Multiple new sections or substantial expansions
- Updated statistics and examples throughout
- Improved comprehensiveness
Changing a date and two sentences won’t trigger re-evaluation. Substantial improvement will.
Pro Tip: Create a “Content Updates” category or tag on your blog. Some readers specifically look for “what’s new” – give them an easy way to find recently refreshed content. This also creates internal linking opportunities and signals ongoing content maintenance to Google.
What Makes Historical Optimization Different From Regular Updates?
Historical optimization is a specific refresh strategy focusing on maximizing the ranking potential of older, established content. It’s more than updating – it’s strategic enhancement of proven performers.
The concept comes from HubSpot’s documented strategy where they saw 106% traffic increase to historically optimized posts.
What defines historical optimization:
1. Focus on Already-Performing Content
You’re not reviving dead posts – you’re amplifying content already generating traffic. Think of it as turning singles into home runs rather than trying to resurrect strikeouts.
Target posts with:
- 50+ organic visits monthly
- Some keyword rankings (even if not page 1)
- Existing backlinks
- Established in Google’s index for 6+ months
2. Comprehensive Enhancement, Not Minor Tweaks
Historical optimization means substantial improvement:
- Doubling word count isn’t unusual
- Adding 5-10 new sections
- Complete examples and case study refresh
- Extensive internal linking improvements
- Major media additions
3. Zero URL Changes
This is non-negotiable for historical optimization. The age, authority, and backlink profile of the URL are assets. Changing URLs destroys the “historical” advantage.
4. Strategic Keyword Expansion
Analyze competitors ranking for 50 keyword variations while you rank for 10. Historical optimization means:
- Identifying semantic keyword gaps
- Adding sections covering those keywords
- Becoming the most comprehensive resource
5. Conversion Optimization Alongside SEO
HubSpot’s approach included:
- Updating CTAs with better offers
- Adding lead magnets and content upgrades
- Improving internal links to conversion pages
- A/B testing headlines and layouts
Historical optimization workflow:
Week 1: Identify top 10 posts by traffic with declining trends
Week 2: Comprehensive competitor analysis for each
Week 3-4: Major content expansions and improvements
Week 5: Technical optimization and republishing
Week 6-8: Monitor and iterate based on performance
Real-world example: Backlinko’s “Skyscraper Technique” post was originally 1,800 words. Through historical optimization, it expanded to 4,200 words with updated examples, new case studies, video content, and enhanced internal linking. Traffic increased 316% year-over-year.
The key difference: Regular updates maintain relevance. Historical optimization transforms good content into definitive resources.
How Does Republishing Strategy Impact Search Rankings?
Your republishing strategy dramatically affects SEO outcomes. The same content refresh can succeed or fail based on how you approach republishing.
Republishing Approach #1: Silent Update
You update content without changing publish date or promoting it.
Pros:
- Maintains original publish date authority
- No risk of duplicate content flags
- Preserves historical SEO equity
Cons:
- Slower re-crawling and re-indexing
- Misses promotional opportunities
- Less social/engagement signals
Best for: Minor updates (updating stats, fixing links, small additions)
Republishing Approach #2: Soft Relaunch
You update “last modified” date and do moderate promotion.
Pros:
- Signals freshness to Google
- Maintains publish date
- Moderate promotional lift
Cons:
- May not trigger full re-evaluation
- Less dramatic results
Best for: Medium updates (20-40% new content, significant improvements)
Republishing Approach #3: Hard Relaunch
You change publish date to current date and promote as “new” content.
Pros:
- Maximum freshness signal
- Full promotional treatment
- Treated as new content in feeds
- Often triggers rapid re-evaluation
Cons:
- Loses “aged content” authority
- May confuse readers who saw it before
- Risk if update isn’t substantial enough
Best for: Major rewrites (50%+ new content, complete overhaul)
Republishing Approach #4: Version 2.0 Strategy
You create a new post building on the old one, linking between them.
