Ever feel like you’re publishing killer content but Google’s giving you the cold shoulder? Here’s the thing: your blog posts might be amazing, but if they’re scattered around your site like lost puzzle pieces, search engines can’t connect the dots. That’s where blog internal linking becomes your secret weapon.
Think of your blog as a city. Without roads connecting the neighborhoods, people (and Google) get lost. Internal links are those roads – guiding visitors and search bots through your content landscape while telling Google, “Hey, this stuff matters!
Today, I’m pulling back the curtain on how strategic internal link building can literally transform your blog’s SEO performance. And trust me, this isn’t rocket science – it’s just smart planning.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Exactly Is Blog Internal Linking (And Why Should You Care)?
Let’s start simple. Blog internal linking is the practice of connecting one page on your website to another page on the same domain. Sounds basic, right?
But here’s where it gets interesting. These links do three magical things simultaneously: they help readers discover more content, they spread “link juice” (SEO authority) across your site, and they tell search engines which pages are most important.
According to a Backlinko study, websites with strong internal linking structures can see ranking improvements of up to 40%. That’s not a typo – forty percent!
How Does Internal Link Building Actually Boost Your Rankings?
Here’s the reality: Google’s crawlers are like tourists in your city. If there are no clear paths between your attractions (blog posts), they’ll miss half the good stuff.
Internal link building creates a roadmap. Each link passes authority from one page to another, strengthening your overall domain. Pages with more internal links pointing to them signal higher importance to search engines.
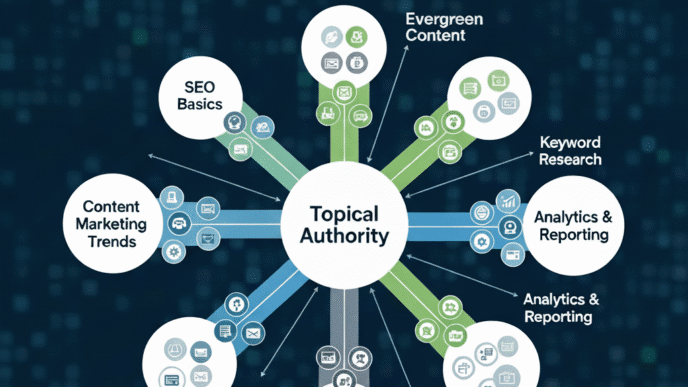
But there’s more. When you strategically link related content, you’re creating topic clusters that establish topical authority. Google loves when you demonstrate expertise across interconnected subjects – it’s like showing your credentials without bragging.
Pro Tip: Pages buried 3+ clicks deep from your homepage get crawled less frequently. Strategic internal linking brings them closer to the surface, increasing their visibility and indexing speed.
What Are The Different Types of Internal Links You Should Know?
Not all internal links are created equal. Let me break down the main categories you’ll be working with:
Navigational links live in your main menu, sidebar, and footer. They’re the backbone of your blog site architecture and help users move between major sections.
Contextual links appear within your actual content. These are the heavy hitters for SEO because they carry the most weight and provide relevant context through surrounding text.
Relational links show up in “related posts” sections or “you might also like” widgets. While useful, they’re typically less powerful than contextual links because they’re often automatically generated.
Here’s a comparison of their impact:
| Link Type | SEO Value | User Experience | Implementation Difficulty |
|---|---|---|---|
| Navigational | Medium | High | Easy |
| Contextual | High | Very High | Medium |
| Relational | Low-Medium | Medium | Easy (automated) |
Why Is Contextual Linking Strategy The Most Powerful Approach?
Let’s get real for a second. If you only focus on one type of internal linking, make it contextual.
A strong contextual linking strategy embeds links naturally within your content where they genuinely add value. When you’re discussing blog SEO fundamentals, you link to that resource at the exact moment readers need deeper information.
Ahrefs analyzed 4 million articles and found that contextual links pass significantly more authority than navigation or footer links. Why? Because they’re surrounded by relevant content that gives Google clear context about what the linked page is about.
The magic happens when your anchor text optimization aligns with the linked page’s focus keyword. Instead of “click here,” you use descriptive phrases like “SEO optimization techniques” that tell both users and search engines what to expect.
How Do You Build An Effective Internal Linking Strategy For Blog SEO And Better Rankings?