Pros:
- Both posts can rank
- Maintains all original backlinks
- Shows evolution of thought
Cons:
- Risk of keyword cannibalization
- Splits authority between URLs
- More complex content management
Best for: When the topic has evolved so dramatically that a completely new approach is warranted
Strategic republishing decision tree:
Is this a minor update (<20% new content)?
├─ YES → Silent Update
└─ NO → Is this 20-50% new content?
├─ YES → Soft Relaunch (update modified date)
└─ NO → Is this 50%+ new content?
├─ YES → Hard Relaunch (new publish date)
└─ NO → Did the topic fundamentally change?
├─ YES → Consider Version 2.0 strategy
└─ NO → Soft Relaunch
Critical republishing mistakes to avoid:
❌ Changing URL structure during republish ❌ Republishing with new date for minimal changes (<20% update) ❌ Not promoting substantially updated content ❌ Forgetting to update modified date on silent updates ❌ Creating duplicate content through Version 2.0 without proper differentiation ❌ Republishing too frequently (wait 6-12 months between major updates)
Pro Tip: Test both soft and hard relaunch strategies on similar posts and compare results. Your specific niche, audience, and domain authority may respond differently to each approach. Data beats assumptions.
How Do You Maintain Evergreen Content Effectively?
Evergreen content maintenance is your long-term SEO insurance policy. These pieces drive consistent traffic year after year – if you maintain them properly.
The Evergreen Maintenance Framework:
Annual Deep Refresh (Once per year)
Schedule comprehensive updates:
- Complete fact-checking and source updates
- New examples and case studies
- Expanded sections based on new developments
- Technical SEO optimization
- Media and visual updates
Time investment: 3-4 hours per post Expected results: Maintain or improve rankings, traffic stability
Quarterly Light Touch (Every 3 months)
Quick maintenance checks:
- Verify links aren’t broken
- Update any time-sensitive references
- Check for major industry changes to mention
- Refresh dates in examples where relevant
Time investment: 30-45 minutes per post Expected results: Prevent decay, maintain freshness signals
Monthly Monitoring (Every month)
Don’t update – just track:
- Keyword ranking changes
- Traffic trends
- New competitor content
- Reader comments or questions
Time investment: 10-15 minutes per post Expected results: Early warning of needed updates
The Evergreen Content Calendar:
Create a spreadsheet tracking:
| Post Title | Last Major Update | Next Scheduled Update | Current Traffic | Ranking Trend | Priority |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| “How to Start a Blog” | Jan 2024 | Jan 2025 | 1,200/mo | Stable | Medium |
| SEO Basics Guide | Mar 2024 | Mar 2025 | 850/mo | Declining | High |
| “Content Marketing 101” | May 2024 | May 2025 | 1,450/mo | Growing | Low |
Automation strategies for scale:
1. Use Google Alerts – Get notified of industry changes relevant to your evergreen content. When major news breaks, you know which posts need updates.
2. Set calendar reminders – Schedule annual refresh dates when you publish. Future-you will thank present-you.
3. Monitor with tools – Use Ahrefs or Semrush position tracking alerts. Get emailed when evergreen posts drop rankings.
4. Create update checklists – Standardized checklists ensure consistent maintenance quality across all posts.
5. Batch updates – Don’t update one post at a time. Batch 5-10 updates quarterly for efficiency.
Evergreen content that needs more frequent attention:
- How-to guides for frequently-updated software (every 6 months)
- Best practices in rapidly evolving fields (every 6 months)
- Beginner’s guides that reference current tools (annually)
- Strategy frameworks when fundamentals stay stable (every 18-24 months)
Evergreen content that needs less attention:
- Concept explanations (every 18-24 months)
- Historical analyses (only as new research emerges)
- Fundamental principles (every 24-36 months)
- Timeless strategies (as needed, possibly 36+ months)
Signs your evergreen content needs immediate attention:
🚨 Traffic dropped 25%+ in 90 days 🚨 Dropped from page 1 to page 2 🚨 Readers commenting about outdated information 🚨 Competitors published comprehensive updates 🚨 Major industry changes occurred 🚨 Primary keyword search intent shifted
Your blog SEO strategy should treat evergreen content like a portfolio of investments requiring ongoing management, not “write once, profit forever” lottery tickets.