Alright, let’s get tactical. Building an internal linking strategy for blog SEO and better rankings isn’t about randomly sprinkling links everywhere. It’s systematic.
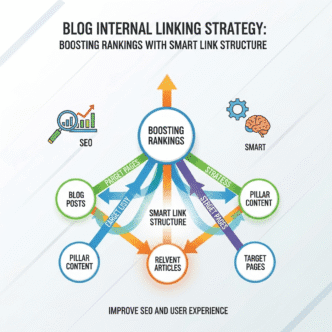
Start by identifying your pillar content – those comprehensive guides that cover broad topics (like your main blog SEO resource). These are your skyscrapers in the city metaphor.
Then create cluster content around each pillar. Each cluster post should link back to its pillar page and to related cluster posts. This creates a topic hub that screams authority to Google.
Here’s the exact framework I use:
- Audit existing content – Identify orphan pages (posts with zero internal links pointing to them)
- Map topic clusters – Group related content around core themes
- Add contextual links – Insert 3-5 relevant internal links per post
- Link to pillar pages – Ensure cluster posts strengthen pillar authority
- Monitor and update – Refresh old posts with links to new content
Pro Tip: Use the “hub and spoke” model. Your pillar page is the hub, cluster posts are spokes. Each spoke should link back to the hub and to other relevant spokes. This creates a tight web of authority around your core topics.
What Is Pillar Content Linking And How Does It Work?
Picture this: you’re building a library. Your pillar pages are the comprehensive encyclopedia volumes, while cluster posts are specialized articles on specific subjects.
Pillar content linking is the strategy of creating these massive, authoritative guides (2,000-5,000+ words) that broadly cover a topic, then supporting them with shorter, focused cluster posts that dive deep into specific subtopics.
Here’s a real example: HubSpot’s marketing statistics page is a pillar. It links out to dozens of cluster posts about email marketing stats, social media stats, and content marketing stats. Each cluster post links back to the main pillar.
This architecture accomplishes two things: it helps readers navigate from broad to specific information naturally, and it concentrates SEO authority around your most important topics.
For your blog about SEO strategies, your pillar might be “Complete Guide to Blog SEO” with clusters about “on-page optimization,” “content strategy,” and yes – “internal linking best practices.”
How Should You Optimize Anchor Text Without Over-Optimizing?
Ah, anchor text – where many bloggers either go too bland (“click here”) or too aggressive (“best cheap insurance NYC buy now”).
Anchor text optimization is about hitting the sweet spot. You want descriptive, natural phrases that give context without screaming “I’m trying to manipulate rankings!”
Here’s the breakdown Google prefers:
- Exact match (5-10%): Your actual focus keyword
- Partial match (20-30%): Variations with additional words
- Branded (10-15%): Your site or brand name
- Generic (10-15%): “Learn more,” “this guide,” etc.
- Natural/LSI (40-50%): Descriptive phrases with related terms
Instead of linking “SEO” five times, vary it: “search engine optimization strategies,” “improving your blog’s visibility,” “ranking factors that matter,” and occasionally the plain keyword.
Real talk from Moz research: Over-optimized anchor text was the #1 factor in Google penalties between 2012-2019. Natural diversity is your friend.
What Role Does Blog Site Architecture Play In Internal Linking?
Your blog site architecture is the foundation everything else builds on. Poor structure = weak internal linking. Period.
The ideal structure follows a pyramid: homepage at top, main category pages below, subcategories next, individual posts at the bottom. No page should be more than 3-4 clicks from your homepage.
Here’s what strong architecture looks like:
Homepage
├── Blog Category 1
│ ├── Pillar Post 1
│ │ ├── Cluster Post A
│ │ ├── Cluster Post B
│ │ └── Cluster Post C
│ └── Pillar Post 2
└── Blog Category 2
└── Pillar Post 3
This structure naturally creates internal linking opportunities. Each level links to pages above and below it, creating a logical flow of authority and user experience.
Pro Tip: Use URL structure to reflect your site architecture. If you have a pillar post at /blog-seo/, cluster posts could live at /blog-seo/internal-linking/, /blog-seo/keyword-research/, etc. This helps both users and search engines understand relationships.
How Many Internal Links Should Each Blog Post Have?