Pro Tip: Mark your top 20 traffic-generating posts as “VIP evergreen” content. These get quarterly checks instead of annual updates. They’re your revenue drivers – treat them accordingly.
What Tools And Metrics Should You Track For Content Refresh ROI?
Measuring your content refresh strategy ROI separates effective updates from wasted effort. Here are the tools and metrics that actually matter.
Essential Tracking Tools:
Google Search Console (Free)
- Track ranking changes by query
- Monitor impressions and clicks
- Identify new keywords you’re ranking for
- See crawl and indexing status
Use for: Primary performance tracking post-refresh
Google Analytics (Free)
- Track organic traffic to updated URLs
- Monitor engagement metrics (time on page, bounce rate)
- Identify traffic sources and referral changes
- Track conversions if applicable
Use for: Traffic and engagement analysis
Ahrefs or Semrush ($99-399/month)
- Automated rank tracking for target keywords
- Backlink monitoring for updated posts
- Competitor comparison
- Content gap identification
Use for: Comprehensive SEO tracking and competitive analysis
Screaming Frog (Free-£149/year)
- Crawl your site to identify refresh opportunities
- Find broken links needing fixes
- Analyze on-page SEO elements
- Track update implementation
Use for: Technical SEO audits and refresh identification
Content Refresh Tracking Spreadsheet (Free) Create a master tracker with these columns:
- URL
- Original publish date
- Last refresh date
- Pre-refresh traffic (30-day avg)
- Post-refresh traffic (30-day avg)
- Pre-refresh average position
- Post-refresh average position
- Hours invested in refresh
- Traffic change %
- ROI score
Key Metrics To Track:
Primary Success Metrics:
1. Organic Traffic Change
Traffic Improvement % = ((New Traffic - Old Traffic) / Old Traffic) × 100
Target: 30-50% increase within 60 days
Excellent: 100%+ increase
2. Keyword Ranking Improvements
Track position changes for:
- Primary target keyword
- 5-10 related keywords
- Long-tail variations
Target: 3-5 position improvement within 30 days
Excellent: Reaching page 1 (top 10)
3. Impressions Growth
Even if rankings haven’t changed, increased impressions show you’re ranking for more keywords.
Impression Growth = ((New Impressions - Old Impressions) / Old Impressions) × 100
Target: 25%+ increase
Excellent: 50%+ increase
Secondary Success Metrics:
4. Click-Through Rate (CTR)
Improved title/meta description should increase CTR:
Target: 0.5-1% CTR improvement
Excellent: 2%+ improvement
5. Time on Page
More comprehensive content should increase engagement:
Target: 15-25% increase
Excellent: 30%+ increase
6. Backlinks Earned
Refreshed content sometimes earns new backlinks:
Target: 1-2 new backlinks within 90 days
Excellent: 5+ new backlinks
7. Conversion Rate
If content has conversion goals:
Target: Maintain or improve conversion rate despite increased traffic
Excellent: 10%+ conversion rate improvement
ROI Calculation Formula:
Content Refresh ROI = ((Traffic Gain × Value Per Visit) - (Hours × Hourly Rate)) / (Hours × Hourly Rate) × 100
Example:
- Traffic gain: +500 visits/month
- Value per visit: $2 (based on conversion rates)
- Monthly value: $1,000
- Hours invested: 3
- Hourly rate: $50
- Cost: $150
ROI = (($1,000 - $150) / $150) × 100 = 567% monthly ROI
Dashboard Setup:
Create a simple dashboard tracking:
| Metric | Pre-Refresh | Post-Refresh (30d) | Post-Refresh (60d) | Change % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organic Traffic | 450 | 615 | 720 | +60% |
| Avg Position | 12 | 8 | 6 | +50% |
| Impressions | 8,500 | 12,300 | 14,800 | +74% |
| CTR | 1.8% | 2.3% | 2.7% | +50% |
| Time on Page | 3:20 | 4:15 | 4:30 | +35% |
When to declare refresh success vs. failure:
✅ Success indicators (keep doing this):
- 30%+ traffic increase within 60 days
- 3+ position improvement for target keyword
- Improved rankings for multiple related keywords
- Better engagement metrics
- New backlinks earned
❌ Failure indicators (analyze what went wrong):
- No traffic change after 60 days
- Rankings stayed flat or declined
- Bounce rate increased significantly
- No new keyword rankings gained
Pro Tip: Set up automated reports in Google Analytics and Search Console that email you weekly performance updates for refreshed content. This keeps results top-of-mind and lets you iterate quickly if something isn’t working.