The million-dollar question! And honestly, there’s no magic number.
A Ahrefs study found that posts with more internal links tend to rank better, but correlation isn’t causation. Quality beats quantity every single time.
My rule of thumb: aim for 3-8 contextual internal links per 1,000 words. For a 2,000-word post, that’s 6-16 links. But these must be relevant – don’t force it.
Consider these factors:
- Content length: Longer posts naturally accommodate more links
- Topic complexity: Comprehensive guides need more supporting links
- Content age: Newer blogs with less content will have fewer linking opportunities
- User intent: How many resources would genuinely help your reader?
Too few links, and you’re missing opportunities. Too many, and you dilute link value while overwhelming readers. Find your balance.
What Are Common Internal Linking Mistakes That Hurt Your SEO?
Let me save you from the faceplants I see constantly. These mistakes are silent SEO killers.
Orphan pages are the worst offender. These posts have zero internal links pointing to them – Google might not even discover they exist. I once audited a client’s site and found 40% of their blog posts were orphans. That’s a massive waste!
Over-linking to your homepage is another trap. Yes, your homepage is important, but linking to it from every post with “return to homepage” does nothing for SEO. Link to relevant content instead.
Using generic anchor text like “click here” or “this page” wastes the opportunity to provide context. Each link is a chance to tell Google what the destination page is about.
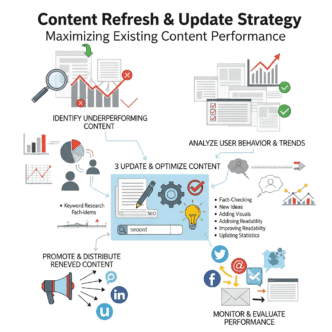
Ignoring deep pages means your oldest or least-visited content never gets a boost. Strategically link to older posts from new content to revive them.
Pro Tip: Run a quarterly internal linking audit using Screaming Frog or Ahrefs. Identify orphan pages, thin linking opportunities, and over-optimized anchor text patterns. This keeps your structure healthy and growing.
How Do You Scale Your Internal Linking As Your Blog Grows?
Here’s the reality: with 10 blog posts, internal linking is easy. With 500? It’s a nightmare without a system.
Scaling your internal linking strategy requires both process and tools. First, create a content spreadsheet tracking every post’s focus keyword, related topics, and existing internal links. This becomes your linking roadmap.
When publishing new content, make it standard practice to:
- Add 3-5 internal links in the new post
- Identify 2-3 older posts where the new content would add value
- Update those older posts with links to your new piece
This “two-way linking” approach ensures new content gets immediate authority while old content stays fresh and interconnected.
Tools like Link Whisper (WordPress plugin) can suggest relevant linking opportunities as you write. Surfer SEO and Clearscope also provide internal linking suggestions based on semantic relevance.
For larger blogs, consider a “content hub” approach where you organize posts into clear topic clusters with dedicated hub pages. Your blog SEO strategy becomes easier to manage when content is grouped logically.
What Tools Can Help You Analyze And Improve Internal Linking?
You can’t improve what you don’t measure. Let me share the tools that actually move the needle.
Google Search Console is free and shows your most linked internal pages. Check which pages have the most internal links and whether they align with your priorities.
Screaming Frog SEO Spider crawls your site like Google does, revealing orphan pages, broken internal links, and linking patterns. The free version handles up to 500 URLs.
Ahrefs Site Audit provides an “Internal Link Opportunities” report that suggests where you should add links based on relevance and authority flow.
Yoast SEO (WordPress) includes basic internal linking suggestions while you write, though it’s not as sophisticated as dedicated tools.
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Tool | Best For | Price | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Search Console | Basic analysis | Free | Link distribution overview |
| Screaming Frog | Technical audits | Free/£149/year | Orphan page detection |
| Ahrefs | Comprehensive SEO | $129+/month | AI-powered suggestions |
| Link Whisper | WordPress users | $77-$297/year | Real-time linking suggestions |
Pro Tip: Start with free tools (Search Console + Screaming Frog) to understand your current state. Invest in paid tools once you’ve maxed out the free options and know exactly what you need.
How Does Internal Linking Support Your Overall Blog SEO Strategy?
Let’s connect the dots. Internal linking isn’t a standalone tactic – it’s a force multiplier for every other SEO effort you make.