How Do You Scale Content Refresh Operations Across Large Sites?
For sites with 100+ posts, manual refresh becomes overwhelming. Here’s how to scale content refresh strategy systematically.
The Tiered Refresh System:
Tier 1: VIP Content (Top 10-20% by traffic)
- Monthly monitoring
- Quarterly light updates
- Annual deep refreshes
- Immediate response to ranking drops
Tier 2: Performing Content (Next 30% by traffic)
- Quarterly monitoring
- Bi-annual light updates
- Every 18-month deep refreshes
Tier 3: Standard Content (Next 40%)
- Semi-annual monitoring
- Annual light updates
- Every 24-month deep refreshes
Tier 4: Archive Content (Bottom 10-20%)
- Annual review to delete, consolidate, or upgrade to Tier 3
- No regular updates unless specific opportunity emerges
Automation and Systematization:
1. Create Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
Document every step:
- Content audit checklist
- Research process
- Update execution steps
- Technical implementation
- Promotion workflow
- Success tracking
Why: Anyone can execute consistently, enabling delegation
2. Build Update Templates
Create templates for common refresh types:
- Statistics update template
- Tool review refresh template
- How-to guide modernization template
- Best practices update template
Why: Reduces decision fatigue and ensures consistency
3. Use Project Management Tools
Implement in Asana, Monday.com, or Notion:
- Refresh pipeline (ideas → in progress → complete)
- Scheduled refresh dates auto-populated
- Team assignments clear
- Progress visible to everyone
Why: Prevents missed updates and enables team collaboration
4. Batch Similar Updates
Instead of random updating:
- Batch all tool reviews in one refresh cycle
- Batch all statistics updates together
- Batch all how-to guides requiring screenshot updates
Why: More efficient to batch similar tasks
5. Leverage AI for First-Pass Updates
Use AI to:
- Identify outdated statistics
- Generate new examples to consider
- Draft expanded sections (human refines)
- Suggest semantic keywords to add
Why: Reduces time per refresh by 30-40%
Team Structure for Scale:
For 100-300 posts:
- 1 Content Strategist (plans refresh schedule)
- 2-3 Content Writers (execute updates)
- 1 SEO Specialist (handles technical optimization)
For 300-1,000 posts:
- 1 Content Director (strategy and prioritization)
- 4-6 Content Writers (execution)
- 2 SEO Specialists (technical optimization and monitoring)
- 1 Project Manager (tracking and coordination)
For 1,000+ posts:
- Full content operations team
- Automated monitoring systems
- Dedicated refresh squad
- Performance analysts
The Quarterly Refresh Cycle:
Q1 Focus: Refresh all time-sensitive content (statistics, trends, tool reviews) Q2 Focus: Refresh seasonal content relevant to upcoming seasons Q3 Focus: Deep refresh top 25% traffic-generating evergreen content Q4 Focus: Comprehensive audit and cleanup of bottom 25% content
Efficiency Metrics to Track:
- Average hours per refresh
- Cost per refresh
- Average traffic gain per refresh
- ROI per refresh
- Refresh completion rate vs. plan
Target benchmarks:
- 2-4 hours per standard refresh
- 30%+ average traffic gain
- 300%+ average ROI
- 85%+ plan completion rate
Pro Tip: Start with a pilot program refreshing just 20 posts. Perfect your system on a manageable scope before scaling. Document what works, what doesn’t, and build your SOP from actual experience rather than theory.
What Are The Biggest Content Refresh Mistakes That Kill Results?
After analyzing hundreds of refresh attempts, I’ve seen the same mistakes repeatedly sabotage results. Here’s what actually kills content refresh strategy effectiveness.
Mistake 1: Superficial Updates That Don’t Move The Needle
Changing a date and calling it “updated” fools nobody – especially not Google.
What it looks like:
- Changing “2023” to “2025” in the intro
- Updating one statistic
- Fixing a broken link
- Calling this a “refresh”
Why it fails: Google’s algorithm detects minimal changes. Without substantial improvements, content won’t re-enter ranking evaluation meaningfully.
Fix: Follow the 20% rule – update at least 20% of content meaningfully or don’t bother.
Mistake 2: Updating Wrong Content
Refreshing posts that never ranked well or have no traffic is low-ROI work.
What it looks like:
- Spending hours updating a post that gets 10 visits/month
- Refreshing content that never ranked for anything
- Ignoring high-traffic declining posts to refresh pet projects
Why it fails: You’re polishing content with no foundation to build on. Starting from zero rankings is harder than improving position 8 to position 3.
Fix: Use the prioritization framework earlier in this guide. Always refresh content with existing traction first.
Mistake 3: Changing URLs During Refresh
This destroys all the accumulated authority you’re trying to leverage.
What it looks like:
- “I’ll optimize the slug while I’m updating”
- Creating new URLs for refreshed content
- Moving content to different URL structures
Why it fails: Backlinks point to old URL. Domain authority attached to old URL. Search history associated with old URL. You lose it all.
Fix: Never change URLs during refresh unless absolutely necessary (wrong keyword in slug). If you must, implement perfect 301 redirects, but expect 4-6 weeks of ranking volatility.
Mistake 4: Not Updating Enough Content
Adding 200 words to a 2,000-word post doesn’t constitute meaningful improvement.
What it looks like:
- Adding one new section
- Updating 2-3 paragraphs
- Minor tweaks throughout
Why it fails: Competitors have 3,500-word comprehensive guides. Your 2,200-word refresh still isn’t competitive.
Fix: Aim to add 30-50% more content in refreshes. If competitors average 3,000 words and you have 1,500, expand to 3,500 words.
Mistake 5: Forgetting Technical SEO
Content updates without technical optimization leave opportunities on the table.
What it looks like:
- Not updating title tags or meta descriptions
- Ignoring internal linking opportunities
- Skipping schema markup
- Forgetting image optimization
Why it fails: You’ve improved content quality but not technical SEO signals. Rankings improve less than they could.
Fix: Use a technical SEO checklist on every refresh ensuring all elements are optimized.
Mistake 6: No Promotion After Refresh
Updated content that sits silently won’t get crawled quickly or earn new signals.
What it looks like:
- Publishing update and moving on
- No social promotion
- No email announcement
- Waiting passively for Google to notice
Why it fails: Re-crawling and re-indexing happen faster with signals. Without promotion, refreshed content may take weeks to get re-evaluated.
Fix: Treat refreshed content like new content – promote it actively across channels.
Mistake 7: Updating Too Frequently
Constantly tweaking content signals instability, not authority.
What it looks like:
- Updating same post every month
- Making minor changes repeatedly
- Never letting updated content stabilize
Why it fails: Google may not trust content that changes constantly. Plus, you’re wasting time on diminishing returns.