Strong internal linking amplifies your keyword targeting by reinforcing topic relevance across multiple pages. When five posts link to your pillar page using variations of your target keyword, Google gets a clear signal about that page’s topic.
It extends content lifespan. That post you published 18 months ago? With strategic internal links from new content, it gets crawled more frequently, receives authority boosts, and can climb rankings again.
Internal linking also reduces bounce rate and increases session duration – both positive UX signals. When readers click through to 2-3 additional posts, Google notices that engagement.
Think of internal linking as the circulatory system of your blog. Your content strategy is the heart, keywords are the blood, and internal links are the vessels carrying authority and relevance throughout your entire site.
What Are Advanced Internal Linking Techniques For Competitive Niches?
Ready to level up? These advanced tactics separate amateur bloggers from SEO pros.
Siloing creates strict topic boundaries. Each silo (topic cluster) links only within itself and to category pages, preventing link juice from spreading too thin. Finance blogs use this heavily – “credit cards” content stays isolated from “investing” content.
Link velocity manipulation involves strategically adding internal links to new posts over time rather than all at once. This mimics natural linking patterns and can trigger re-crawls.
Authority hoarding means consciously limiting internal links to your most competitive pages, keeping that authority concentrated. If you’re targeting a killer money keyword, you might link TO that page from 20 posts while only linking FROM it to 2-3 essential resources.
Dynamic contextual linking uses plugins or code to automatically insert relevant internal links based on keyword matching. This scales beautifully but requires careful setup to avoid over-optimization.
Pro Tip: The Wikipedia linking model is brilliant. They link to broader topics early in articles, then to specific related topics later. First mention of a concept? Link to the definitive resource. This creates natural, hierarchical linking that both users and Google love.
How Do You Measure The Success Of Your Internal Linking Strategy?
You’ve implemented the strategy – now what? Measuring success separates guesswork from growth.
Track these metrics monthly:
Organic traffic to previously orphaned pages: After adding internal links, monitor whether these pages start getting search traffic.
Pages per session: Strong internal linking should increase the average number of pages users visit. Aim for a 10-20% increase over 3-6 months.
Crawl stats in Search Console: Check if Google is discovering and indexing your pages faster. Better internal linking means better crawlability.
Rankings for pillar content: Your main pillar pages should see ranking improvements as you build out supporting cluster content with strategic linking.
Internal link clicks in Google Analytics: Set up event tracking to see which internal links actually get clicked. This reveals which linking strategies resonate with readers.
According to Search Engine Journal, websites that improved their internal linking structure saw an average 25% increase in organic traffic within six months – but only when they measured and optimized continuously.
What’s The Connection Between Internal Linking And User Experience?
Here’s a truth bomb: SEO and UX are the same thing now. Google’s entire algorithm has evolved to reward sites that genuinely help users.
Internal linking done right IS user experience optimization. When someone reading about keyword research naturally discovers your guide on content optimization through a contextual link, that’s seamless UX.
Poor internal linking creates frustration. Dead ends, irrelevant suggestions, or missing connections all hurt. I’ve seen beautifully written blogs get ignored because readers couldn’t find related content.
The best internal linking is invisible to users – it just feels natural. Links appear exactly when readers need more information, using language that clearly indicates what they’ll find.
Pro Tip: Read your posts aloud and notice where you reference concepts that deserve deeper explanation. Those are your natural internal linking opportunities. If YOU want more context at that moment, so does your reader.
How Often Should You Update Your Internal Linking Structure?
Your blog internal linking isn’t a set-it-and-forget-it task. It’s a living system that needs regular maintenance.
I recommend a monthly mini-audit where you:
- Add internal links to your newest posts from relevant older content
- Check for broken internal links
- Identify your top 10 performing posts and ensure they have strong internal linking support
Then conduct a quarterly deep audit covering:
- Orphan page identification and linking
- Anchor text diversity analysis
- Site architecture optimization
- Link distribution across topics
Every time you publish new content, immediately update 2-3 older posts with relevant links to the new piece. This creates bidirectional linking from day one.
Remember: as your blog grows and evolves, your internal linking needs to evolve too. New pillar content requires restructuring. Changing focus areas need link redistribution.