Fix: Wait 6-12 months between substantial refreshes unless there’s a compelling reason (major industry change, competitor displacement).
Mistake 8: Ignoring User Intent Shifts
Sometimes search intent for a keyword changes over time.
What it looks like:
- Your 2020 post about “best email marketing” focused on features
- Now searchers want pricing comparisons and ease-of-use
- You refresh with more features instead of addressing new intent
Why it fails: Content quality is judged by how well it satisfies current search intent, not past intent.
Fix: Always check current top-ranking content before refreshing. If intent shifted, adjust your content accordingly.
Expert Insight: “The biggest refresh mistake I see is bloggers treating it like busywork – checking a box – rather than genuine improvement. If you wouldn’t publish it as new content today, don’t just update the date and call it refreshed.” – Lily Ray, Amsive Digital
How Do Different Blog Types Approach Content Refresh Strategy?
Content refresh strategy implementation varies significantly by blog type and business model. Here’s what actually works for each.
B2B SaaS Blogs
Refresh frequency: Every 6-12 months Primary focus: Product updates, feature changes, pricing accuracy
Strategy:
- Aggressively refresh product comparison posts quarterly
- Update integration guides when APIs change
- Refresh case studies with newer customer examples
- Maintain feature accuracy religiously
- Update pricing information immediately
Example: HubSpot refreshes their product-related content every 3-6 months to reflect platform updates, new features, and changing best practices.
E-commerce Content Blogs
Refresh frequency: Seasonal + annual Primary focus: Product availability, pricing, trends
Strategy:
- Refresh buying guides 4-6 weeks before seasonal peaks
- Update product roundups when new models release
- Refresh “best of [year]” content annually
- Remove discontinued products promptly
- Add emerging products as they gain traction
Example: Wirecutter updates product reviews continuously as new models release and testing completes.
Affiliate Marketing Sites
Refresh frequency: Quarterly to bi-annual Primary focus: Product updates, pricing, affiliate link maintenance
Strategy:
- Refresh top-earning posts quarterly
- Update affiliate links immediately when programs change
- Refresh reviews when new versions release
- Monitor and update pricing displays
- Add new alternatives as they emerge
News/Magazine Sites
Refresh frequency: Rarely (focus on new content) Primary focus: Historical updates only
Strategy:
- Update breaking news as story develops
- Add “Editor’s note” to outdated articles
- Archive old news rather than refreshing
- Refresh evergreen explainers annually
- Focus resources on new content, not refreshes
Personal Brand/Thought Leadership
Refresh frequency: Annual to bi-annual Primary focus: Updated perspectives, new examples
Strategy:
- Refresh popular posts with evolved thinking
- Update examples and case studies
- Add commentary on how views have changed
- Maintain authentic voice and perspective
- Focus on timeless pieces worth maintaining
Niche Authority Sites
Refresh frequency: Every 12-18 months Primary focus: Comprehensive topic coverage, EEAT signals
Strategy:
- Deep refresh top 20% traffic posts annually
- Expand thin content to be more comprehensive
- Update all statistics and research
- Strengthen internal linking between topics
- Maintain position as definitive resource
Technical Documentation/Tutorial Sites
Refresh frequency: Continuous (as software updates) Primary focus: Accuracy, current screenshots, working examples
Strategy:
- Update immediately when software changes
- Refresh screenshots with every major version
- Test all code examples regularly
- Add notes about version differences
- Deprecate outdated tutorials properly
Recipe/Food Blogs
Refresh frequency: Bi-annual to annual Primary focus: Better photos, updated techniques, nutrition info
Strategy:
- Refresh photos to current quality standards
- Update nutrition information as recipes improve
- Add new tips from reader feedback
- Update servings/timing based on testing
- Refresh seasonal recipes before their season
Finance/Investment Blogs
Refresh frequency: Quarterly Primary focus: Current market conditions, regulation changes, data accuracy
Strategy:
- Update market data quarterly
- Refresh posts when regulations change
- Update tax-related content annually
- Maintain accuracy religiously (YMYL)
- Add disclaimers when outdated but kept for historical value
Comparison by refresh priority:
| Blog Type | Update Frequency | Top Priority | Second Priority |
|---|---|---|---|
| B2B SaaS | 6-12 months | Product accuracy | Case studies |
| E-commerce | Seasonal + Annual | Buying guides | Product availability |
| Affiliate | Quarterly | Top earners | Product updates |
| News | Rarely | Breaking updates | Evergreen explainers |
| Personal Brand | Annual | Popular posts | Evolved perspectives |
| Niche Authority | 12-18 months | Top traffic | Comprehensive coverage |
| Technical Docs | Continuous | Software changes | Screenshots |
| Recipe | Bi-annual | Photos | Techniques |
| Finance | Quarterly | Data accuracy | Regulatory changes |
Your specific approach should align with your blog type, audience expectations, and business model.