Real-World Examples: Brands Crushing It With Internal Linking
Let’s look at who’s actually walking the walk.
HubSpot is the gold standard. Their blog follows a strict pillar-cluster model with every post fitting into clear topic categories. A single pillar post might have 30+ cluster posts linking to it, while linking out to 10-15 related resources itself.
Backlinko (Brian Dean) uses “bucket brigades” – those little transitional phrases – to introduce internal links naturally. Every comprehensive guide links to 5-7 related resources using perfect anchor text optimization.
Neil Patel’s blog implements automated related post suggestions but also manually adds 3-5 contextual links per post. His older content gets continuously updated with links to newer posts, keeping everything fresh.
Healthline demonstrates internal linking at scale. With thousands of medical articles, they use topic clusters, medical condition categories, and symptom-based linking to create an interconnected health information ecosystem.
The common thread? Strategic planning, consistent execution, and continuous optimization. They didn’t build perfect internal linking overnight – they systematically improved it over time.
Pro Tips For Maintaining Natural Internal Link Flow
After years of doing this, here are the patterns that separate natural linking from spammy tactics:
Never force irrelevant links. If a connection isn’t obvious to your reader, don’t make it. Trust your instinct.
Vary your link position. Don’t always link in the first paragraph or always at the end. Distribute links where they naturally support your narrative.
Use transition phrases to introduce links smoothly: “Speaking of which,” “This connects to,” “As we covered in,” “For more on this.”
Link to competitors when appropriate. Yes, really. Linking to authoritative external sources (including competitors) when they genuinely add value builds trust and shows Google you’re not in an echo chamber.
Think three levels deep: From any post, a reader should be able to easily access related content, broader topic overviews, AND more specific deep-dives. This creates natural discovery paths.
Expert Insight: “The biggest internal linking mistake I see is treating it as an afterthought. Plan your linking strategy BEFORE you write, not after. Know which pillar you’re supporting and which cluster posts you’ll reference.” – Lily Ray, SEO Director at Amsive Digital
FAQs
How many internal links is too many in a blog post?
There’s no strict limit, but aim for 3-8 contextual links per 1,000 words. More than 20 links in a typical blog post starts looking spammy and dilutes link value. Focus on quality over quantity.
Should I link to my homepage in every blog post?
No. Only link to your homepage when contextually relevant. Navigation menus already provide that connection. Use internal links to connect related content instead.
Do internal links help with indexing new content?
Absolutely. Internal links help Google discover new pages faster. A well-linked post can be indexed within hours, while orphan pages might take weeks or never get indexed.
Can I update old posts with new internal links without hurting SEO?
Yes! Updating old posts with relevant internal links actually signals freshness to Google and can improve rankings. Just ensure the additions are genuinely relevant.
What’s better: sidebar links or in-content links?
In-content (contextual) links carry significantly more SEO weight because they’re surrounded by relevant content. Sidebar and footer links are useful for navigation but less powerful for SEO.
Should I use nofollow for any internal links?
Generally no. Nofollow tells Google not to pass authority, which defeats the purpose of internal linking. The rare exception might be for user-generated content sections or login pages.
Final Thoughts: Building Your Internal Linking System For Long-Term Success
Here’s the bottom line: blog internal linking isn’t about gaming Google – it’s about creating genuinely useful connections that help both search engines and humans understand your content.
Start small. If you have 50 blog posts, spend a weekend identifying your 3-5 pillar topics and organizing cluster content around them. Add contextual links connecting related pieces. That alone will create measurable improvement.
Then make it systematic. Every new post should strengthen your blog site architecture by linking to relevant existing content and getting linked from updated older posts.
The blogs dominating search results in 2025 aren’t necessarily producing more content – they’re producing CONNECTED content. They understand that internal link building transforms isolated posts into comprehensive knowledge ecosystems.
Your competitors are either ignoring this entirely (giving you an easy advantage) or implementing it poorly (giving you a quality advantage). Either way, you win by being strategic.
So grab your content inventory, map those topic clusters, and start building those connections. Your future self (and your organic traffic numbers) will thank you.
Remember: Rome wasn’t built in a day, and neither is a perfectly interwoven content structure. But every link you add strategically is a road in your city, making it easier for visitors and search engines to explore everything you’ve built.
Now get out there and start linking!