What’s The Future Of Content Refresh And Maintenance?
The content refresh strategy landscape is evolving rapidly. Here’s what’s coming and how to prepare.
AI-Powered Automatic Refresh Detection
Current state: Manual audits identify refresh needs Near future: AI analyzes your content daily, flagging refresh opportunities automatically
What’s emerging:
- AI detection of outdated statistics
- Automatic identification of broken links
- Alerts when competitors publish superior content
- Suggested refresh priority based on ROI probability
Tools developing this: Clearscope, MarketMuse, Frase
Prepare: Start building a structured content database now. AI needs clean data to make good recommendations.
Automated Content Updates
Current state: Humans research and write all updates Near future: AI drafts updates, humans review and approve
What’s possible:
- AI monitors authoritative sources for updated statistics
- Auto-generated draft sections with new data
- Suggested expansions based on competitor analysis
- Automated internal link suggestions
Reality check: This will augment, not replace, human editors. AI can draft, but expertise and judgment remain human.
Prepare: Develop AI prompting skills now. Learn to guide AI to produce content matching your voice and standards.
Real-Time Content Freshness
Current state: Static content updated manually every 6-12 months Near future: Dynamic content elements updating automatically
What’s emerging:
- Statistics pulled from live data sources
- Product prices/availability updating real-time
- Dynamic publication dates reflecting update frequency
- Automated “last verified” timestamps
Example: A “Best SEO Tools” post with pricing that updates automatically via API integration, ensuring accuracy without manual updates.
Prepare: Identify which data in your content could be dynamically sourced. Build relationships with data providers offering APIs.
Predictive Refresh Recommendations
Current state: React to ranking drops Near future: Predict content decay before it happens
What’s developing:
- Machine learning models predicting when content will decline
- Proactive refresh recommendations before rankings drop
- Risk scoring for content decay likelihood
- ROI projections for refresh investments
Prepare: Track refresh results meticulously. Historical data trains prediction models.
Automated Content Consolidation
Current state: Manual identification of content to merge Near future: AI suggests content consolidation opportunities
What’s emerging:
- Detection of keyword cannibalization
- Recommendations for merging thin content
- Automated redirect planning
- Content consolidation impact predictions
Prepare: Audit your content now for consolidation opportunities. Manual experience teaches you what to look for.
User-Driven Content Updates
Current state: Creators decide what to update Near future: Reader feedback directly triggers updates
What’s possible:
- Comment analysis identifying outdated sections
- User reports of inaccuracies triggering reviews
- Crowdsourced updates from expert communities
- Automatic prioritization based on user needs
Example: A reader reports outdated pricing. System flags the section, AI drafts an update, editor approves, and content updates within hours.
Prepare: Build engaged communities around your content. User feedback becomes your best refresh trigger.
Version Control for Content
Current state: Overwrites with no history Near future: Full version control like code repositories
What’s emerging:
- Track every content change over time
- Revert to previous versions if needed
- A/B test different versions
- Analyze which updates actually improved performance
Prepare: Document your changes now. Build the habit of tracking what you updated and why.
Expert Prediction: “By 2027, content refresh will shift from reactive maintenance to predictive optimization. AI will tell you what to update before rankings decline. The competitive advantage will go to whoever executes fastest, not whoever identifies opportunities first.” – Kevin Indig, Growth Advisor
Pro Tip: Don’t wait for perfect automation. Start systematizing your refresh process manually now. When AI tools mature, you’ll be ready to integrate them into an already-functional system rather than trying to build from scratch.
FAQs
How often should I refresh my blog content?
It depends on content type. Time-sensitive content (statistics, tool reviews) needs refreshing every 6-12 months. Evergreen how-to guides should be updated every 12-18 months. Historical content may only need updates every 24-36 months. Monitor traffic and rankings to identify when specific posts need attention.
Should I change the publish date when I update content?
For minor updates (<20% new content), keep the original publish date and update “last modified” date only. For major rewrites (50%+ new content), consider updating the publish date to signal substantial freshness. Never change dates for minor tweaks.
Will updating old content hurt my rankings?
No, if done properly. Substantial, quality updates typically improve rankings within 30-60 days. Superficial changes have minimal impact. The only risk is if you accidentally worsen the content or change something that was already working well. Always improve, don’t just change.
How much new content should I add during a refresh?
Aim for at least 20% new or substantially modified content. Better yet, add 30-50% more content than the original. Analyze competitors ranking in positions 1-3 and ensure your refreshed version is more comprehensive than theirs.
Can I refresh content that never ranked well?
Refreshing poorly-performing content is lower ROI than refreshing content that already has some traction (rankings, traffic, backlinks). Focus your refresh efforts on content ranking positions 5-20 first. Once those are optimized, consider whether poor performers are worth saving or should be deleted/consolidated.
How do I know if my content refresh was successful?
Track these metrics for 60 days post-refresh: organic traffic changes, keyword ranking improvements, impressions growth, and engagement metrics (time on page, bounce rate). Success typically means 30%+ traffic increase and 3-5 position improvements for target keywords within 60 days.
Final Thoughts: Building Your Content Refresh System
Here’s the final reality check about content refresh strategy: most bloggers are sitting on goldmines they’ve forgotten exist. While they obsess over publishing new content, their existing posts are slowly dying.
The irony? Refreshing existing content delivers faster results with less effort than creating new content. You’ve already done the hard work – researching, writing, publishing, earning initial authority. Now you just need to maintain and amplify what you’ve built.
Your competitors are making one of two mistakes: either they’re abandoning old content to decay (easy to outrank them), or they’re refreshing randomly without strategy (easy to be more systematic and effective).
You’re going to do neither. You’re going to build a systematic content refresh operation that:
- Identifies high-ROI refresh opportunities quarterly
- Updates strategically using proven frameworks
- Tracks results obsessively
- Compounds success over time
The blogs dominating search results in 2027 won’t be the ones publishing the most new content. They’ll be the ones maintaining comprehensive, current, best-in-class content libraries that compound authority over time.
Start small. Identify your top 10 posts by traffic. Refresh one per week using the framework in this guide. Track results. Refine your process. Then scale.
In 12 months, you’ll have refreshed 52 posts while your competitors published 52 new posts and watched their old content decay. Your content library gets stronger. Theirs gets diluted.
The compound effect of content refresh is real. Each update strengthens an existing asset. Each refresh builds on previous authority. Each improvement compounds over time.
The best time to start refreshing content was six months ago. The second best time is right now.
Your content library is waiting. Stop letting it decay. Start making it work harder.
Related posts:
- Blog Post Optimization Checklist: On-Page SEO for Maximum Rankings
- Mastering On-Page SEO Elements: Meta Tags, HTML, and Image Optimization Explained (Visual guide)
- The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide to Title Tags and Meta Descriptions
- What is Internal Linking? A Complete Beginner’s Guide to Boosting Your SEO